Long-lived satellites
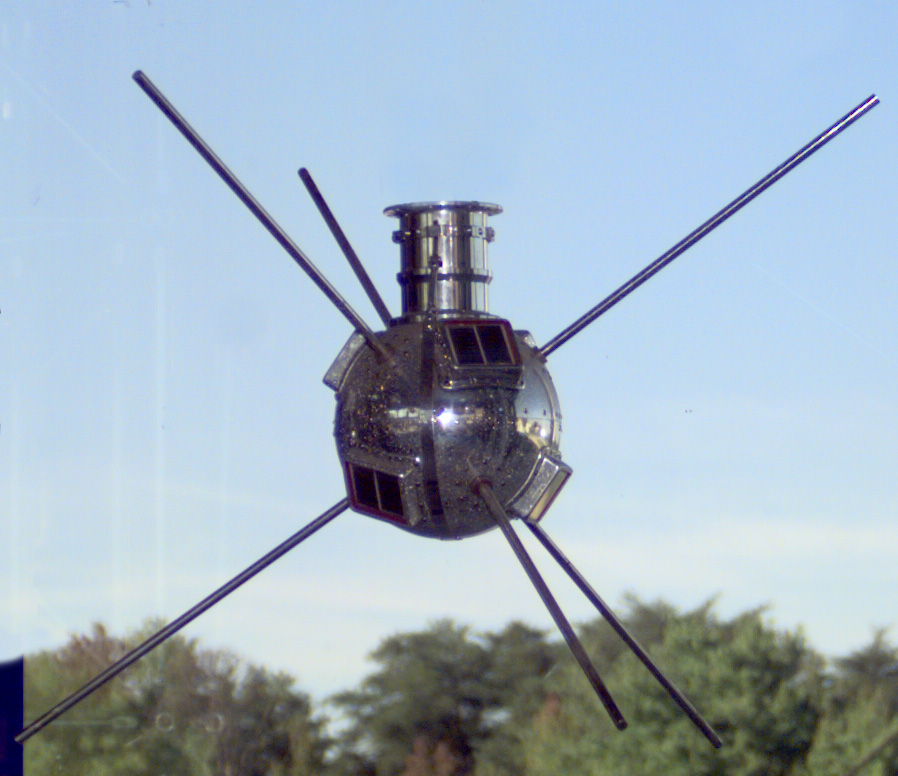

Less than six months ago, we celebrated the 60th anniversary of Sputnik-1 , and now our 60th anniversary is celebrated by another satellite that has been in orbit all this time: Avant-garde-1 . This “grapefruit” weighing 1.46 kg and 16.5 cm in diameter was the third attempt to launch the Avangard satellite, the second American and the 4th satellite in the world. And although its batteries failed in June 1958 , but he stopped transmitting signals in May 1964 - many other old satellites working for decades and having long and very entertaining stories are in orbit. About them today will be discussed.
GPS SVN-23 - 25 years 2 months and 1 day
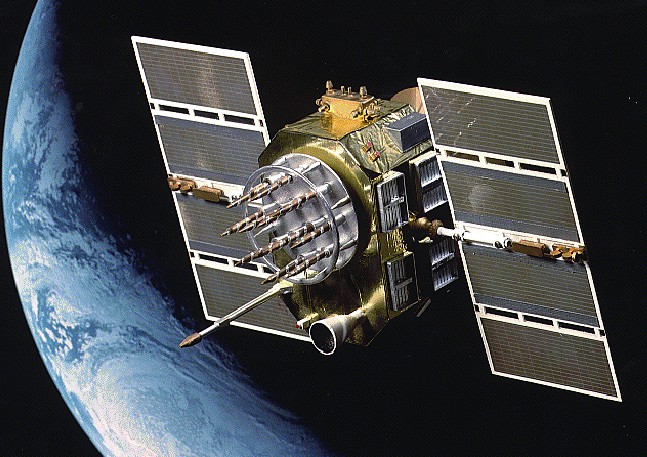
Launched on November 26, 1990 and launched into the required orbit on December 30, the GPS satellite also known as the USA-66 worked in a group until December 2004, when it was transferred to the reserve. At that time, it was almost twice as long as its warranty period (which was 7.5 years), but in February 2008 it was decided to bring it back into operation. As a result, he worked until January 25, 2016, when he was transferred to a grave orbit and finally disconnected. At the moment of its shutdown, the software bug caused the shutdown of all remaining 15 GPS satellites for 13.7 microseconds.
Landsat 5 - 29 years 3 months and 4 days
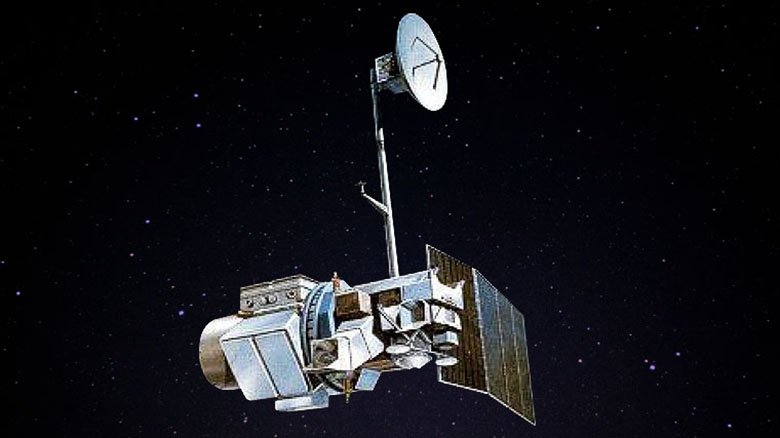

Landsat 5 became the oldest explorer of the Earth - launched on March 1, 1984, it took more than 2.5 million images of the Earth before the end of 2012, when one of its gyroscopes failed. The satellite still had 2 working gyros, which were enough for work - but the mission leadership decided not to risk it and turn off the device. He took the last pictures on January 6, 2013, and after 9 days went to the burial orbit. The mission of the device ended on June 5, 2013, when the device ran out of fuel and was given the command to turn off all systems.
The device was proposed to be returned to Earth with the help of Shuttles, but this required leaving a lot of fuel to reduce the orbit (Shuttles could not get to its working orbit). However, in the end, it was decided to spend the remaining fuel to extend his mission. On February 10, 2013, he entered the Guinness Book of Records as the longest-used satellite to monitor the earth. It is assumed that it will enter the dense layers of the atmosphere in 2034.
IMP-8 - 32 years 11 months and 11 days

The oldest scientific satellite in terrestrial orbit: launched on October 26, 1973 with a planned duration of 10 years, it worked until October 7, 2006 . Intended for measuring the properties of the Earth’s magnetic field and the interaction of the solar wind with it, in its long history it managed to assist the mission of Ulysses and his main long-lived competitors - Voyagers. This unit has become a source for over a thousand scientific publications.
GOES 3 - 38 years and 13 days
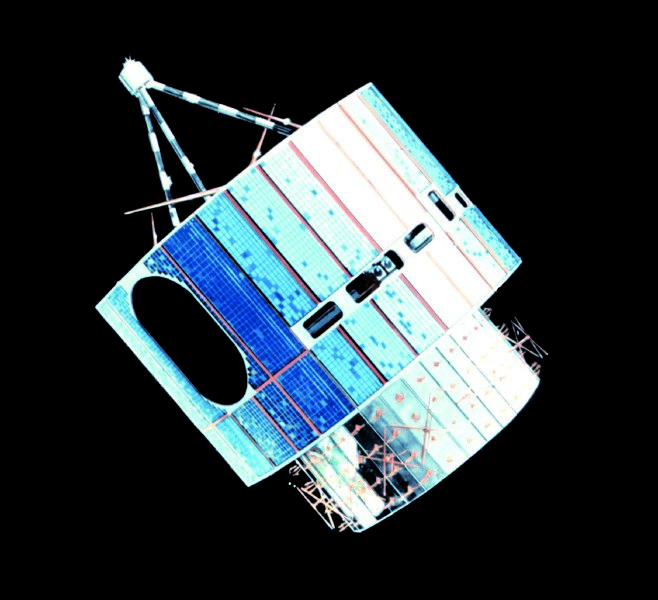
Satellite GOES 3 could well take the place of the next satellite, if not for the failure of its cameras: launched on June 16, 1978, it became the third meteorological satellite of the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration ( NOAA ). On the satellite, cameras of the visible and infrared spectrum were installed to observe the clouds, wind, and surface temperature on the day / night side of the Earth. The satellite was located in a geosynchronous orbit, and its stabilization was carried out by rotation, so that the satellite could observe the Earth less than 10% of the total time.
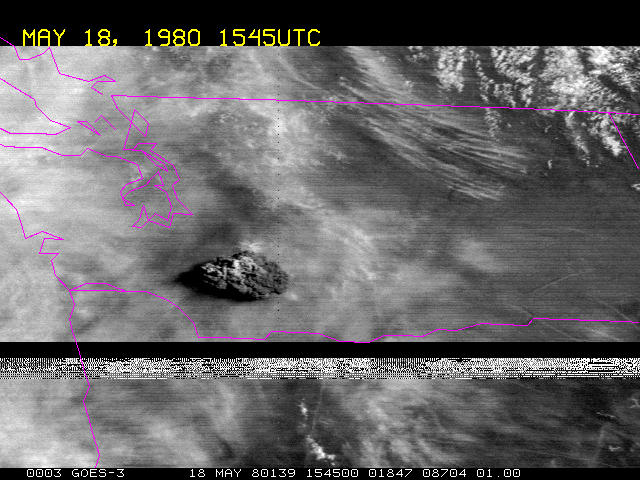
Picture of the 1980 St. Helens eruption made by GOES 3
In 1988, his cameras were out of order, and he lost the opportunity to work as intended, but retained the ability to communicate with the land. The satellite decided not to turn off, but to change the inclination of its orbit so that it flew over the Pacific Ocean, and transferred it to the University of Hawaii in Manoa, which through PEACESAT program carried out with it the broadcast of training programs, disaster relief, medical services and a number of other services for residents of the Pacific Islands in 1990-1995.
In 1995, the device began to run out of fuel, used to maintain the exact position, and it was transferred to the polar orbit, where it could provide communication for Amundsen-Scott station for 6.5 hours per day at a speed of 1 Mbit / s. In this role, he worked until June 15, 2016, when it was decided to permanently disable it. After 14 days of maneuvering, he reached the burial orbit and on June 29, 2016 was finally turned off.
ATS-3 - 39 years
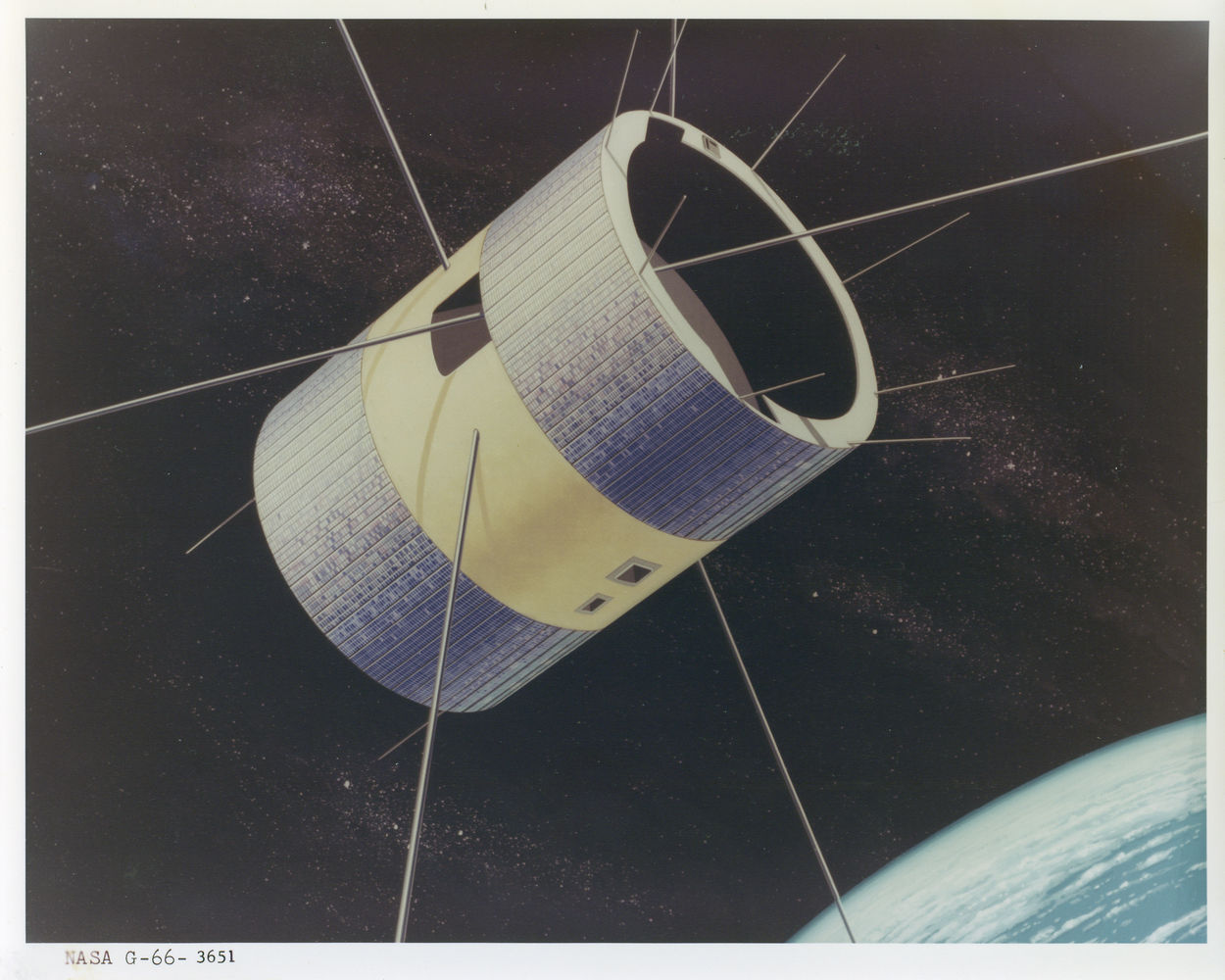
ATS-3 is one of the oldest communication satellites, and its part-time meteorological functions in geostationary orbit allowed it to set a record of a different kind: it took a snapshot of it on November 10, 1967 (5 days after launch) only slightly to give way to the first colored photographs of the earth - they were made by satellite dodge in august.
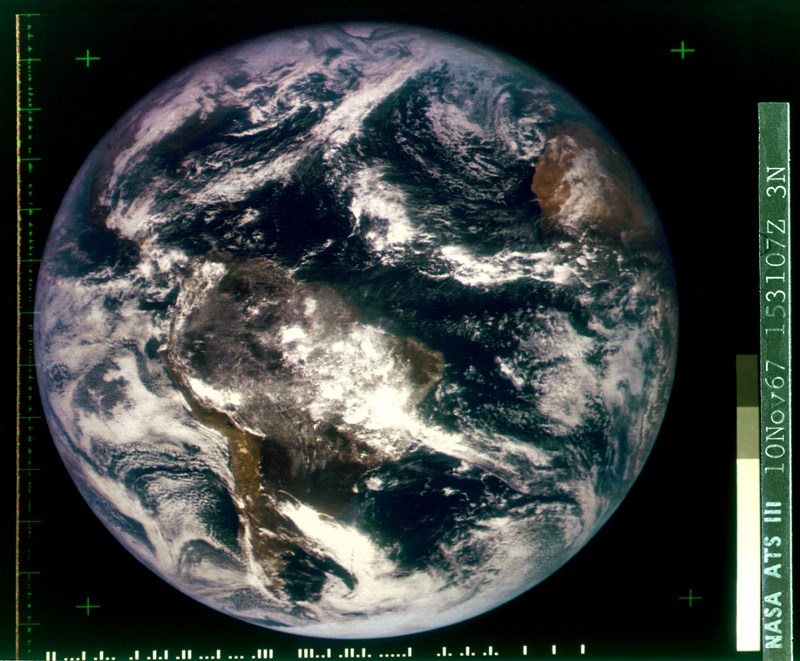
In total, he worked for meteorological purposes for 11 years instead of the planned 3 years, and as a communication satellite - until 2001, holding the title of the oldest satellite of this kind until 2008, when he gave this title to another satellite below.
Voyager 2 - 40 years 6 months and 21 days
With their fellow Voyager 1 (which is 26 days younger), they are the oldest satellites in continuous operation. Voyager 1 and 2 have already moved away from the Sun by 21.1 and 17.5 billion km, and continue to move away (Voyager 1 should move away from us on 1 holy day by 2027). Recently, Voyager-1 turned on its engines after 37 years and 20 days of inactivity — this was necessary in order to save some more energy required for the operation of gyroscopes. Perhaps the Voyagers will be able to maintain their performance until 2036 - thus, Voyager-2 may also reach a distance of 1 sv. a day in working condition, as well as will last 59 years - thereby setting a record that is almost impossible to beat. In general, you can write about Voyagers almost infinitely .
AMSAT-OSCAR-7 - 43 years 4 months and 2 days
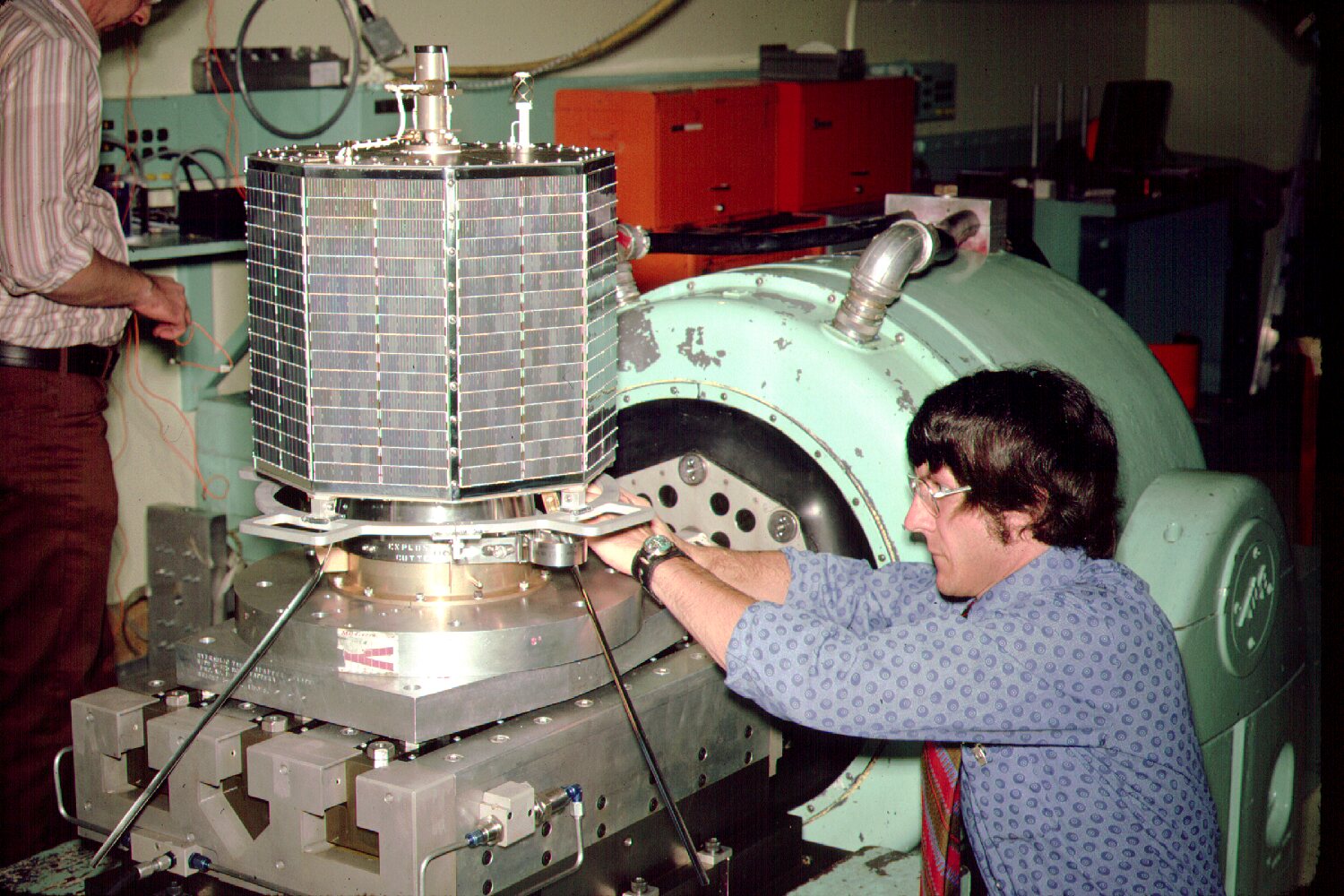
Satellite on the vibration stand
AMSAT-OSCAR-7 is the oldest communication and amateur satellite: launched on November 15, 1974, it lost its batteries in 1981, and since then it interrupts its work when the Sun does not shine on its solar panels (this happens when the orbit is in the shadow of the Earth, which happens in summer and autumn), but he himself has retained the ability to work until now. In addition to communication by radio amateurs, in the summer of 1982 it was also used by the Polish anti-communist movement “Fighting Solidarity” since, since December of the previous year, due to the introduction of martial law, ordinary telephone communication was tapped, and ordinary amateur stations were easily spotted. The satellite continues to function and with the help of these data on frequencies and orbital parameters it can be tried to detect.
LES1 - lost for 46 years
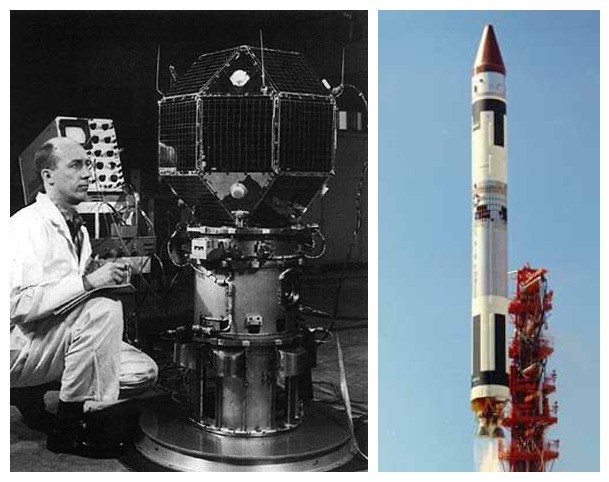
It was one of the 9 satellites of the Lincoln Experimental Satellite series designed for X-band communications experiments. Due to the failure of the acceleration stage, this satellite, launched as early as February 11, 1965, remained in a circular orbit at 2,800 km instead of an elliptical orbit at 2,800x15,000 km, but this did not prevent experiments with it during the next 2 years. However, then the connection with him was lost, and in the period from 1967 to 2013, he was silent until one radio amateur caught his signal at 237 MHz.
Transit 5B-5 - 53 years 3 months and 4 days

Refers to the Transit series of navigation satellites intended for the US Navy. This satellite was launched on December 13, 1964, and only 19 days later the satellite stopped responding to commands from the ground, and therefore another satellite was launched to replace it. However, despite the fact that the connection with him was impossible, he still continues to transmit telemetry at a frequency of 136.65 MHz, which, if desired, can be detected . Due to the fact that his batteries and RITEG have not worked for a long time, communication with him is possible only when the Sun shines on him.
Russian satellites
I thought it would be interesting for everyone to find out how these world achievements relate to what we managed to achieve. So far the numbers are not so impressive, but most of all it’s not even depressing, but the fact that most of our satellites are military , there is a chronic shortage of meteorological satellites, satellite satellites are used by other satellites , and in terms of science, Russia periodically turns out without any scientific satellites.

Our oldest navigation satellites are Glonass No. 716 and 717 that have been in operation for 11 years 3 months and 23 days. The 715th colleague, launched together with them on December 25, 2006, recently went out of order , and from 716, the connection was lost earlier - but the 717th continues to work properly only with scheduled interruptions for prevention (for the Sail series satellites of the Cyclone navigation system " Indicate a record of 12 years - but I could not find information about this satellite).

One of the oldest Russian satellites is Gonets-D1, which is part of the satellite communication system of the same name , which has worked in orbit for 20 years - since its launch on February 19, 1996 up to 2015. Of those satellites that remain in service, the oldest are the Yamal-202 communication satellite, launched on November 24, 2003 and having been working for 14 years 3 months and 20 days ( Alcatel Space manufactured the payload for it) and the oldest - an amateur satellite RS-15 launched December 26, 1994 - although its transmitter apparently failed, its beacon still continues to operate at 29.3525 MHz after 23 years and 3.5 months.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410065/