Russia will launch glass reflector satellites into orbit
 On May 4, 1976, NASA sent a very unusual satellite called LAGEOS (LAser GEOdynamics Satellite, in the photo) into orbit. He had no electronics, engines, or power supplies on board. In fact, it is just a brass ball with a diameter of 60 cm and a mass of 407 kg with an aluminum coating. 426 corner reflectors are evenly spaced on the ball, of which 422 are filled with fused quartz, and 4 are made of germanium (for infrared radiation). The satellite went into orbit 5860 km, where it will rotate the next 8.4 million years, storing a plate with a message to descendants from a group of scientists under the leadership of Karl Sagan.
On May 4, 1976, NASA sent a very unusual satellite called LAGEOS (LAser GEOdynamics Satellite, in the photo) into orbit. He had no electronics, engines, or power supplies on board. In fact, it is just a brass ball with a diameter of 60 cm and a mass of 407 kg with an aluminum coating. 426 corner reflectors are evenly spaced on the ball, of which 422 are filled with fused quartz, and 4 are made of germanium (for infrared radiation). The satellite went into orbit 5860 km, where it will rotate the next 8.4 million years, storing a plate with a message to descendants from a group of scientists under the leadership of Karl Sagan.On October 22, 1992, a similar LAGEOS-2 satellite built by the Italian Space Agency (orbital altitude 5620 km) was launched. As you can guess from the design and the materials used, these passive satellites have a single role - the reflection of the laser beam. Laser location is carried out from dozens of observation posts of the International Laser Ranging Service, which has more than 40 stations around the world.
Now the international scientific community plans to build a third such satellite, LAGEOS-3, which will enable laser location to be much more accurate than its predecessors.
Unfortunately, Russia does not participate in this international project. But he is going to launch his own two Blitz-M glass reflectors, a thousand times more accurate than foreign ones, the newspaper Izvestia writes .
LAGEOS-3 is a joint international program that will be the result of cooperation of scientists from France, Germany, Great Britain, Italy, Spain and the USA. According to the plans of the developers, for the first time in history, LAGEOS-3 will measure the quasistationary property of the Earth - the gravitational magnetic dipole moment predicted by Einstein's General Theory of Relativity.
In 2009, Russia also launched the first reflector satellite called BLITS (Ball of the Lens In The Space - a spherical lens in space). The glass sphere is placed in an orbit at an altitude of 800 km. However, in 2013, the satellite crashed, colliding with a debris from another spacecraft. Presumably, it was a fragment of the Chinese meteorological spacecraft Fengyun-1C, on which in 2007 Beijing tested its anti-satellite weapon. Or the wreckage of two communications satellites of Russia and the United States, which collided with each other in 2009. According to NASA , now a third of all space debris in orbit was formed as a result of these two incidents of 2007 and 2009, and at an altitude of 800 km of debris is especially large.
The upgraded Blitz-M devices will be a continuation of the Blitz project. They have a larger diameter (220 mm) and mass (16.56 kg) than the first satellite (170 mm and 7.53 kg). In addition, they will be taken to a higher orbit - 1,500 km.
“These specialized satellites and laser reflectors that are produced in our country are the best in the world,” Alexander Ipatov, scientific director of the Institute of Applied Astronomy, told Izvestiya. - No wonder our reflectors put on foreign vehicles. The main function of Blitz-M is to create the most accurate coordinate system on Earth. The difficulty is that the core of our planet is liquid and changes its position. Linking the coordinate system to the Earth's geocenter is the most difficult. Current measurements using lasers and radio interferometry technology differ by 6 cm. Why - no one knows. ”
Glass balls will help clarify the model of the gravitational field of the Earth and its influence on the orbits of spacecraft. Therefore, they will increase the accuracy of satellite positioning systems, such as GPS and GLONASS. In addition, these data will clarify the pattern of movement of tectonic plates - it means that it will be possible to more reliably predict earthquakes.
Russian satellites will provide a reflection of the laser signal with an error less than 0.1 mm. This is a thousand times higher accuracy than LAGEOS, noted in the Systems for Precision Instrument Engineering Scientific and Production Corporation. It was there that developed the technology of ultra-precise production of multi-layer spherical lenses and launched three spherical space satellites (two will be sent into orbit, one will remain on Earth as a control instance).
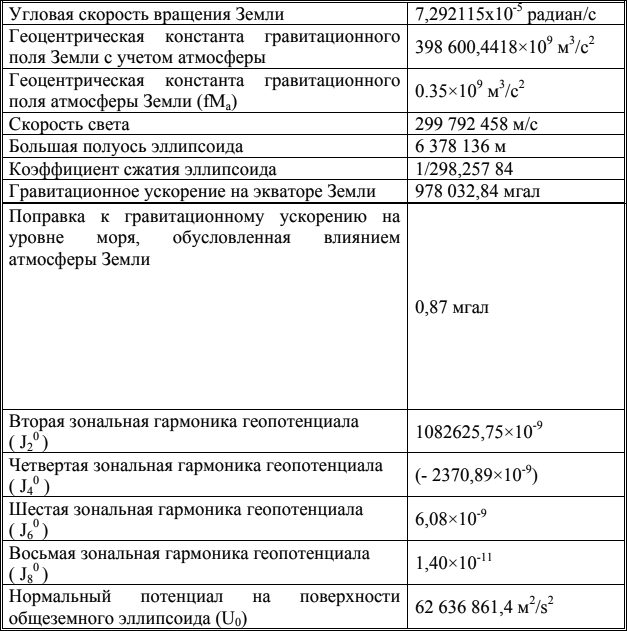
Thus, the Russian reflecting satellites will help to clarify the International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS), the origin of which is the center of mass of the Earth. Refining the ITRS will help clarify the Russian Earth coordinate system PZ-90 (Earth Parameters 1990) - a system of geodetic parameters, including the fundamental geodesic constants, parameters of the common ellipsoid, parameters of the Earth’s gravitational field, geocentric coordinate system and parameters of its connection with other coordinate systems (see scientific brochure "Parameters of the Earth 1990" , published by the Military Topographical Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation).
Geodesic constants and parameters of the general earth ellipsoid ПЗ 90.02
Two Russian Blitz-M satellites are planned to be launched together with the Gonets system spacecraft in October 2018.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410419/