Hubble Space Telescope (article plus video)
There are three objects in Earth’s orbit, which even people far from astronomy and astronautics know about: the Moon, the International Space Station and the Hubble Space Telescope. The latter is as much as eight years older than the ISS and has found the Mir Orbital Station. Many consider it just a big camera in space. The reality is a little more complicated, not for nothing that people who work with this unique apparatus respectfully call it a celestial observatory.

A lot of pictures!
The history of the construction of Hubble - is the constant overcoming of difficulties, the struggle for funding and the search for solutions to unforeseen situations. The role of Hubble in science is priceless. It is impossible to compile a complete list of discoveries in astronomy and related directions, made thanks to telescope images, so many papers refer to the information he received. Nevertheless, official statistics speak of nearly 15 thousand publications.
The idea to place a telescope in orbit arose almost a hundred years ago. The scientific substantiation of the importance of building such a telescope in the form of an article published by astrophysicist Lyman Spitzer in 1946. In 65, he was made head of the committee of the Academy of Sciences, which defined the tasks of such a project.
In the sixties, we managed to carry out several successful launches and deliver simpler devices to orbit, and in the 68th, NASA gave Hubble's forerunner the green light — the LST, the Large Space Telescope, with a larger mirror diameter — 3 meters against Hubble 2.4 — and an ambitious the task of launching it as early as 72, with the help of the space shuttle, which was then in development. But the estimated project estimate came out too expensive, there were difficulties with money, and in 74th the financing was completely canceled. The active lobbying of the project by astronomers, the involvement of the European Space Agency and the simplification of the characteristics up to approximately Hubble allowed in 78th to receive funding from Congress in the amount of 36 million dollars ridiculous in the total costs, which is now equal to about 137 million.
At the same time, the future telescope was named after Edwin Hubble , an astronomer and cosmologist who confirmed the existence of other galaxies, created the theory of the expansion of the Universe and gave his name not only to the telescope, but also to scientific law and magnitude.
The telescope was developed by several companies responsible for different elements, of which the most complex: the optical system, which Perkin-Elmer was involved in, and the spacecraft that Lockheed created. The budget has grown to $ 400 million.
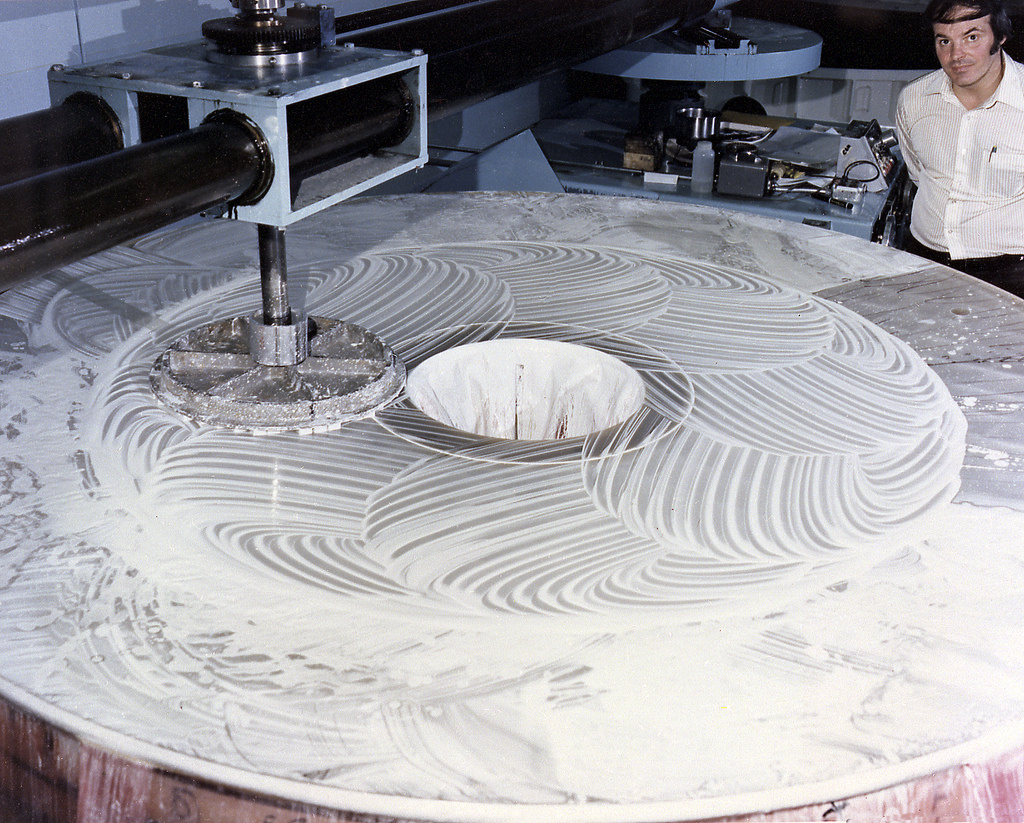
Lockheed delayed the creation of the apparatus for three months and exceeded its budget by 30%. If you look at the construction history of devices of similar complexity, this is a normal situation. At Perkin-Elmer, everything was much worse. The company polished the mirror on innovative technology to the end of the 81st year, greatly exceeding the budget and spoiling relations with NASA. Interestingly, the mirror disc was made by Corning , which today produces Gorilla Glass, which is actively used in telephones. By the way, Kodak received a contract for the manufacture of a spare mirror using traditional polishing methods, if problems arise with polishing the main mirror. Delays in the creation of other components slowed down the process to the point that the quote from NASA’s description of work schedules that were “uncertain and changing daily” became well-known .

The launch was only possible by the year '86, but due to the Challenger disaster, the shuttles launch was suspended for the time being.
Hubble was put in parts in storage in special nitrogen-purged chambers, which cost six million dollars a month.
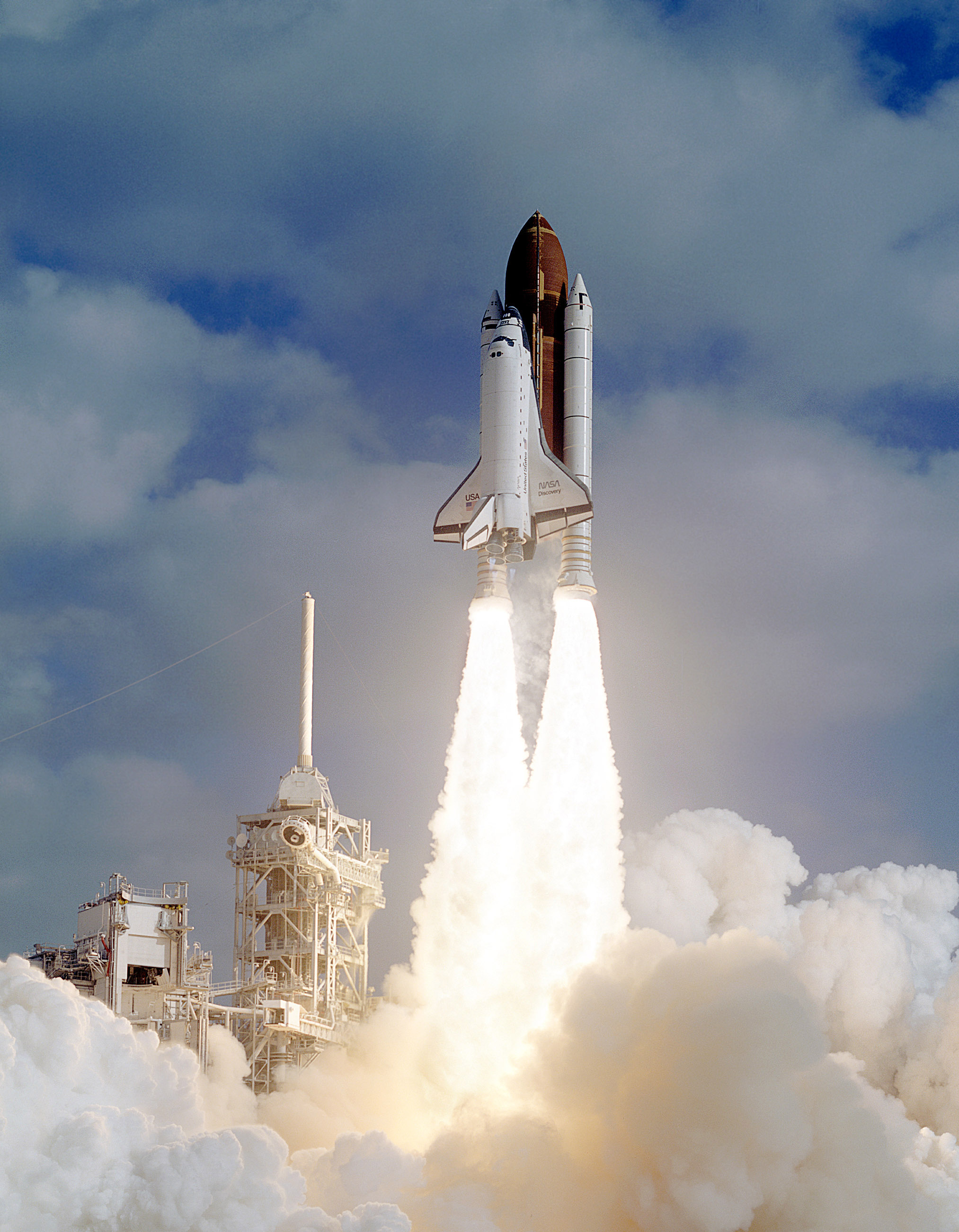
As a result, on April 24, 1990, the Discovery shuttle launched with a telescope into orbit. At this point, Hubble spent $ 2.5 billion. Total costs today are approaching ten billion.

Since the launch, there have been several dramatic events involving Hubble, but the main thing happened at the very beginning.
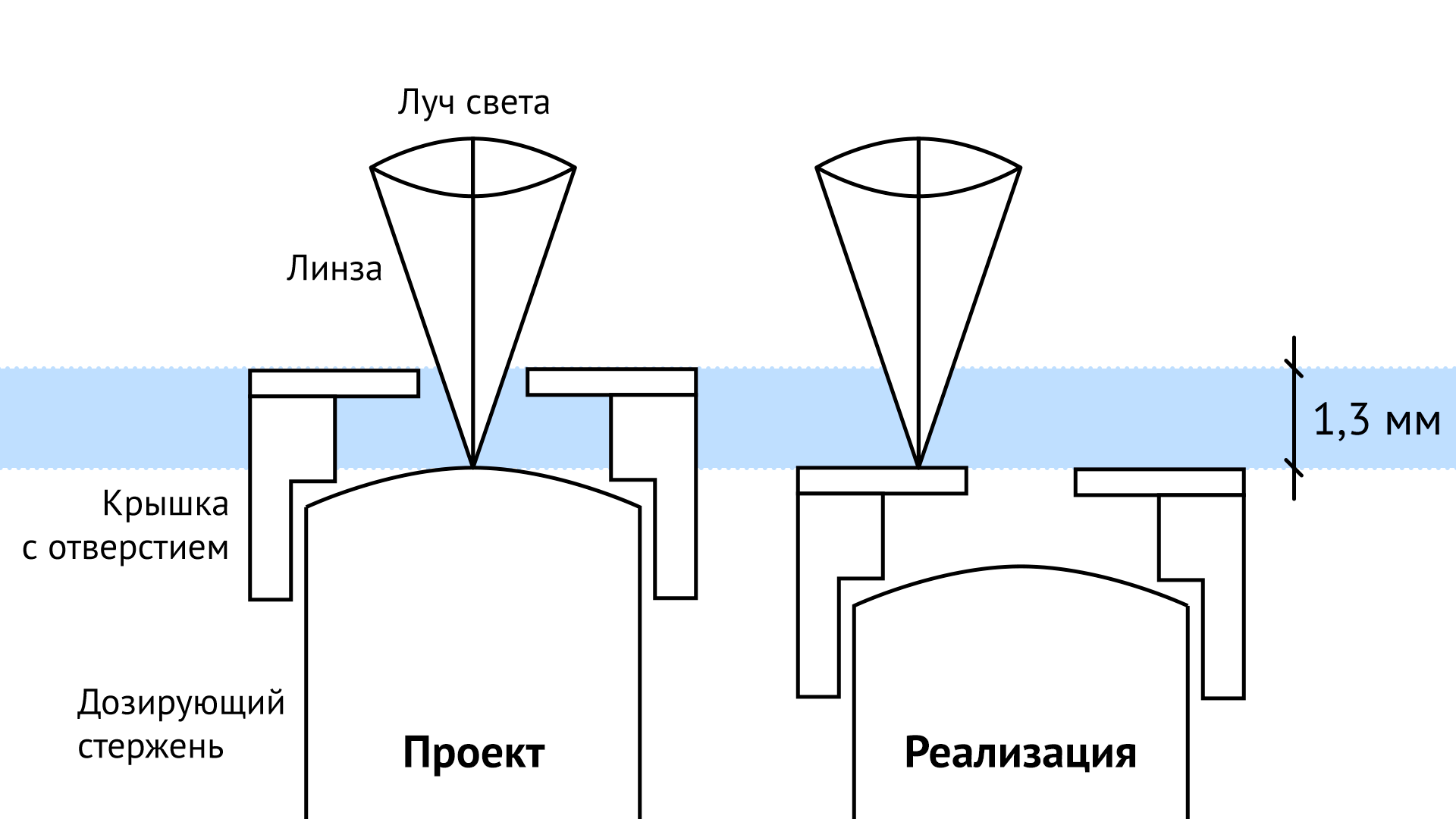
When, after the launch into orbit, the telescope began its work, it turned out that its sharpness is an order of magnitude lower than the calculated one. Instead of a tenth of an arc second, a whole second was obtained. After several checks, it turned out that the telescope mirror is too flat at the edges: for as many as two micrometers it does not coincide with the calculated one. The aberration due to this, in the literal sense of a microscopic defect, made most of the planned studies impossible.
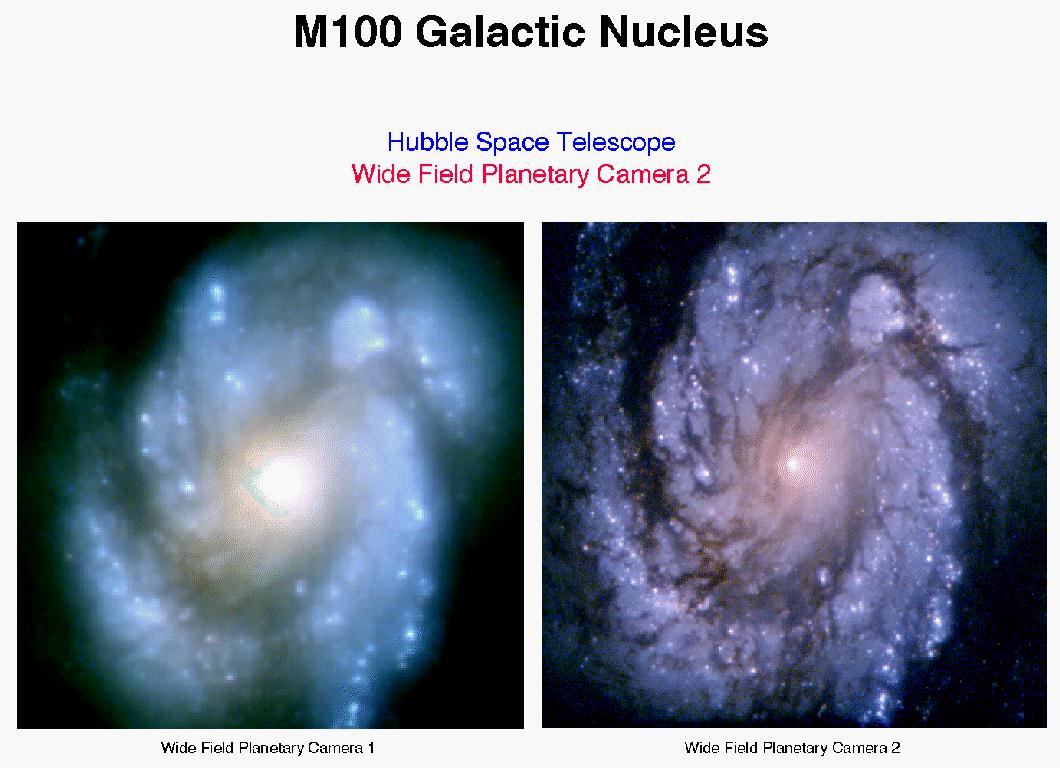
A commission was assembled, whose members found the reason: an incredibly accurately calculated mirror was incorrectly polished. Moreover, even before the launch, the same deviations were shown by the pair of null-correctors used in the tests - the devices that were responsible for the desired curvature of the surface. But then they did not trust this testimony, relying on the testimony of the main null corrector, which showed the correct results and which was used for polishing. And one of the lenses of which, as it turned out, was incorrectly installed.
Human factor.
It was technically impossible to establish a new mirror directly in orbit, and it was too expensive to lower the telescope and then output it again. The solution was found elegant.
Yes, the mirror was made wrong. But it was done wrong with very high accuracy. The distortion was known, and it remained only to compensate, for which we developed a special correction system COSTAR . It was decided to install it as part of the first expedition to service the telescope. Such an expedition is a complex 10-day operation with astronaut exits into outer space. More futuristic work and can not imagine, but this is just maintenance. In total, there were four expeditions during the operation of the telescope, with two missions within the third.
On December 2, 1993, the shuttle Endeavor, for which it was the fifth flight, delivered astronauts to the telescope. They installed Costar and replaced the camera.
Costar corrected the spherical aberration of the mirror, playing the role of the most expensive points in history. The optical correction system performed its task until 2009, when the need for it was no longer due to the use of its own corrective optics in all new devices. She gave up a precious place in the telescope spectrograph and took pride of place in the National Museum of Aeronautics and Astronautics, after dismantling in the framework of the fourth expedition to service Hubble in 2009 year.
Operated and monitored by a telescope in real time 24/7 from the control center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The tasks of the center are divided into two types: technical (maintenance, management and monitoring of the condition) and scientific (selection of objects, preparation of tasks and data collection itself). Every week, Hubble receives more than 100,000 different commands from Earth: these are corrective orbit instructions, and tasks for shooting space objects.
At MCC, the day is divided into three shifts, each of which is assigned a separate team of three to five people. During expeditions to the telescope itself, the staff of workers increases to several dozen.
By the way, there is a separate site developed by Chris Pete, where you can track the position of the celestial observatory. There is also data on other artificial orbital objects:
www.heavens-above.com
Hubble is a busy telescope, but even its tight schedule makes it possible to help absolutely anyone, even a non-professional, astronomer. Each year, the Space Telescope Institute for Space Research receives thousands of applications for booking time from astronomers from different countries. About 20% of applications are approved by the expert committee and, according to NASA, thanks to international inquiries, plus or minus 20,000 observations are made annually. All of these applications are docked, programmed and sent to Hubble from the same center in Maryland.
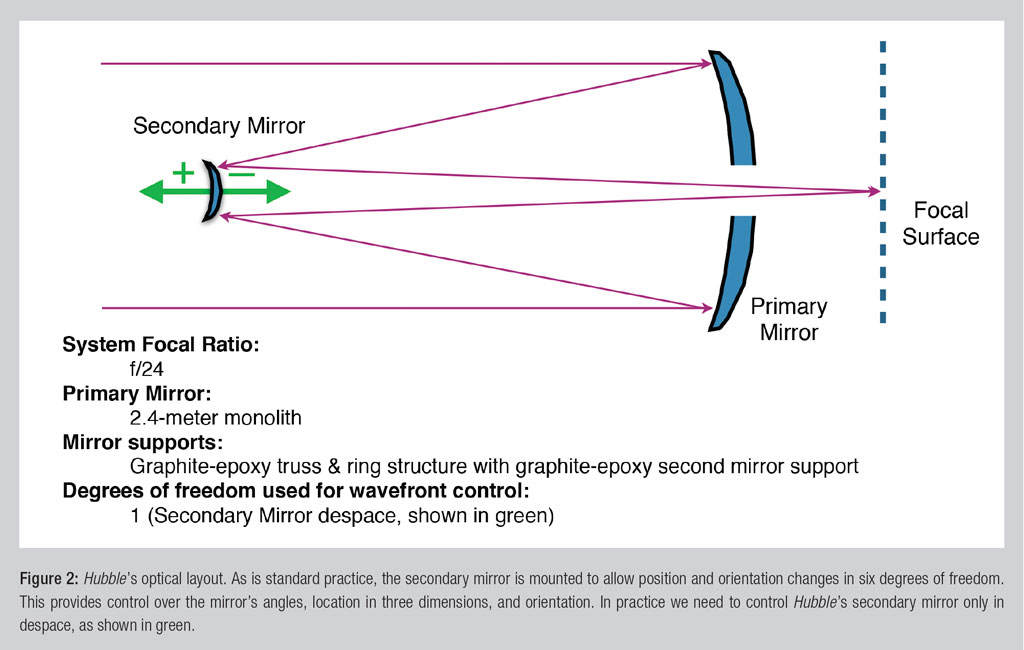
The main optics of the Hubble is made on the system Richie-Chretien . It consists of a round, hyperbolically curved mirror 2.4 m in diameter with a hole in the center. This mirror reflects on the secondary mirror also a hyperbolic form, which reflects a beam suitable for digitization into the central hole of the primary one. To filter out the extra parts of the spectrum and highlight the desired ranges using all sorts of filters.
In such telescopes they use exactly the system of mirrors, and not lenses, as in cameras. There are many reasons for this: temperature fluctuations, polishing tolerances, overall dimensions and the absence of beam losses inside the lens itself.
The main optics at Hubble has not changed since the beginning. A set of various tools that use it, completely changed for several serving expeditions. Hubble updated the toolkit, and during its existence there worked thirteen different tools. Today he carries six, one of which is in hibernation.
Wide-angle and planetary cameras of the first and second generation, and the Wide-angle camera of the third now answered for the photos in the optical range.
The potential of the first WFPC was never revealed due to problems with the mirror. And the expedition of the 93rd year, having established Costar, at the same time replaced it with the second version.
The WFPC2 camera had four square matrices, the images from which formed a large square. Nearly. One matrix - just the same “planetary” - received an image with a higher magnification, and when restoring the scale, this part of the image captures less than sixteenth part of the total square instead of a quarter, but in higher resolution. The remaining three matrices were responsible for the “wide angle”. That is why the full shots of the camera look like a square, which has eaten three blocks from one corner, and not because of problems with downloading files or other problems.
WFPC2 was replaced by WFC3 in 2009. The difference between them is well illustrated by the re-mounted Pillars of Creation, about which later.
In addition to the optical and near infrared range of the wide-angle camera, Hubble sees:
Hubble’s photographs are not exactly photographs in the conventional sense. A lot of information is not available in the optical range. Many space objects actively radiate in other bands. Hubble is equipped with a variety of devices with a variety of filters that allow you to capture data that astronomers later process and can be reduced to a visual image. The richness of the colors is provided by the different radiation ranges of the stars and the particles ionized by them, as well as their reflected light.
There is a lot of photos, I will tell only about several, the most fascinating. All photos have their ID, which is easily located on the Hubble site spacetelescope.org or directly on Google. Many pictures are on the site in high resolution, but here I leave screensize versions.
ID: opo9544a
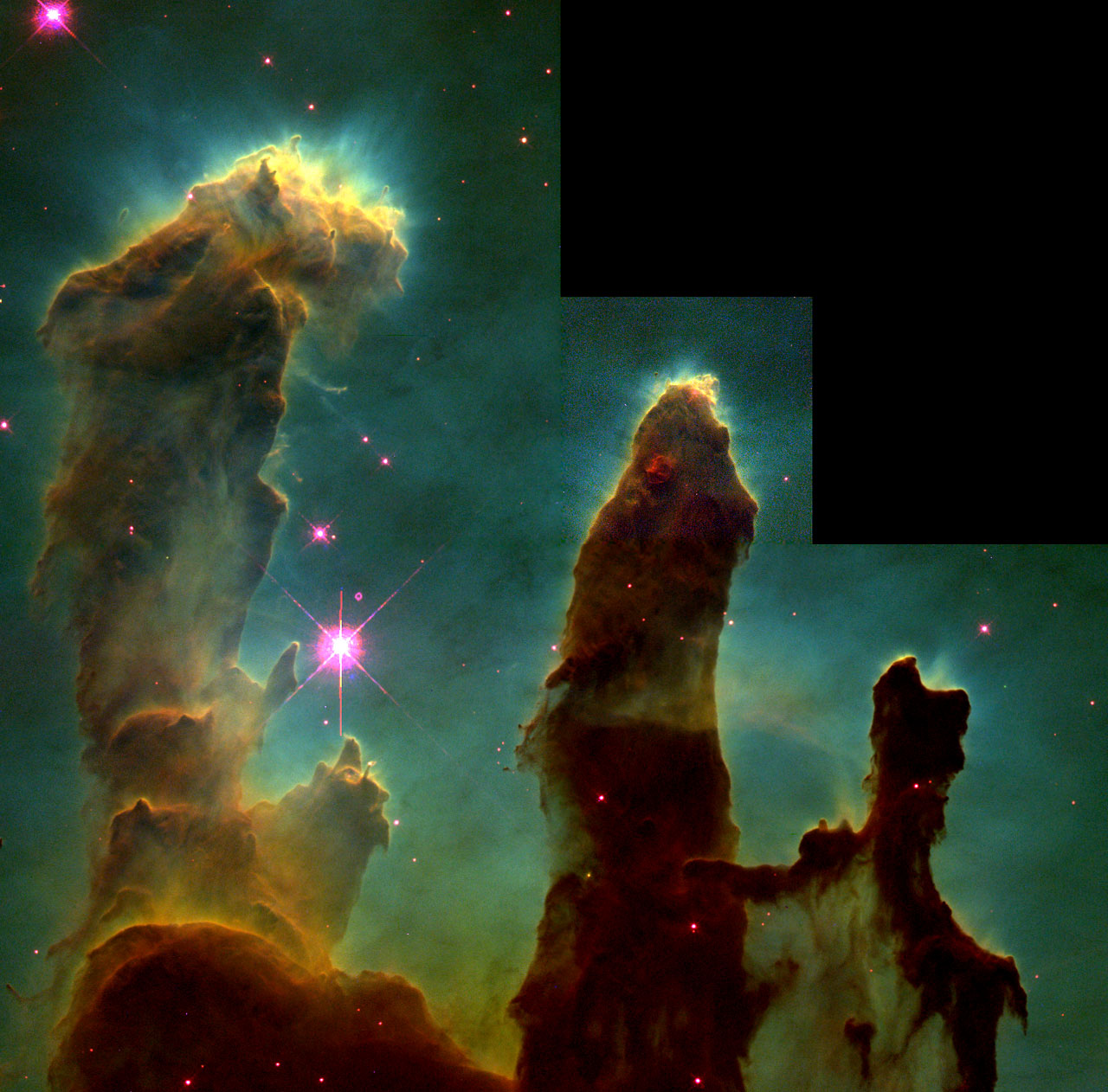

Hubble made his most famous shot on April 1, 95, without being distracted from clever work on fool's day. These are the Pillars of Creation, so named because of the formation of stars from these clusters of gas, and because they resemble the form. The picture shows a small piece of the central part of the Eagle Nebula. This nebula is interesting because the large stars in its center partially dispelled it, and also from the side of the Earth. Such luck allows you to look into the very center of the nebula and, for example, take the famous expressive picture.
Other telescopes also filmed this region in different ranges, but in the optical pillars they are most impressive: ionized by those very stars that dispelled some of the nebula, the gas glows blue, green and red, creating beautiful colors.
In 2014, the Pillars were redrawn with the updated Hubble equipment: the WFPC2 camera shot the first version and the WFC3 shot the second version.
ID: heic1501a

ID: heic1107a
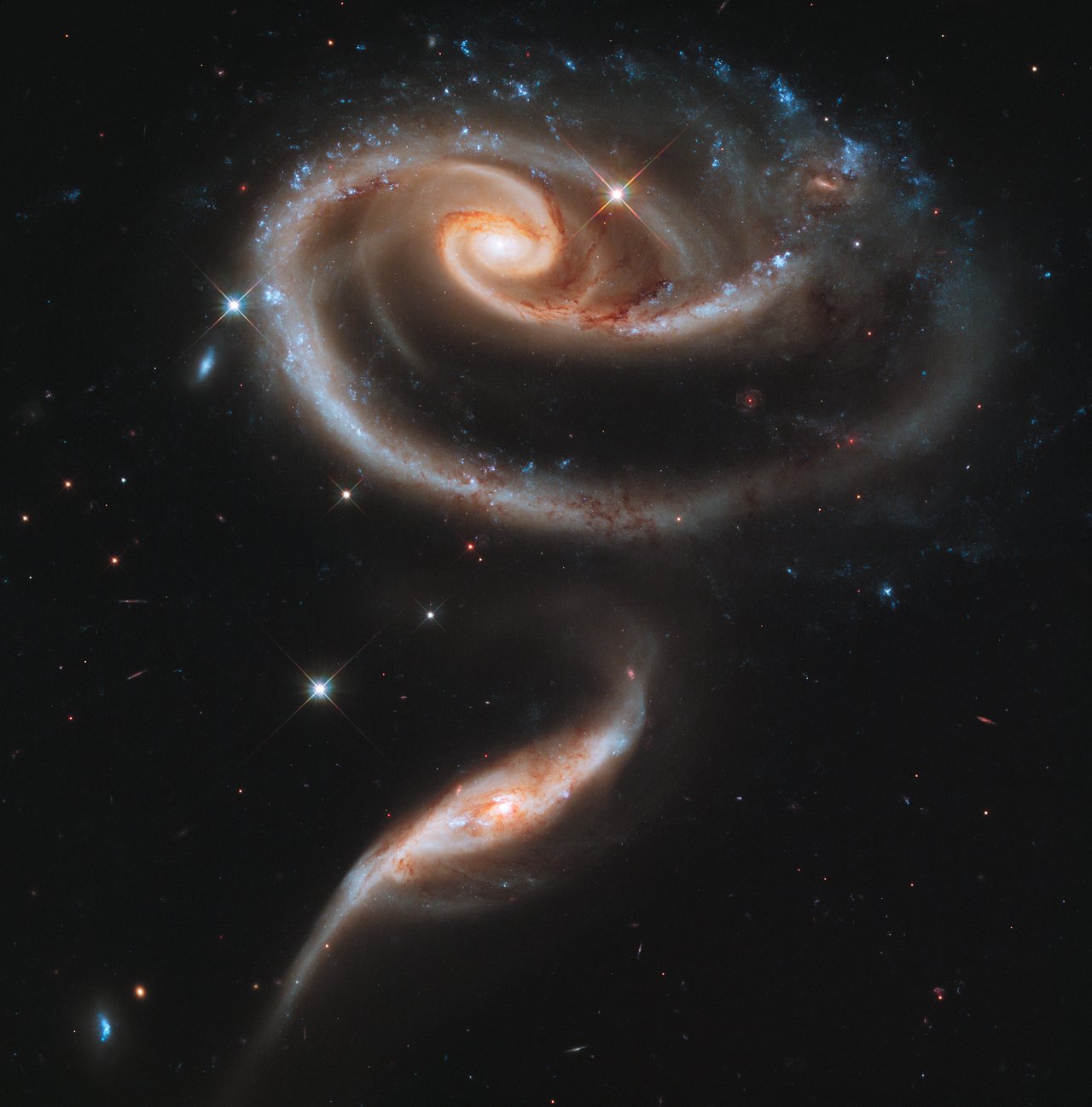

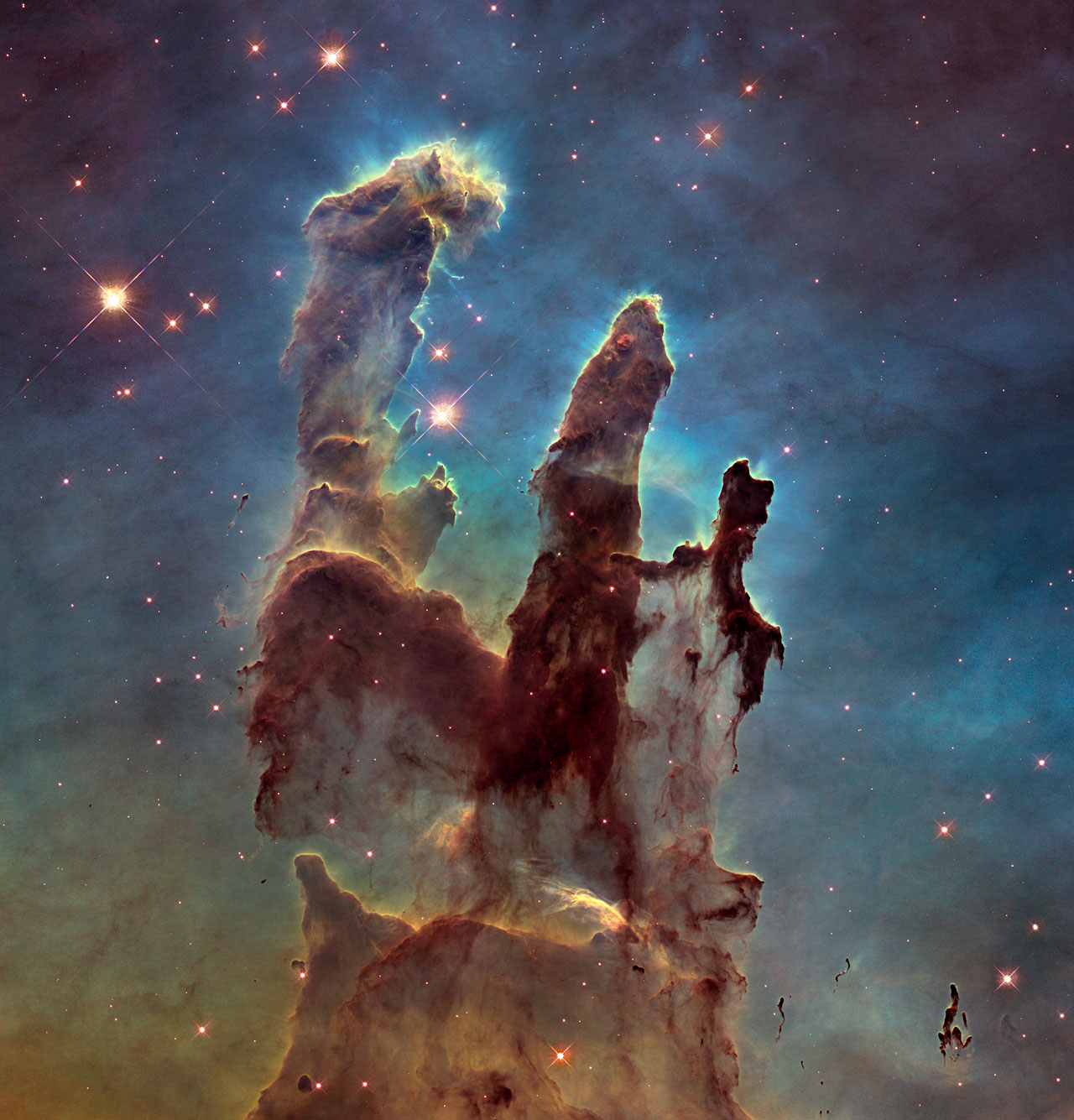
Object Arp 273 is a beautiful example of communication between galaxies that are close to each other. The asymmetric form of the top is a consequence of the so-called tidal interactions with the bottom. Together they form a grand flower, donated to humanity in 2011.
ID: opo0328a
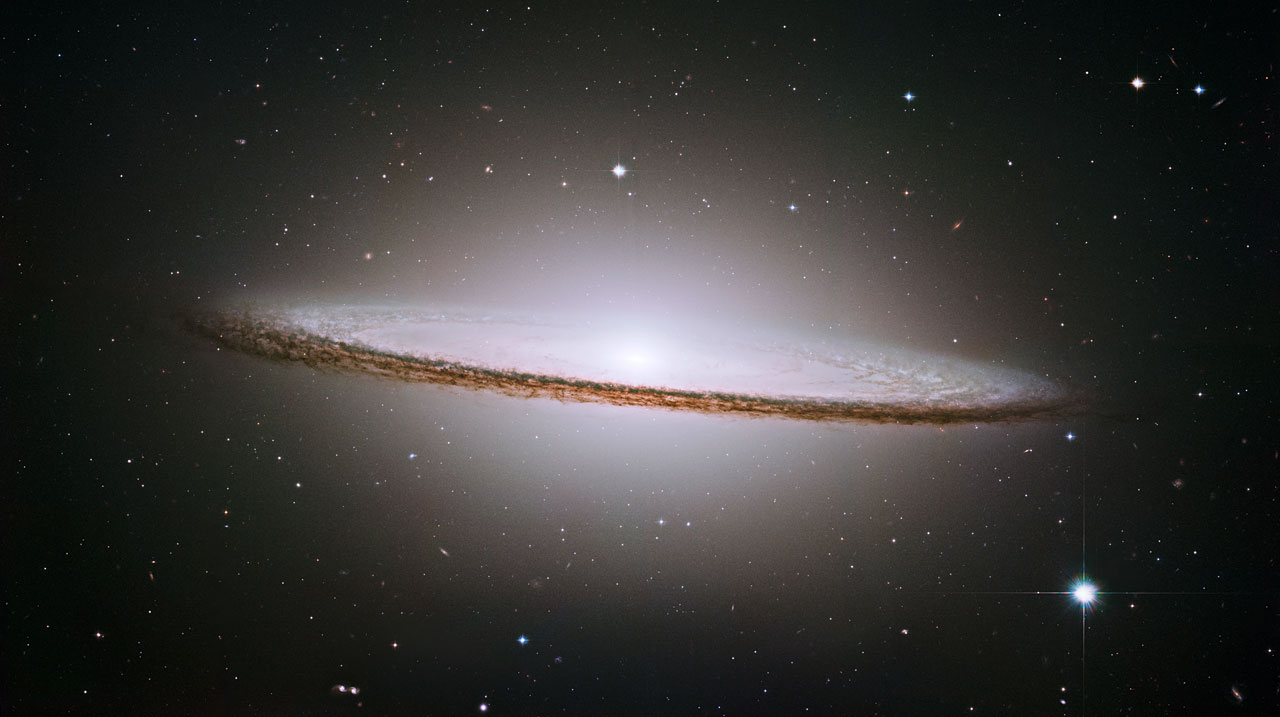

Messier 104 is a majestic galaxy, which seems to have been invented and painted in Hollywood. But no, the beautiful hundred-fourth is located on the southern edge of the Virgo constellation. And it is so bright that it is visible even in home telescopes. Hubble this beauty posed in 2004 year.
A new view of the Horsehead Nebula in the infrared spectrum - the image for the 23rd anniversary of Hubble
ID: heic1307a
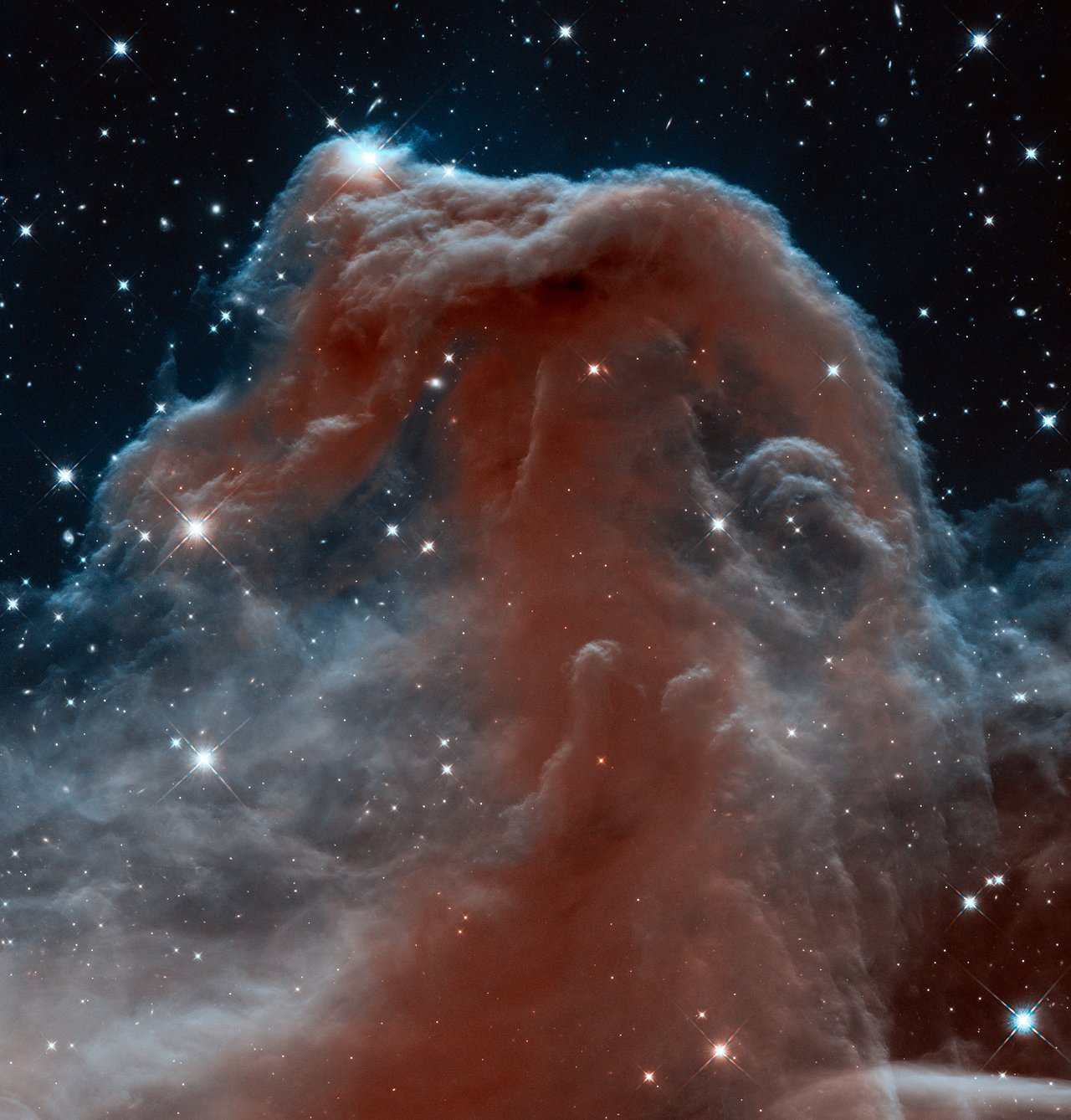

In 2013, Hubble recalled Barnard 33 in the infrared spectrum. And the gloomy Horsehead Nebula in the constellation of Orion, almost opaque and black in the visible range, appeared in a new light. That is, the range.
Before that, Hubble had already photographed her in 2001:
ID: heic0105a
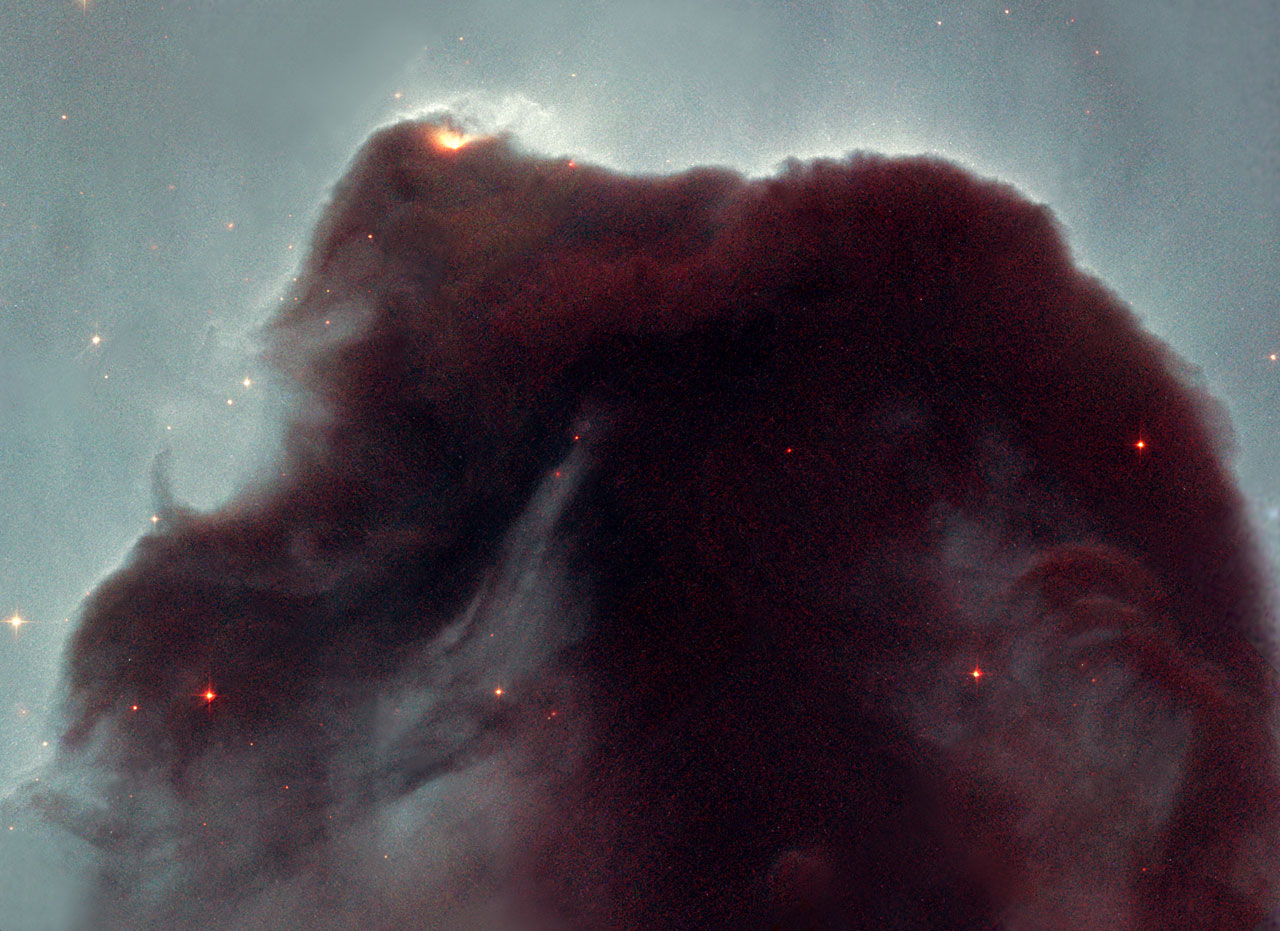

Then she won an online voting on a jubilee object for eleven years in orbit. Interestingly, as before the photographs of Hubble, the Horsehead was one of the most captured objects.
ID: heic1118a
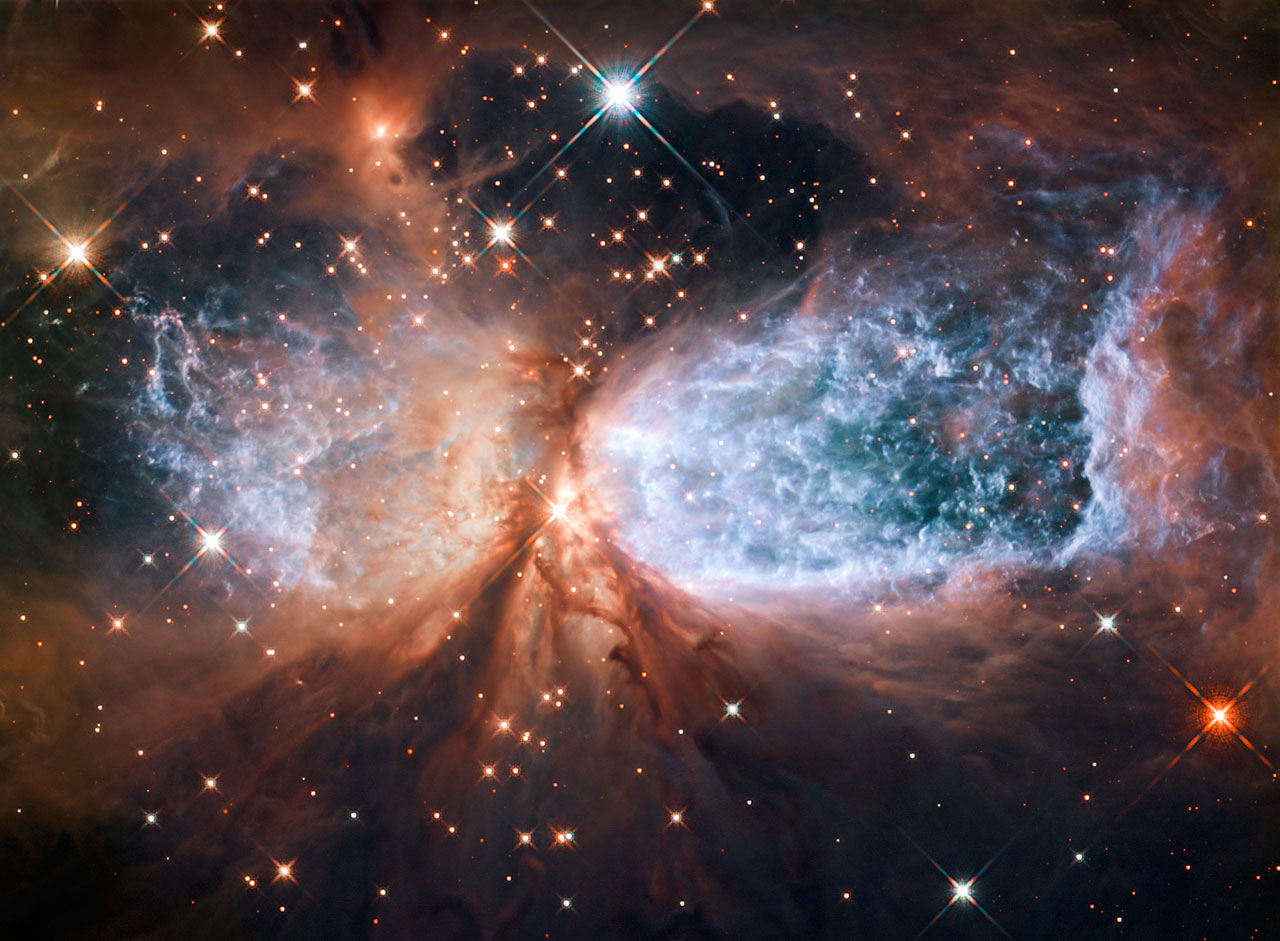

S106 is a star-forming region in the constellation Cygnus. The beautiful structure is due to emissions of a young star that is shrouded in donut-shaped dust in the center. This dust curtain has gaps above and below, through which the matter of the star is pulled out more actively, forming a shape resembling a known optical illusion . The picture was taken at the end of 2011.
ID: heic0609a
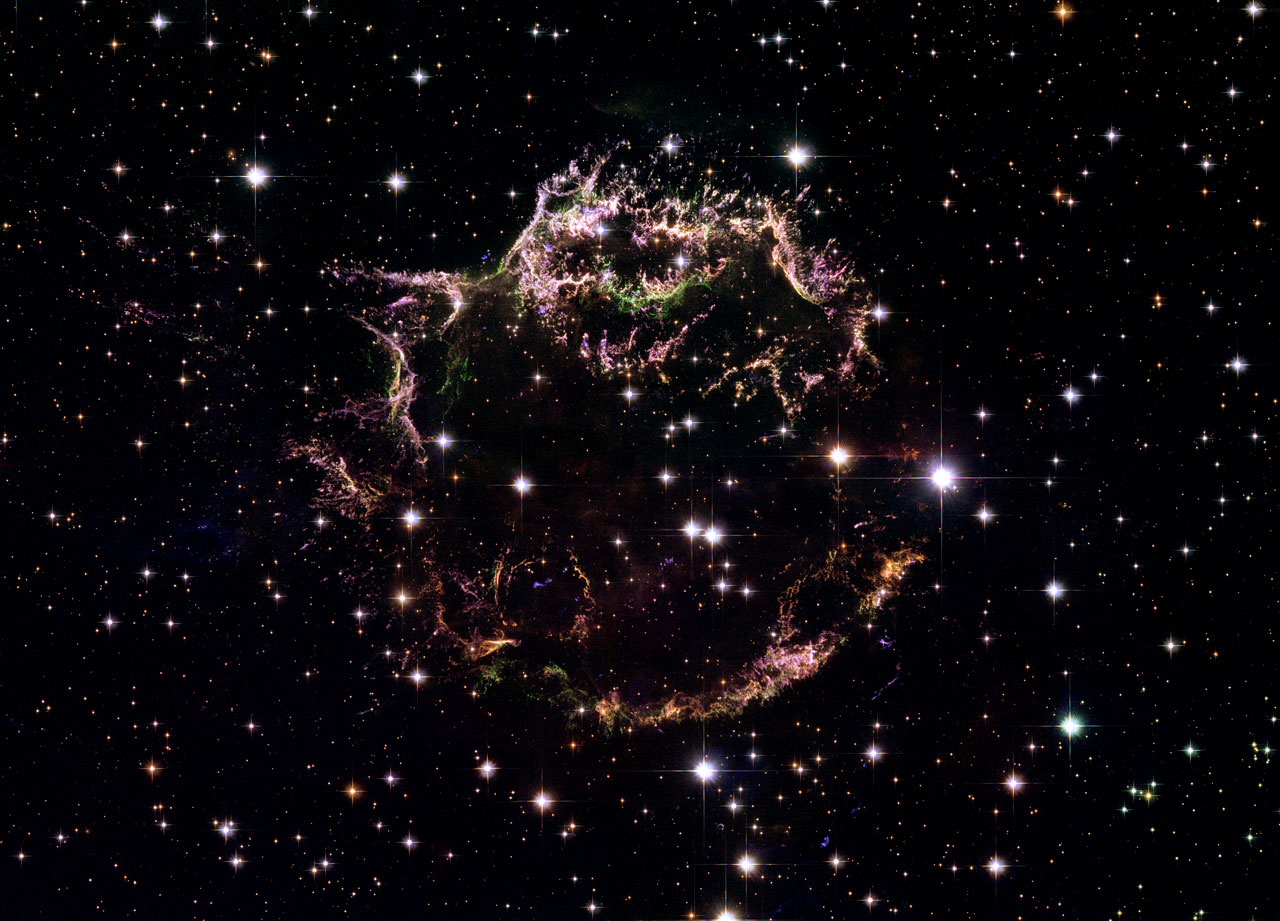

You have probably heard of the Supernova explosions. And this picture vividly shows one of the scenarios of the further fate of such objects.
In the photo of the year 2006 - the consequences of the explosion of the star Cassiopeia A, what happened right in our galaxy. Perfectly visible is a wave of matter scattering from the epicenter, with a complex and detailed structure.
ID: heic1311a
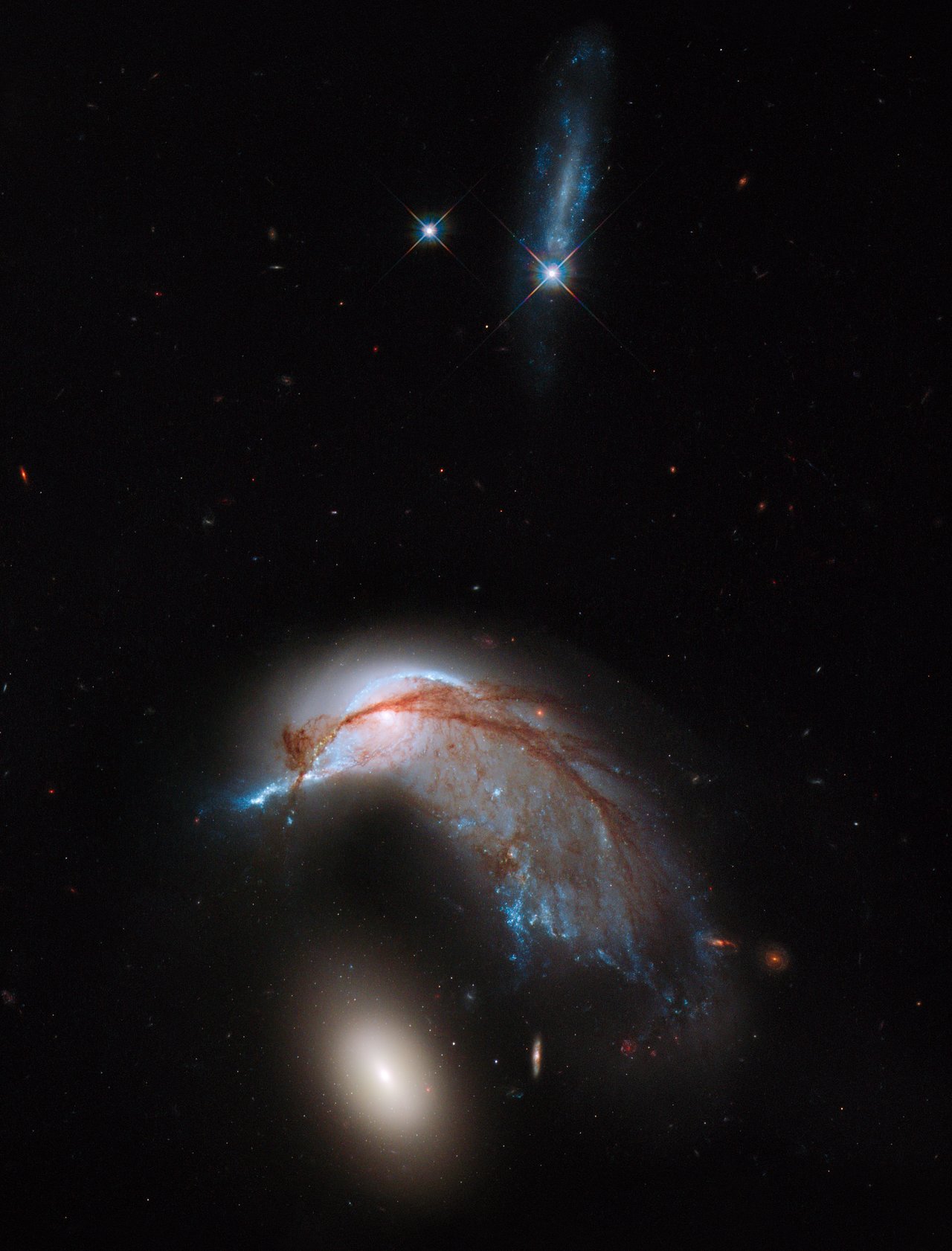

And again, a snapshot showing the effects of the interaction of two galaxies that are close to one another during their ecumenical journey.
NGC 2936 and 2937 collided and influenced each other. This is in itself an interesting event, but in this case one more aspect was added: the current shape of the galaxies resembles a penguin with an egg, which works as a big plus for the popularity of these galaxies.
In the cute picture of 2013, you can see traces of the collision: for example, the penguin's eye is formed, for the most part, by galactic egg bodies.
Knowing the age of both galaxies, you can finally answer what happened before: an egg or a penguin.
ID: heic0910h
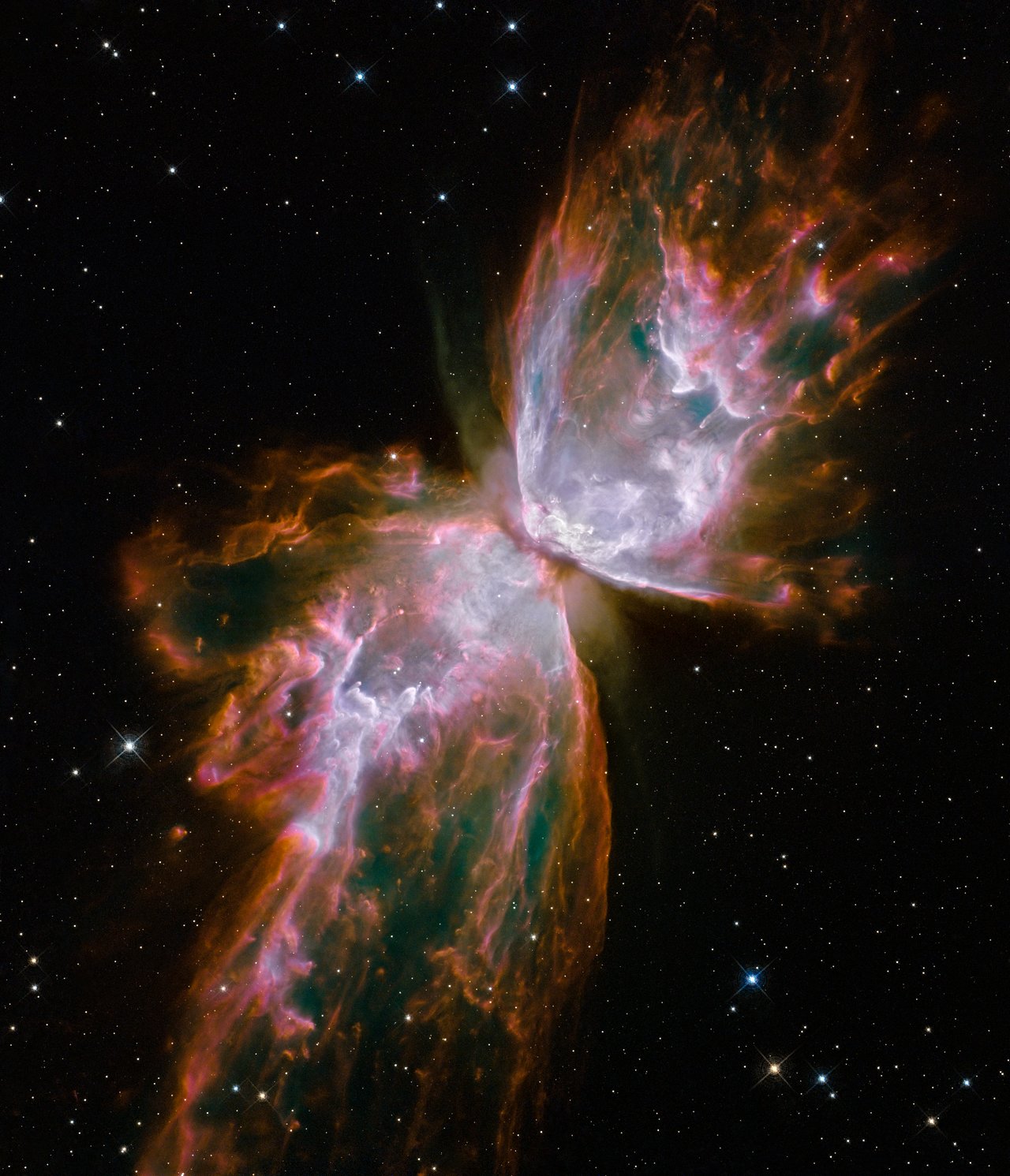

Sometimes heated to 20 thousand degrees, the flow of gas flying at a speed of almost a million km / h look like the wings of a fragile butterfly, you just need to find the right angle. Hubble did not have to search, the NGC 6302 nebula — it is also called the Butterfly Nebula or the Beetle — turned itself to be the right side for us.
These wings are created by the dying star of our galaxy in the constellation of Scopyon. The shape of the wings gas streams get again because of the ring of dust around the star. The same dust covers the star itself from us. Perhaps the ring was formed by the loss of matter by a star along the equator at relatively low speed, and the wings by a faster loss from the poles.
The photo was taken in 2009.
There are several Hubble images that have Deep Field in their names. These are frames with a huge multi-day exposure time, showing a small piece of the starry sky. In order to remove them, we had to very carefully select the area suitable for such an exposure. It should not have been blocked by the Earth and the Moon, there should not be any bright objects nearby and so on. As a result, Deep Field has become very useful for astronomers frames, which can be used to study the processes of the formation of the universe.
The most recent such frame - Hubble Extreme Deep Field of 2012 - quite boring at the narrow-minded gaze - is an unprecedented shot with an exposure of two million seconds (~ 23 days), showing 5.5 thousand galaxies, the dimmest of which have a brightness of ten billions less of human sight sensitivity.
ID: heic1214a
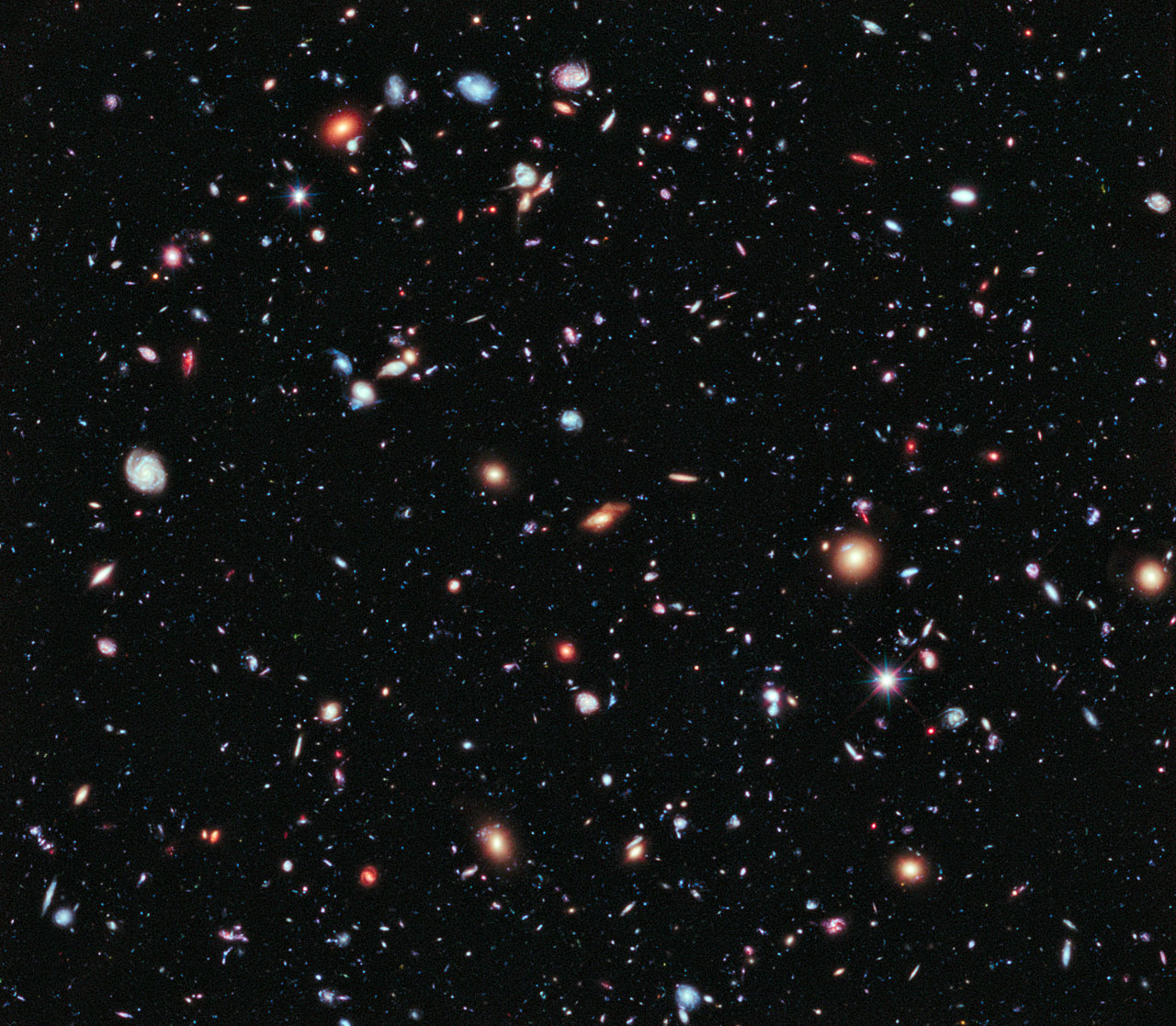

And this incredible picture freely lies on the Hubble site, showing everyone a tiny part 1/30 000 000 of our sky, on which thousands of galaxies are visible.
The value of the Hubble telescope is so great that it ceased to be a purely scientific achievement, becoming a cultural phenomenon a long time ago, often appearing in cinema and other forms of art in different forms.
Of course, Hollywood could not get past the story with a mirror, and in the movie “Naked Gun 2 and a half” 91, his image can be seen in the scene of the evening depression of Lieutenant Frank Drebin among the photos of the main disasters of the century.

An even more respectful reference can be found in the large-scale fantasy madhouse “Armageddon” of the 98th year, where Hubble takes the first pictures of a huge meteorite flying to Earth.

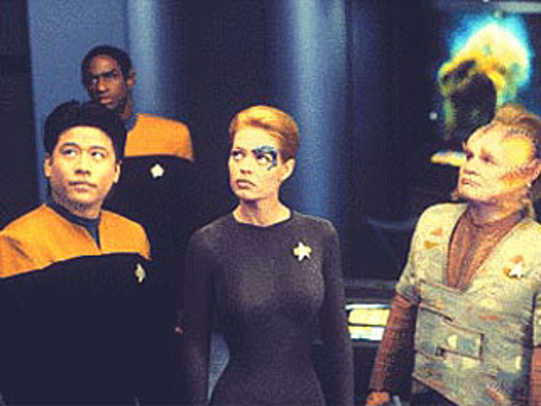
One of the first notable appearances taken by the telescope in mass culture is the fourth season of Star Trek Voyager in 97th year.

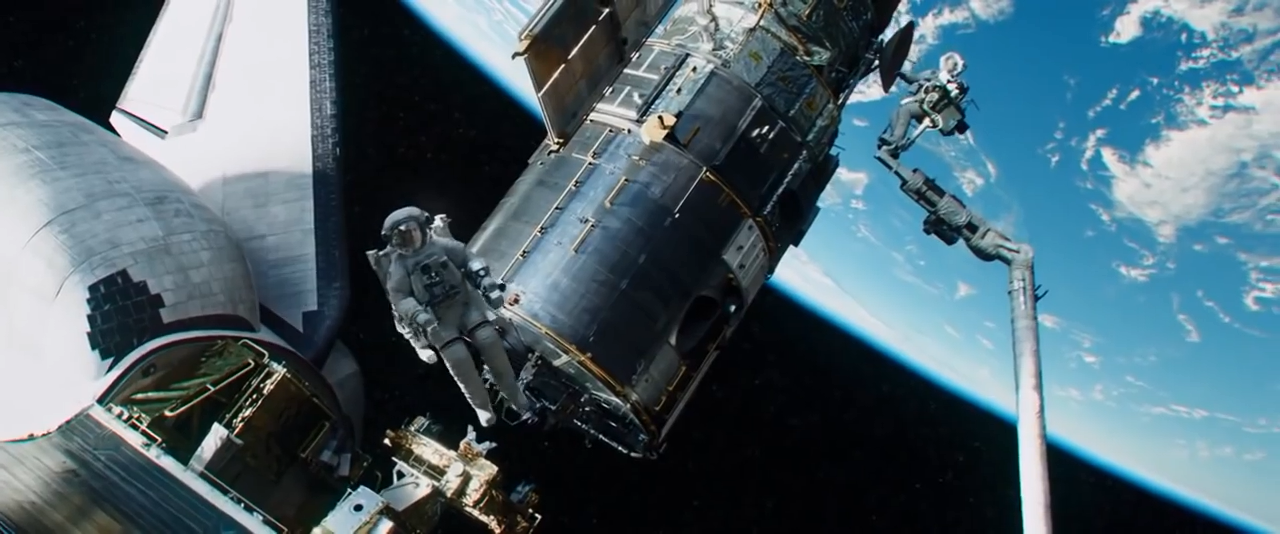
Hubble has starred in films and television a lot, and listing all of his films has been taking him too long. One of the most beautiful uses of photographs of the telescope, in addition to the documentary, can be called the 97th Contact with Jodie Foster. Also, the outset of the recent Gravity occurs during the repair mission at Hubble.

From the unexpected uses of Hubble’s legacy: memetic space leggings. Well, as prints for clothes in general.

Hubble should fall out of orbit after 2030. This fact seems sad, but in fact the telescope for many years exceeded the duration of its original mission. The telescope was upgraded several times, the equipment was changed for an ever more perfect one, but these modifications did not concern the main optics. And in the coming years, mankind will receive a more advanced replacement for the old fighter when they launch the telescope of James Webb. But after that, Hubble will continue to work until it fails. Incredible labor volumes of scientists, engineers, astronauts, people of other professions and money of American and European taxpayers were invested in the telescope.
In response, humanity has an unprecedented database of scientific data and objects of art that help to understand the structure of the universe and create a fashion for science.
It is difficult to understand the value of Hubble is not an astronomer, but for us it is an excellent symbol of the achievements of mankind. Not trouble-free, with a complex history, the telescope became a successful project, which, hopefully, will work for more than ten years for the benefit of science.
In the format of the article, I prepared the story of Hubble for Hicktimes, but initially we made a video. It has a voice-over text with historical, technical and simply beautiful illustrations.

A lot of pictures!
The history of the construction of Hubble - is the constant overcoming of difficulties, the struggle for funding and the search for solutions to unforeseen situations. The role of Hubble in science is priceless. It is impossible to compile a complete list of discoveries in astronomy and related directions, made thanks to telescope images, so many papers refer to the information he received. Nevertheless, official statistics speak of nearly 15 thousand publications.
Story
The idea to place a telescope in orbit arose almost a hundred years ago. The scientific substantiation of the importance of building such a telescope in the form of an article published by astrophysicist Lyman Spitzer in 1946. In 65, he was made head of the committee of the Academy of Sciences, which defined the tasks of such a project.
In the sixties, we managed to carry out several successful launches and deliver simpler devices to orbit, and in the 68th, NASA gave Hubble's forerunner the green light — the LST, the Large Space Telescope, with a larger mirror diameter — 3 meters against Hubble 2.4 — and an ambitious the task of launching it as early as 72, with the help of the space shuttle, which was then in development. But the estimated project estimate came out too expensive, there were difficulties with money, and in 74th the financing was completely canceled. The active lobbying of the project by astronomers, the involvement of the European Space Agency and the simplification of the characteristics up to approximately Hubble allowed in 78th to receive funding from Congress in the amount of 36 million dollars ridiculous in the total costs, which is now equal to about 137 million.
At the same time, the future telescope was named after Edwin Hubble , an astronomer and cosmologist who confirmed the existence of other galaxies, created the theory of the expansion of the Universe and gave his name not only to the telescope, but also to scientific law and magnitude.
The telescope was developed by several companies responsible for different elements, of which the most complex: the optical system, which Perkin-Elmer was involved in, and the spacecraft that Lockheed created. The budget has grown to $ 400 million.
Lockheed delayed the creation of the apparatus for three months and exceeded its budget by 30%. If you look at the construction history of devices of similar complexity, this is a normal situation. At Perkin-Elmer, everything was much worse. The company polished the mirror on innovative technology to the end of the 81st year, greatly exceeding the budget and spoiling relations with NASA. Interestingly, the mirror disc was made by Corning , which today produces Gorilla Glass, which is actively used in telephones. By the way, Kodak received a contract for the manufacture of a spare mirror using traditional polishing methods, if problems arise with polishing the main mirror. Delays in the creation of other components slowed down the process to the point that the quote from NASA’s description of work schedules that were “uncertain and changing daily” became well-known .

The launch was only possible by the year '86, but due to the Challenger disaster, the shuttles launch was suspended for the time being.
Hubble was put in parts in storage in special nitrogen-purged chambers, which cost six million dollars a month.
As a result, on April 24, 1990, the Discovery shuttle launched with a telescope into orbit. At this point, Hubble spent $ 2.5 billion. Total costs today are approaching ten billion.

Since the launch, there have been several dramatic events involving Hubble, but the main thing happened at the very beginning.
When, after the launch into orbit, the telescope began its work, it turned out that its sharpness is an order of magnitude lower than the calculated one. Instead of a tenth of an arc second, a whole second was obtained. After several checks, it turned out that the telescope mirror is too flat at the edges: for as many as two micrometers it does not coincide with the calculated one. The aberration due to this, in the literal sense of a microscopic defect, made most of the planned studies impossible.

A commission was assembled, whose members found the reason: an incredibly accurately calculated mirror was incorrectly polished. Moreover, even before the launch, the same deviations were shown by the pair of null-correctors used in the tests - the devices that were responsible for the desired curvature of the surface. But then they did not trust this testimony, relying on the testimony of the main null corrector, which showed the correct results and which was used for polishing. And one of the lenses of which, as it turned out, was incorrectly installed.

Human factor.
It was technically impossible to establish a new mirror directly in orbit, and it was too expensive to lower the telescope and then output it again. The solution was found elegant.
Yes, the mirror was made wrong. But it was done wrong with very high accuracy. The distortion was known, and it remained only to compensate, for which we developed a special correction system COSTAR . It was decided to install it as part of the first expedition to service the telescope. Such an expedition is a complex 10-day operation with astronaut exits into outer space. More futuristic work and can not imagine, but this is just maintenance. In total, there were four expeditions during the operation of the telescope, with two missions within the third.
On December 2, 1993, the shuttle Endeavor, for which it was the fifth flight, delivered astronauts to the telescope. They installed Costar and replaced the camera.
Costar corrected the spherical aberration of the mirror, playing the role of the most expensive points in history. The optical correction system performed its task until 2009, when the need for it was no longer due to the use of its own corrective optics in all new devices. She gave up a precious place in the telescope spectrograph and took pride of place in the National Museum of Aeronautics and Astronautics, after dismantling in the framework of the fourth expedition to service Hubble in 2009 year.
Control
Operated and monitored by a telescope in real time 24/7 from the control center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The tasks of the center are divided into two types: technical (maintenance, management and monitoring of the condition) and scientific (selection of objects, preparation of tasks and data collection itself). Every week, Hubble receives more than 100,000 different commands from Earth: these are corrective orbit instructions, and tasks for shooting space objects.
At MCC, the day is divided into three shifts, each of which is assigned a separate team of three to five people. During expeditions to the telescope itself, the staff of workers increases to several dozen.
By the way, there is a separate site developed by Chris Pete, where you can track the position of the celestial observatory. There is also data on other artificial orbital objects:
www.heavens-above.com
Hubble is a busy telescope, but even its tight schedule makes it possible to help absolutely anyone, even a non-professional, astronomer. Each year, the Space Telescope Institute for Space Research receives thousands of applications for booking time from astronomers from different countries. About 20% of applications are approved by the expert committee and, according to NASA, thanks to international inquiries, plus or minus 20,000 observations are made annually. All of these applications are docked, programmed and sent to Hubble from the same center in Maryland.
Optics
Current toolkit:
NICMOS
Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer
Camera and multi-object near-infrared spectrometer
ACS
Advanced Camera for Surveys
Advanced camera overview
WFC3
Wide field camera 3
Wide angle camera 3
Cos
Cosmic Origins Spectrograph
UV Spectrograph
STIS
Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph
Space Telescope Recording Spectrograph
Fgs
Fine Guidance Sensor
Guidance system
Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer
Camera and multi-object near-infrared spectrometer
ACS
Advanced Camera for Surveys
Advanced camera overview
WFC3
Wide field camera 3
Wide angle camera 3
Cos
Cosmic Origins Spectrograph
UV Spectrograph
STIS
Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph
Space Telescope Recording Spectrograph
Fgs
Fine Guidance Sensor
Guidance system
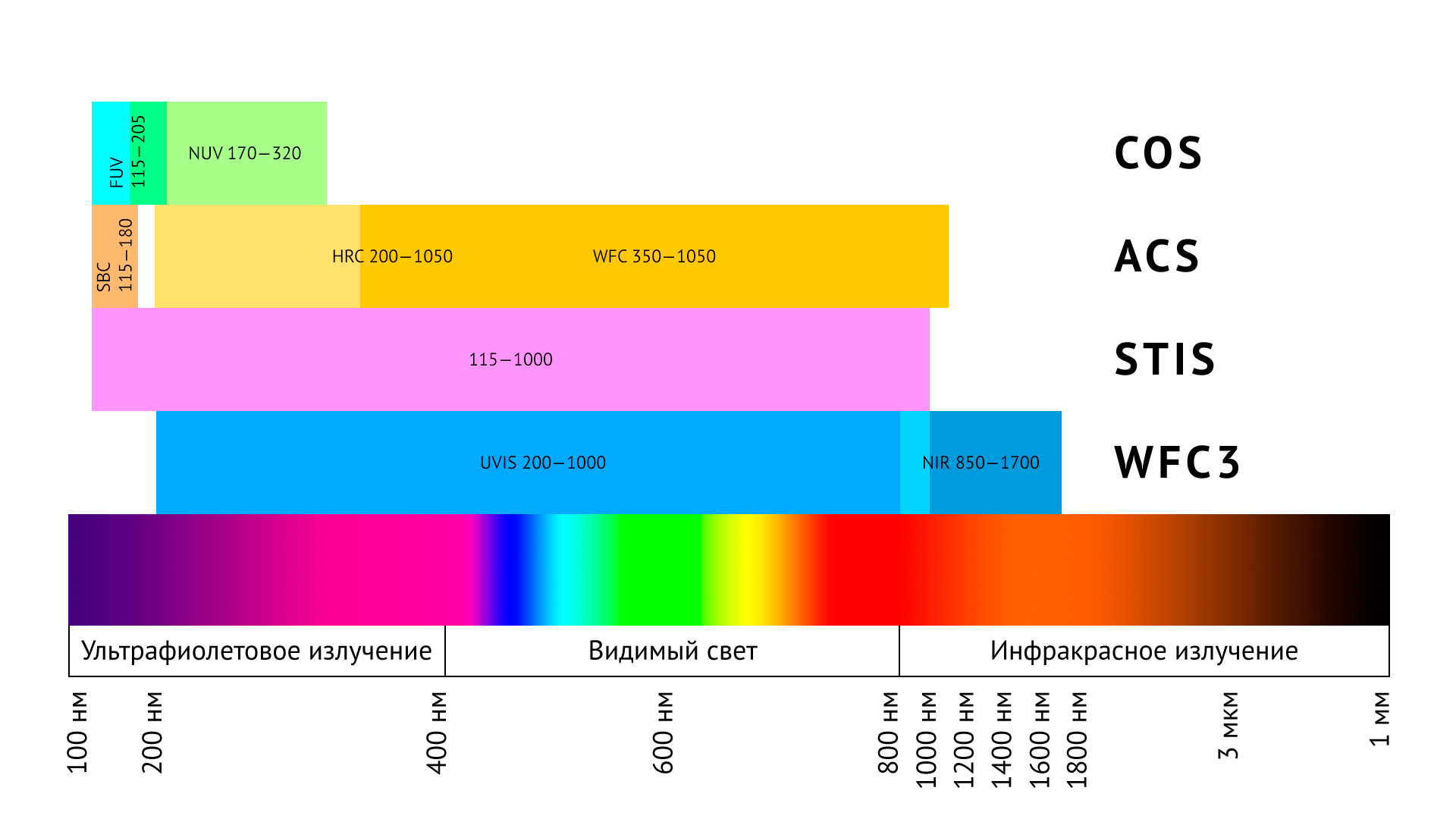
The main optics of the Hubble is made on the system Richie-Chretien . It consists of a round, hyperbolically curved mirror 2.4 m in diameter with a hole in the center. This mirror reflects on the secondary mirror also a hyperbolic form, which reflects a beam suitable for digitization into the central hole of the primary one. To filter out the extra parts of the spectrum and highlight the desired ranges using all sorts of filters.

In such telescopes they use exactly the system of mirrors, and not lenses, as in cameras. There are many reasons for this: temperature fluctuations, polishing tolerances, overall dimensions and the absence of beam losses inside the lens itself.
The main optics at Hubble has not changed since the beginning. A set of various tools that use it, completely changed for several serving expeditions. Hubble updated the toolkit, and during its existence there worked thirteen different tools. Today he carries six, one of which is in hibernation.
Wide-angle and planetary cameras of the first and second generation, and the Wide-angle camera of the third now answered for the photos in the optical range.
The potential of the first WFPC was never revealed due to problems with the mirror. And the expedition of the 93rd year, having established Costar, at the same time replaced it with the second version.
The WFPC2 camera had four square matrices, the images from which formed a large square. Nearly. One matrix - just the same “planetary” - received an image with a higher magnification, and when restoring the scale, this part of the image captures less than sixteenth part of the total square instead of a quarter, but in higher resolution. The remaining three matrices were responsible for the “wide angle”. That is why the full shots of the camera look like a square, which has eaten three blocks from one corner, and not because of problems with downloading files or other problems.

WFPC2 was replaced by WFC3 in 2009. The difference between them is well illustrated by the re-mounted Pillars of Creation, about which later.
In addition to the optical and near infrared range of the wide-angle camera, Hubble sees:
- using the STIS spectrograph in the near and far ultraviolet, as well as from the visible to the near infrared;
- ibid using one of the ACS channels, the other channels of which cover a huge frequency range from infrared to ultraviolet;
- weak point sources in the ultraviolet range spectrograph COS .

Snapshots
Hubble’s photographs are not exactly photographs in the conventional sense. A lot of information is not available in the optical range. Many space objects actively radiate in other bands. Hubble is equipped with a variety of devices with a variety of filters that allow you to capture data that astronomers later process and can be reduced to a visual image. The richness of the colors is provided by the different radiation ranges of the stars and the particles ionized by them, as well as their reflected light.
There is a lot of photos, I will tell only about several, the most fascinating. All photos have their ID, which is easily located on the Hubble site spacetelescope.org or directly on Google. Many pictures are on the site in high resolution, but here I leave screensize versions.
Pillars of creation
ID: opo9544a

Hubble made his most famous shot on April 1, 95, without being distracted from clever work on fool's day. These are the Pillars of Creation, so named because of the formation of stars from these clusters of gas, and because they resemble the form. The picture shows a small piece of the central part of the Eagle Nebula. This nebula is interesting because the large stars in its center partially dispelled it, and also from the side of the Earth. Such luck allows you to look into the very center of the nebula and, for example, take the famous expressive picture.
Other telescopes also filmed this region in different ranges, but in the optical pillars they are most impressive: ionized by those very stars that dispelled some of the nebula, the gas glows blue, green and red, creating beautiful colors.
In 2014, the Pillars were redrawn with the updated Hubble equipment: the WFPC2 camera shot the first version and the WFC3 shot the second version.
ID: heic1501a

Rose made from galaxies
ID: heic1107a

Object Arp 273 is a beautiful example of communication between galaxies that are close to each other. The asymmetric form of the top is a consequence of the so-called tidal interactions with the bottom. Together they form a grand flower, donated to humanity in 2011.
Magic Sombrero Galaxy
ID: opo0328a

Messier 104 is a majestic galaxy, which seems to have been invented and painted in Hollywood. But no, the beautiful hundred-fourth is located on the southern edge of the Virgo constellation. And it is so bright that it is visible even in home telescopes. Hubble this beauty posed in 2004 year.
A new view of the Horsehead Nebula in the infrared spectrum - the image for the 23rd anniversary of Hubble
ID: heic1307a

In 2013, Hubble recalled Barnard 33 in the infrared spectrum. And the gloomy Horsehead Nebula in the constellation of Orion, almost opaque and black in the visible range, appeared in a new light. That is, the range.
Before that, Hubble had already photographed her in 2001:
ID: heic0105a

Then she won an online voting on a jubilee object for eleven years in orbit. Interestingly, as before the photographs of Hubble, the Horsehead was one of the most captured objects.
Hubble captures the star-forming region of S106
ID: heic1118a

S106 is a star-forming region in the constellation Cygnus. The beautiful structure is due to emissions of a young star that is shrouded in donut-shaped dust in the center. This dust curtain has gaps above and below, through which the matter of the star is pulled out more actively, forming a shape resembling a known optical illusion . The picture was taken at the end of 2011.
Cassiopeia A: The colorful consequences of the death of a star
ID: heic0609a

You have probably heard of the Supernova explosions. And this picture vividly shows one of the scenarios of the further fate of such objects.
In the photo of the year 2006 - the consequences of the explosion of the star Cassiopeia A, what happened right in our galaxy. Perfectly visible is a wave of matter scattering from the epicenter, with a complex and detailed structure.
Image of Hubble Arp 142
ID: heic1311a

And again, a snapshot showing the effects of the interaction of two galaxies that are close to one another during their ecumenical journey.
NGC 2936 and 2937 collided and influenced each other. This is in itself an interesting event, but in this case one more aspect was added: the current shape of the galaxies resembles a penguin with an egg, which works as a big plus for the popularity of these galaxies.
In the cute picture of 2013, you can see traces of the collision: for example, the penguin's eye is formed, for the most part, by galactic egg bodies.
Knowing the age of both galaxies, you can finally answer what happened before: an egg or a penguin.
A butterfly emerging from the remnants of a star in the planetary nebula NGC 6302
ID: heic0910h

Sometimes heated to 20 thousand degrees, the flow of gas flying at a speed of almost a million km / h look like the wings of a fragile butterfly, you just need to find the right angle. Hubble did not have to search, the NGC 6302 nebula — it is also called the Butterfly Nebula or the Beetle — turned itself to be the right side for us.
These wings are created by the dying star of our galaxy in the constellation of Scopyon. The shape of the wings gas streams get again because of the ring of dust around the star. The same dust covers the star itself from us. Perhaps the ring was formed by the loss of matter by a star along the equator at relatively low speed, and the wings by a faster loss from the poles.
The photo was taken in 2009.
Deep field
There are several Hubble images that have Deep Field in their names. These are frames with a huge multi-day exposure time, showing a small piece of the starry sky. In order to remove them, we had to very carefully select the area suitable for such an exposure. It should not have been blocked by the Earth and the Moon, there should not be any bright objects nearby and so on. As a result, Deep Field has become very useful for astronomers frames, which can be used to study the processes of the formation of the universe.
The most recent such frame - Hubble Extreme Deep Field of 2012 - quite boring at the narrow-minded gaze - is an unprecedented shot with an exposure of two million seconds (~ 23 days), showing 5.5 thousand galaxies, the dimmest of which have a brightness of ten billions less of human sight sensitivity.
ID: heic1214a

And this incredible picture freely lies on the Hubble site, showing everyone a tiny part 1/30 000 000 of our sky, on which thousands of galaxies are visible.
Masscult
The value of the Hubble telescope is so great that it ceased to be a purely scientific achievement, becoming a cultural phenomenon a long time ago, often appearing in cinema and other forms of art in different forms.
Of course, Hollywood could not get past the story with a mirror, and in the movie “Naked Gun 2 and a half” 91, his image can be seen in the scene of the evening depression of Lieutenant Frank Drebin among the photos of the main disasters of the century.

An even more respectful reference can be found in the large-scale fantasy madhouse “Armageddon” of the 98th year, where Hubble takes the first pictures of a huge meteorite flying to Earth.

One of the first notable appearances taken by the telescope in mass culture is the fourth season of Star Trek Voyager in 97th year.

Hubble has starred in films and television a lot, and listing all of his films has been taking him too long. One of the most beautiful uses of photographs of the telescope, in addition to the documentary, can be called the 97th Contact with Jodie Foster. Also, the outset of the recent Gravity occurs during the repair mission at Hubble.

From the unexpected uses of Hubble’s legacy: memetic space leggings. Well, as prints for clothes in general.

Hubble (1990 - 203_)
Hubble should fall out of orbit after 2030. This fact seems sad, but in fact the telescope for many years exceeded the duration of its original mission. The telescope was upgraded several times, the equipment was changed for an ever more perfect one, but these modifications did not concern the main optics. And in the coming years, mankind will receive a more advanced replacement for the old fighter when they launch the telescope of James Webb. But after that, Hubble will continue to work until it fails. Incredible labor volumes of scientists, engineers, astronauts, people of other professions and money of American and European taxpayers were invested in the telescope.
In response, humanity has an unprecedented database of scientific data and objects of art that help to understand the structure of the universe and create a fashion for science.
It is difficult to understand the value of Hubble is not an astronomer, but for us it is an excellent symbol of the achievements of mankind. Not trouble-free, with a complex history, the telescope became a successful project, which, hopefully, will work for more than ten years for the benefit of science.
Roller
In the format of the article, I prepared the story of Hubble for Hicktimes, but initially we made a video. It has a voice-over text with historical, technical and simply beautiful illustrations.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/410735/