Life-giving bandage unremovable
It is not yet clear whether this discovery will lead to an increase in the income of plastic surgeons or to a decrease. But it can be said for sure that the scars that supposedly decorate someone will become much smaller, and they themselves will no longer be so noticeable. And all it was necessary to combine the basis for a package with a pair of ingredients. However, it was not so easy ...

As long as humans manage to ruin and maim themselves, world surgery will remain without work. And despite the low invasiveness of most operations, the scars after them remain. And sometimes it remains such that, in general, recovered patients fall into the clinical depression of their own appearance. After burns, for example, or after ragged wounds.
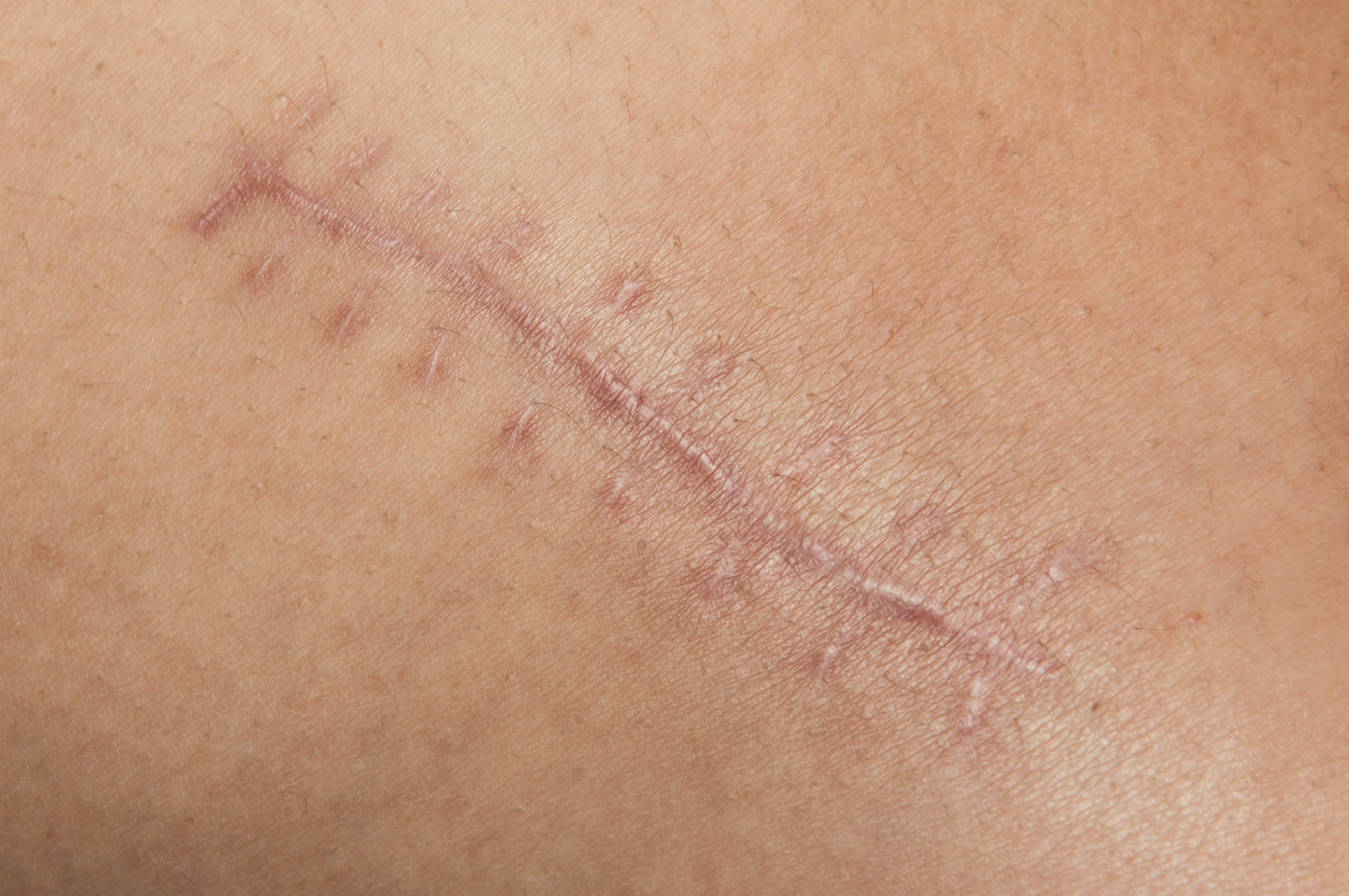
Even acne (the medical name for acne) can turn any beauty into a monster. Therefore, from specialists in regenerative medicine there is a constant request, periodically turning into a cry, to develop something really working: not just healing wounds, but with minimal consequences for appearance.
So in many areas it is easier to prevent than to correct. Moreover, in this case it is completely clear what to work with. Scar tissue mainly consists of unidirectional collagen and is not so much like skin. Scars are more sensitive to ultraviolet, do not stretch, do not sweat and do not overgrow with hair.
There are several competing methods of skin restoration: skin grafting (own / alien, solid flap / stretched flap with many holes), xeno-skin, stem cells, wound coverings. Each of them is better in something, worse in something. For extensive burns, for example, your skin is simply nowhere to take. And if we are talking about abdominal surgery, then there are features of the formation of a scar. And from it already not to get to anywhere. Nearly. At least, it is possible to reduce the scar itself, and to accelerate healing at the same time, says senior researcher at the Inorganic Nanomaterials Laboratory at NUST MISiS PhD Anton Manakhov. Tear off the bandage is not necessary - it eventually biodegrades, being replaced by new skin.

The funny thing is that polycaprolactone underlies the new medical material. This material is known primarily as one of the few approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for injection into the lips, cheeks and other objects of plastic surgery. In its pure form, it is sold, however, at a high price. The Company Directory worth one hundred grams costs 11 thousand, half a kilo comes at a discount - forty. There are cheaper ways to produce it. Not for nothing, on the basis of polycaprolactone and starch, even biodegradable packages do. However, Anton Manakhov says that his students can make one hundred fifty - two hundred square meters of new material out of a pound of polycaprolactone, so it’s not so expensive for a circle. Subtleties, as usual, lie in the technology of production.
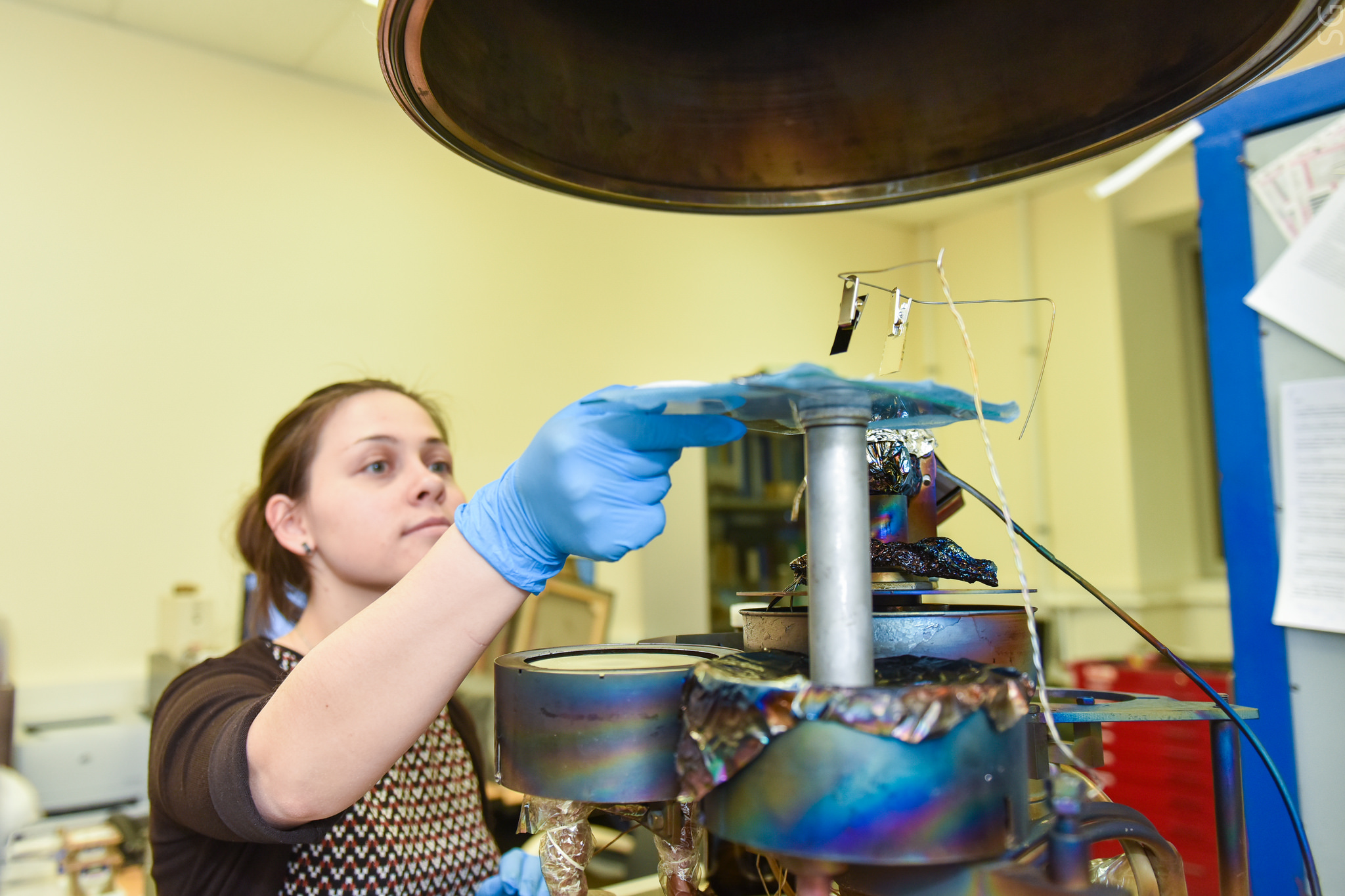

“We synthesized the base fibers from polycaprolactone by electroforming,” says Elizaveta Permyakova, one of the project participants, an employee of the laboratory “Inorganic Nanomaterials of NITA“ MISiS ”. “Then we placed the substrate in a magnetron, where, using plasma treatment, a polyethylene-like polymer containing carboxyl groups was applied onto its surface.”

Anton Manakhov explained that the polymer was applied to increase the hydrophilic properties of the material. The thickness of the polymer layer was several nanometers, so the decomposition of polycaprolactone was not affected. In addition, the polymer itself, containing carboxyl groups, eventually decomposes in a biological medium. If antibiotic properties need to be strengthened, silver ions can be sprayed onto the base in parallel, the work manager emphasized.
“The next stage was taken by our biochemistry colleagues Anastasia Solovyova and Svetlana Miroshnichenko,” noted Manakhov. - which are attached to a part of carboxyl groups growth factors, proteins: fibrinogen, vitronectin, fibronectin. The latter is perhaps the most important. By the way, the addition of proteins does not reduce the hydrophilicity of the polymer, we checked the contact angle of wetting. "

The first stage of testing has already passed, the second is now ending on animals, it is being held at the Research Institute of Experimental and Clinical Lymphology in Novosibirsk. According to Elizabeth, under the dressing and damaged, and burned area of the skin heal significantly faster. Therefore, instead of the formation of scar tissue, there is a regeneration of normal superficial tissues of the skin. Antibacterial components reduce inflammation, and blood plasma components stimulate tissue regeneration.

The results of in vitro showed that when using innovative dressings, the process of cell regeneration was accelerated twice. Soon there will be results of testing the drug in vivo. In the meantime, you can get acquainted in more detail with the scientific article of the authors.

As long as humans manage to ruin and maim themselves, world surgery will remain without work. And despite the low invasiveness of most operations, the scars after them remain. And sometimes it remains such that, in general, recovered patients fall into the clinical depression of their own appearance. After burns, for example, or after ragged wounds.

Even acne (the medical name for acne) can turn any beauty into a monster. Therefore, from specialists in regenerative medicine there is a constant request, periodically turning into a cry, to develop something really working: not just healing wounds, but with minimal consequences for appearance.
Hidden at the request of reading us at breakfast

So in many areas it is easier to prevent than to correct. Moreover, in this case it is completely clear what to work with. Scar tissue mainly consists of unidirectional collagen and is not so much like skin. Scars are more sensitive to ultraviolet, do not stretch, do not sweat and do not overgrow with hair.
There are several competing methods of skin restoration: skin grafting (own / alien, solid flap / stretched flap with many holes), xeno-skin, stem cells, wound coverings. Each of them is better in something, worse in something. For extensive burns, for example, your skin is simply nowhere to take. And if we are talking about abdominal surgery, then there are features of the formation of a scar. And from it already not to get to anywhere. Nearly. At least, it is possible to reduce the scar itself, and to accelerate healing at the same time, says senior researcher at the Inorganic Nanomaterials Laboratory at NUST MISiS PhD Anton Manakhov. Tear off the bandage is not necessary - it eventually biodegrades, being replaced by new skin.

The funny thing is that polycaprolactone underlies the new medical material. This material is known primarily as one of the few approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for injection into the lips, cheeks and other objects of plastic surgery. In its pure form, it is sold, however, at a high price. The Company Directory worth one hundred grams costs 11 thousand, half a kilo comes at a discount - forty. There are cheaper ways to produce it. Not for nothing, on the basis of polycaprolactone and starch, even biodegradable packages do. However, Anton Manakhov says that his students can make one hundred fifty - two hundred square meters of new material out of a pound of polycaprolactone, so it’s not so expensive for a circle. Subtleties, as usual, lie in the technology of production.

“We synthesized the base fibers from polycaprolactone by electroforming,” says Elizaveta Permyakova, one of the project participants, an employee of the laboratory “Inorganic Nanomaterials of NITA“ MISiS ”. “Then we placed the substrate in a magnetron, where, using plasma treatment, a polyethylene-like polymer containing carboxyl groups was applied onto its surface.”

Anton Manakhov explained that the polymer was applied to increase the hydrophilic properties of the material. The thickness of the polymer layer was several nanometers, so the decomposition of polycaprolactone was not affected. In addition, the polymer itself, containing carboxyl groups, eventually decomposes in a biological medium. If antibiotic properties need to be strengthened, silver ions can be sprayed onto the base in parallel, the work manager emphasized.
“The next stage was taken by our biochemistry colleagues Anastasia Solovyova and Svetlana Miroshnichenko,” noted Manakhov. - which are attached to a part of carboxyl groups growth factors, proteins: fibrinogen, vitronectin, fibronectin. The latter is perhaps the most important. By the way, the addition of proteins does not reduce the hydrophilicity of the polymer, we checked the contact angle of wetting. "

The first stage of testing has already passed, the second is now ending on animals, it is being held at the Research Institute of Experimental and Clinical Lymphology in Novosibirsk. According to Elizabeth, under the dressing and damaged, and burned area of the skin heal significantly faster. Therefore, instead of the formation of scar tissue, there is a regeneration of normal superficial tissues of the skin. Antibacterial components reduce inflammation, and blood plasma components stimulate tissue regeneration.

The results of in vitro showed that when using innovative dressings, the process of cell regeneration was accelerated twice. Soon there will be results of testing the drug in vivo. In the meantime, you can get acquainted in more detail with the scientific article of the authors.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410155/