Kubernetes Authentication with GitHub OAuth and Dex
I present to your attention a tutorial for generating accesses to the Kubernetes cluster using Dex, dex-k8s-authenticator and GitHub.

Local meme from Kubernetes Russian-language chat in Telegram
We use Kubernetes to create dynamic environments for the development team and QA. Thus, we want to give them access to the cluster for both dashboards and kubectl. Unlike OpenShift, vanilla Kubernetes does not have native authentication, so we use third-party tools for this.
In this configuration, we use:
We tried to use Google OIDC, but unfortunately we could not get them with the groups, so the integration with GitHub completely satisfied us. Without group mapping, it’s not possible to create group-based RBAC policies.
So, how does our authorization process in Kubernetes work in a visual representation:
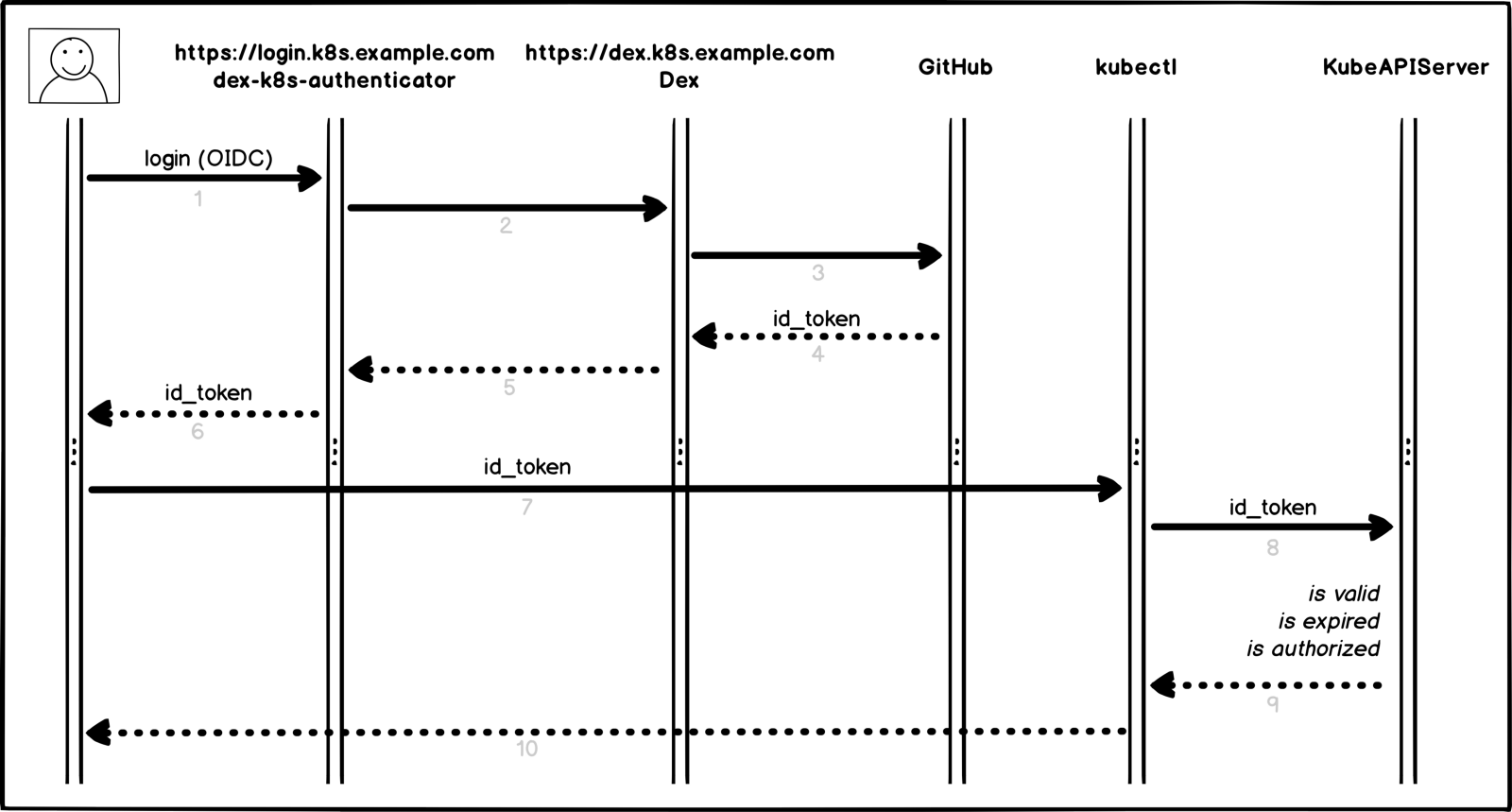
Authorization process
A little more detail and the points:
Of course, we already have the Kubernetes cluster (
If you do not have HELM, it is very easy to install.
First we need to set up GitHub.
Go to the organization's settings page (
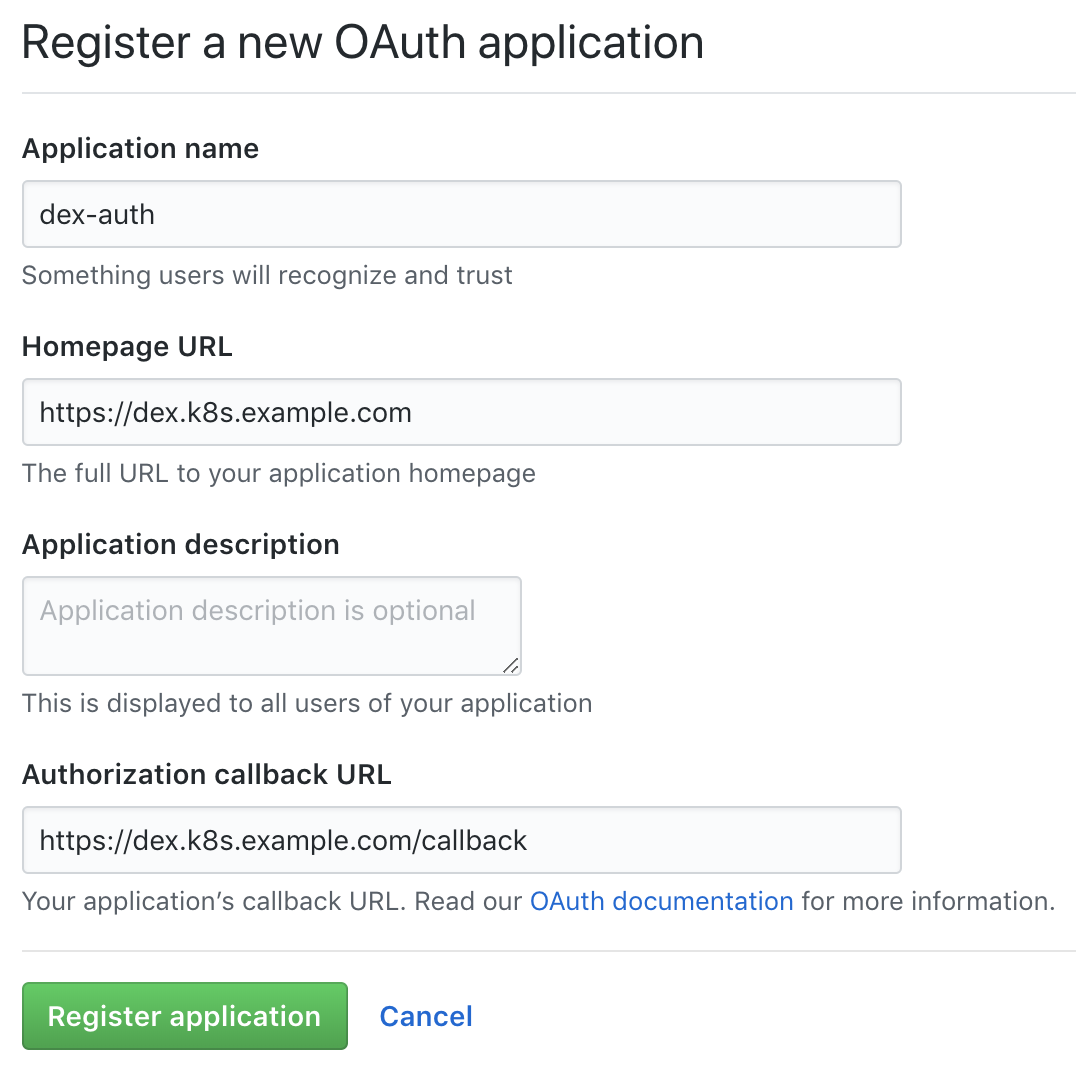
Creating a new application in GitHub
Fill in the fields with the required URLs, for example:
Be careful with links, it is important not to lose slashes.
In response to the completed form, GitHub will generate a
Prepare DNS records for subdomains
Create SSL certificates:
ClusterIssuer with the name
For kubeAPIServer to work, you need to configure the OIDC and update the cluster:
We use kops to deploy clusters, but this works similarly for other cluster managers .
For Dex to work, you must have a certificate and a key from the Kubernetes wizard, which will pull it out of there:
Clone the dex-k8s-authenticator repository:
With the help of values-files we can flexibly set variables for our HELM-charts .
We describe the configuration for Dex:
And for dex-k8s-authenticator:
Install Dex and dex-k8s-authenticator:
Check the service operability (Dex should return code 400, and dex-k8s-authenticator code 200):
Create a ClusterRole for the group, in our case with read-only access:
Create a configuration for the ClusterRoleBinding:
Now we are ready for testing.
Go to the login page (

Login page
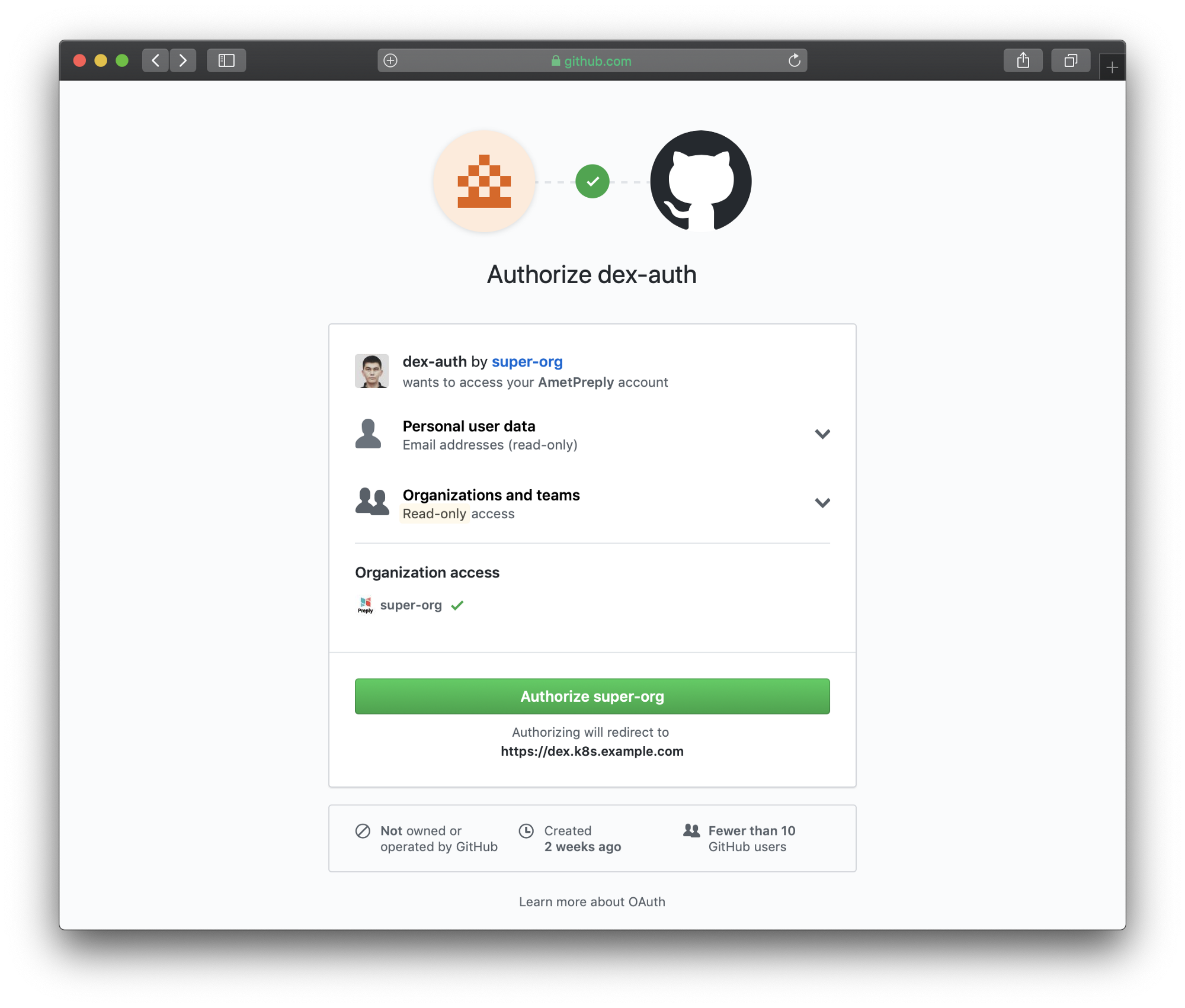
Login page redirected to GitHub

Follow the generated instructions for access
After copying from the web page, we can use kubectl to manage our cluster resources:
And it works, all GitHub users in our organization can see the resources and go to the subs, but they have no rights to change them.

Local meme from Kubernetes Russian-language chat in Telegram
Introduction
We use Kubernetes to create dynamic environments for the development team and QA. Thus, we want to give them access to the cluster for both dashboards and kubectl. Unlike OpenShift, vanilla Kubernetes does not have native authentication, so we use third-party tools for this.
In this configuration, we use:
- dex-k8s-authenticator - web application for generating the kubectl config
- Dex - OpenID Connect Provider
- GitHub - just because we use GitHub in our company
We tried to use Google OIDC, but unfortunately we could not get them with the groups, so the integration with GitHub completely satisfied us. Without group mapping, it’s not possible to create group-based RBAC policies.
So, how does our authorization process in Kubernetes work in a visual representation:

Authorization process
A little more detail and the points:
- User logs in to dex-k8s-authenticator (
login.k8s.example.com) - dex-k8s-authenticator redirects the request to Dex (
dex.k8s.example.com) - Dex redirects to the GitHub login page.
- GitHub generates the necessary authorization information and returns it to Dex
- Dex transmits the received information to the dex-k8s-authenticator
- User gets OIDC token from github
- dex-k8s-authenticator adds a token to kubeconfig
- kubectl transfers a token to KubeAPIServer
- KubeAPIServer, based on the transferred token, returns access to kubectl
- User gets access from kubectl
Preparatory actions
Of course, we already have the Kubernetes cluster (
k8s.example.com ) installed, and also the HELM pre-installed. We also have an organization on GitHub (super-org).If you do not have HELM, it is very easy to install.
First we need to set up GitHub.
Go to the organization's settings page (
https://github.com/organizations/super-org/settings/applications ) and create a new application (Authorized OAuth App):
Creating a new application in GitHub
Fill in the fields with the required URLs, for example:
- Homepage URL:
https://dex.k8s.example.com - Authorization callback URL:
https://dex.k8s.example.com/callback
Be careful with links, it is important not to lose slashes.
In response to the completed form, GitHub will generate a
Client ID and Client secret , save them in a safe place, they will be useful to us (for example, we use Vault to store secrets): Client ID: 1ab2c3d4e5f6g7h8 Client secret: 98z76y54x32w1 Prepare DNS records for subdomains
login.k8s.example.com and dex.k8s.example.com , as well as SSL certificates for ingress.Create SSL certificates:
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Certificate metadata: name: cert-auth-dex namespace: kube-system spec: secretName: cert-auth-dex dnsNames: - dex.k8s.example.com acme: config: - http01: ingressClass: nginx domains: - dex.k8s.example.com issuerRef: name: le-clusterissuer kind: ClusterIssuer --- apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Certificate metadata: name: cert-auth-login namespace: kube-system spec: secretName: cert-auth-login dnsNames: - login.k8s.example.com acme: config: - http01: ingressClass: nginx domains: - login.k8s.example.com issuerRef: name: le-clusterissuer kind: ClusterIssuer EOF kubectl describe certificates cert-auth-dex -n kube-system kubectl describe certificates cert-auth-login -n kube-system ClusterIssuer with the name
le-clusterissuer should already exist, but if not, create it with HELM: helm install --namespace kube-system -n cert-manager stable/cert-manager cat << EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: ClusterIssuer metadata: name: le-clusterissuer namespace: kube-system spec: acme: server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory email: k8s-admin@example.com privateKeySecretRef: name: le-clusterissuer http01: {} EOF KubeAPIServer configuration
For kubeAPIServer to work, you need to configure the OIDC and update the cluster:
kops edit cluster ... kubeAPIServer: anonymousAuth: false authorizationMode: RBAC oidcClientID: dex-k8s-authenticator oidcGroupsClaim: groups oidcIssuerURL: https://dex.k8s.example.com/ oidcUsernameClaim: email kops update cluster --yes kops rolling-update cluster --yes We use kops to deploy clusters, but this works similarly for other cluster managers .
Dex and dex-k8s-authenticator configuration
For Dex to work, you must have a certificate and a key from the Kubernetes wizard, which will pull it out of there:
sudo cat /srv/kubernetes/ca.{crt,key} -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- AAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBCCCCCC -----END CERTIFICATE----- -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- DDDDDDDDDDDEEEEEEEEEEFFFFFF -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----- Clone the dex-k8s-authenticator repository:
git clone git@github.com:mintel/dex-k8s-authenticator.git cd dex-k8s-authenticator/ With the help of values-files we can flexibly set variables for our HELM-charts .
We describe the configuration for Dex:
cat << \EOF > values-dex.yml global: deployEnv: prod tls: certificate: |- -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- AAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBCCCCCC -----END CERTIFICATE----- key: |- -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- DDDDDDDDDDDEEEEEEEEEEFFFFFF -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY----- ingress: enabled: true annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true" path: / hosts: - dex.k8s.example.com tls: - secretName: cert-auth-dex hosts: - dex.k8s.example.com serviceAccount: create: true name: dex-auth-sa config: | issuer: https://dex.k8s.example.com/ storage: # https://github.com/dexidp/dex/issues/798 type: sqlite3 config: file: /var/dex.db web: http: 0.0.0.0:5556 frontend: theme: "coreos" issuer: "Example Co" issuerUrl: "https://example.com" logoUrl: https://example.com/images/logo-250x25.png expiry: signingKeys: "6h" idTokens: "24h" logger: level: debug format: json oauth2: responseTypes: ["code", "token", "id_token"] skipApprovalScreen: true connectors: - type: github id: github name: GitHub config: clientID: $GITHUB_CLIENT_ID clientSecret: $GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET redirectURI: https://dex.k8s.example.com/callback orgs: - name: super-org teams: - team-red staticClients: - id: dex-k8s-authenticator name: dex-k8s-authenticator secret: generatedLongRandomPhrase redirectURIs: - https://login.k8s.example.com/callback/ envSecrets: GITHUB_CLIENT_ID: "1ab2c3d4e5f6g7h8" GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET: "98z76y54x32w1" EOF And for dex-k8s-authenticator:
cat << EOF > values-auth.yml global: deployEnv: prod dexK8sAuthenticator: clusters: - name: k8s.example.com short_description: "k8s cluster" description: "Kubernetes cluster" issuer: https://dex.k8s.example.com/ k8s_master_uri: https://api.k8s.example.com client_id: dex-k8s-authenticator client_secret: generatedLongRandomPhrase redirect_uri: https://login.k8s.example.com/callback/ k8s_ca_pem: | -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- AAAAAAAAAAABBBBBBBBBBCCCCCC -----END CERTIFICATE----- ingress: enabled: true annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true" path: / hosts: - login.k8s.example.com tls: - secretName: cert-auth-login hosts: - login.k8s.example.com EOF Install Dex and dex-k8s-authenticator:
helm install -n dex --namespace kube-system --values values-dex.yml charts/dex helm install -n dex-auth --namespace kube-system --values values-auth.yml charts/dex-k8s-authenticator Check the service operability (Dex should return code 400, and dex-k8s-authenticator code 200):
curl -sI https://dex.k8s.example.com/callback | head -1 HTTP/2 400 curl -sI https://login.k8s.example.com/ | head -1 HTTP/2 200 RBAC configuration
Create a ClusterRole for the group, in our case with read-only access:
cat << EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: cluster-read-all rules: - apiGroups: - "" - apps - autoscaling - batch - extensions - policy - rbac.authorization.k8s.io - storage.k8s.io resources: - componentstatuses - configmaps - cronjobs - daemonsets - deployments - events - endpoints - horizontalpodautoscalers - ingress - ingresses - jobs - limitranges - namespaces - nodes - pods - pods/log - pods/exec - persistentvolumes - persistentvolumeclaims - resourcequotas - replicasets - replicationcontrollers - serviceaccounts - services - statefulsets - storageclasses - clusterroles - roles verbs: - get - watch - list - nonResourceURLs: ["*"] verbs: - get - watch - list - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods/exec"] verbs: ["create"] EOF Create a configuration for the ClusterRoleBinding:
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: dex-cluster-auth namespace: kube-system roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-read-all subjects: - kind: Group name: "super-org:team-red" EOF Now we are ready for testing.
Tests
Go to the login page (
https://login.k8s.example.com ) and log in using a GitHub account:
Login page

Login page redirected to GitHub

Follow the generated instructions for access
After copying from the web page, we can use kubectl to manage our cluster resources:
kubectl get po NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mypod 1/1 Running 0 3d kubectl delete po mypod Error from server (Forbidden): pods "mypod" is forbidden: User "amet@example.com" cannot delete pods in the namespace "default" And it works, all GitHub users in our organization can see the resources and go to the subs, but they have no rights to change them.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/436238/