Scientific analysis of the infrastructure of Bitcoin and Ethereum has shown a great centralization of networks.
 From 2015 to 2017, a group of scientists from Cornell University, the Israeli Technion and the Cryptocurrency Initiatives and Contracts (IC3) organization conducted a long-term study of the infrastructure status of various cryptocurrency networks, including Bitcoin and Ethereum. They studied the parameters of the work of thousands of nodes - and now they published the first results of their work . The main conclusion was that the networks are not at all as decentralized as one might think. Neither of which the uniform distribution of computing resources and bandwidth and speech is not.
From 2015 to 2017, a group of scientists from Cornell University, the Israeli Technion and the Cryptocurrency Initiatives and Contracts (IC3) organization conducted a long-term study of the infrastructure status of various cryptocurrency networks, including Bitcoin and Ethereum. They studied the parameters of the work of thousands of nodes - and now they published the first results of their work . The main conclusion was that the networks are not at all as decentralized as one might think. Neither of which the uniform distribution of computing resources and bandwidth and speech is not.In principle, and so everyone knew that the existence of a true P2P system would be possible only if every miner worked as an individual node in the network. But in reality, calculations are now being made in pools that play the role of peculiar "supernods". It turns out that three or four nodes control 50-60% of the calculations in the network (four in Bitcoin, three in Ethereum).
This is a purely centralized structure, where "power" is concentrated in the hands of several players, and not at all a decentralized system, which was conceived by the founder of Bitcoin Satoshi Nakamoto. It should be noted that this obvious fact is not at all a confirmation of Natalya Kasperskaya’s bold thesis , that “Bitcoin is the development of American intelligence services for the purpose of quickly financing intelligence services of the United States, England, Canada in different countries,” and the creator of Bitcoin Satoshi Nakamoto is the pseudonym of “a group of American cryptographers ".
Scientific research simply confirms the well-known fact of the concentration of calculations in pools — for the first time this problem was investigated so thoroughly by scientific methodology.
Here are some more interesting facts that the study revealed.
Bitcoin network is underused
The bandwidth of Bitcoin nodes is larger than that of Ethereum, and over the past year, the average median channel has increased bandwidth by 70%.
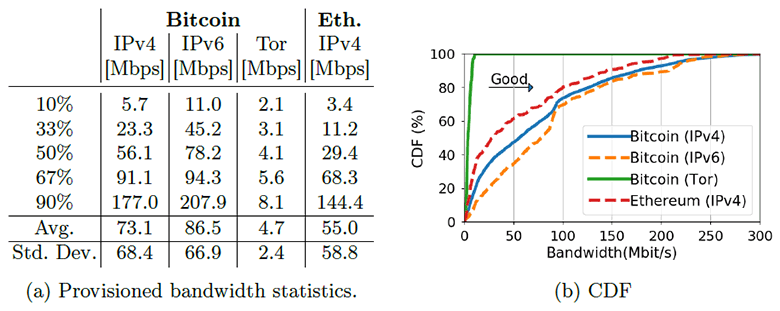
This means that the maximum block size can be increased without affecting the level of decentralization. That is, if everyone was satisfied with the level of decentralization in 2016, then with an increase in the block size by 70%, the same level will remain in 2017. At the same time, the number of transactions processed will increase in the same proportion.
Opponents of increasing block size say that it will increase the load on the CPU and the use of disk space. But scientists believe that this argument does not stand up to criticism, because the cost of these resources has now decreased to a negligible value. For example, a 1 terabyte drive in 2016 cost $ 85, and now $ 70.
The authors say that the arguments against increasing the size of the blocks are purely “political” in nature, and from a technical point of view, nothing prevents them from doing so.
Ethereum network is better distributed around the world than Bitcoin
In the Bitcoin network, nodes are more clustered, both geographically and by network delays.
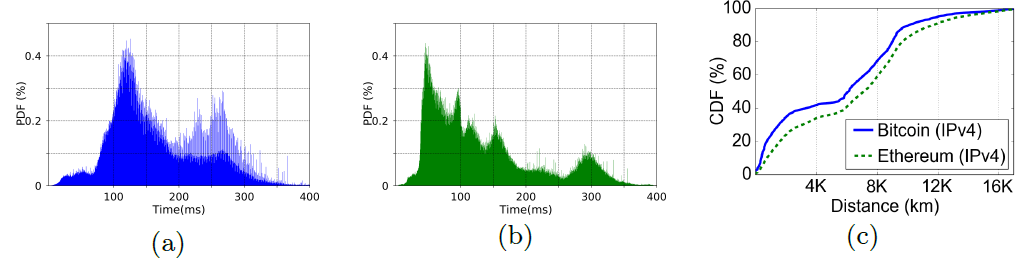
Bar graphs of P2P delays in Bitcoin (a) and Etherium (b), as well as CDF of geographical distances between nodes
The difference is not so big and significant, it's just a curious fact. The researchers also pay attention to the fact that there are more nodes in the Etherium network than in Bitcoin.
The reason they believe that a larger number of Bitcoin nodes are located in data centers (56%) than in Etherium (28%). Researchers note that moving nodes to data centers is a dangerous symptom. One of the hypotheses is the disguise of the real number of nodes and the preparation for the Sibyl attack to influence public opinion. The attack is that the victim in the peer-to-peer network connects only to the nodes controlled by the attacker, with clear consequences.
Ethereum is wasting computing power.
The Etherium network spends more hashes on lost blocks (uncles) than Bitcoin (here such blocks are called orphans).
This means that Ethereum could greatly benefit from relay circuits like Falcon and FIBER , which are used in Bitcoin. This will reduce the percentage of lost blocks.
Ethereum is more supportive of weak miners.
In a perfectly fair system, miners will have fewer reasons to pool, because the system will not give preference to large miners over small ones.
Researched identified the level of "honesty" for large and small miners as a quotient from dividing the blocks that the miner gave to the chain, to the lost blocks.
The overall level of “honesty” in both systems is comparable, but in the Bitcoin system there is a much stronger diversity in honesty for small nodes. That is, here the work of small nodes is much more unpredictable than in Ethereum. Obviously, this is due to the higher frequency of the blocks in Ethereum.
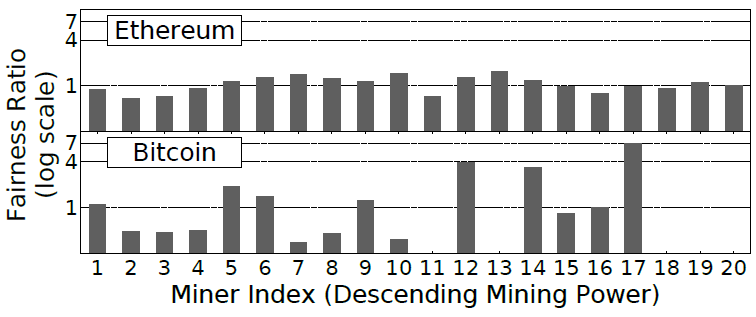
Miner Index. Distribution of "honesty" in the Bitcoin and Etherium systems
The scientific article was published on January 11, 2018 on the site of preprints arXiv.org (arXiv: 1801.03998v1).
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/409757/