App for iOS and Android on Kotlin + Flutter UI

Introduction
Hello. Some time ago, I decided to do my project for Android and iOS at the same time. Naturally, the question arose about the choice of technology. A couple of weeks, I watched the popular stacks and chose Kotlin / Native. Since I am an Android developer, I’ve been familiar with Kotlin for a long time, but I didn’t have much experience with Swift and I wanted to get most of the code common to both platforms. Therefore, the question immediately arose, and how to write a UI for iOS. A quick glance at the market prompted Flutter, which allows you to write UI for two platforms at the same time. Actually, this is how the story began.
The article describes the Flutter build experience as a UI and Kotlin for the main logic. Important: under the cut a lot of pictures and instructions on how to build a project
Table of contents
- Creating a shared library on Kotlin
- Creating an Android Application
- Create an iOS project
- Adding Flutter to Android Application
- Adding Flutter to an iOS project
- Conclusion
Part 1
Creating a shared library on Kotlin
- Choosing the Kotlin Mobile Shared library
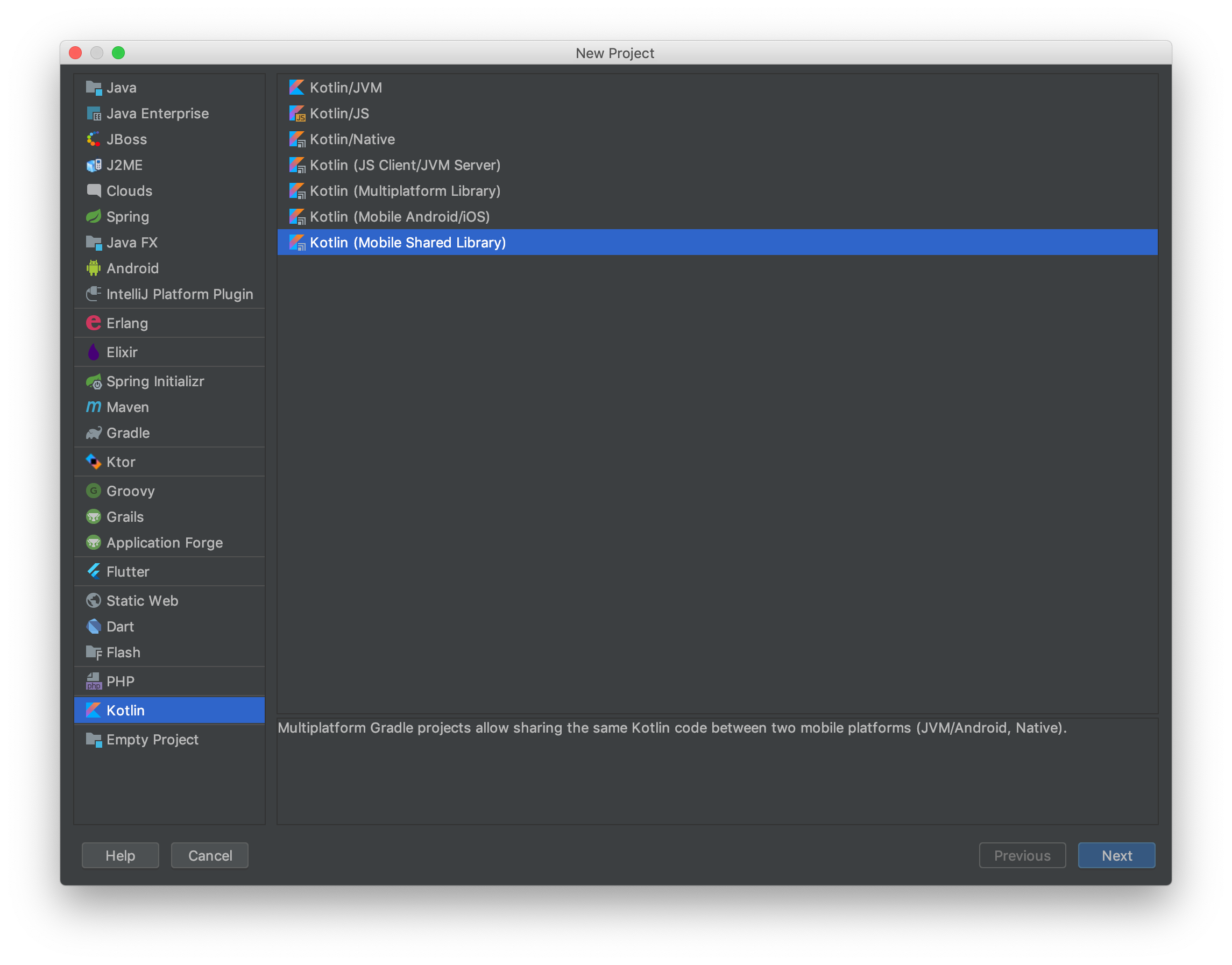
- Further
- We specify our working folder, here I made a separate folder for the project. Since I will have 4 different projects and it is more convenient to keep them in one place.
- It remains to indicate in
local.propertiespath tosdk.dirand the project starts to build, I have the path/Users/vlad/Library/Android/sdk
- Project structure, change package names from
sample наhabr.example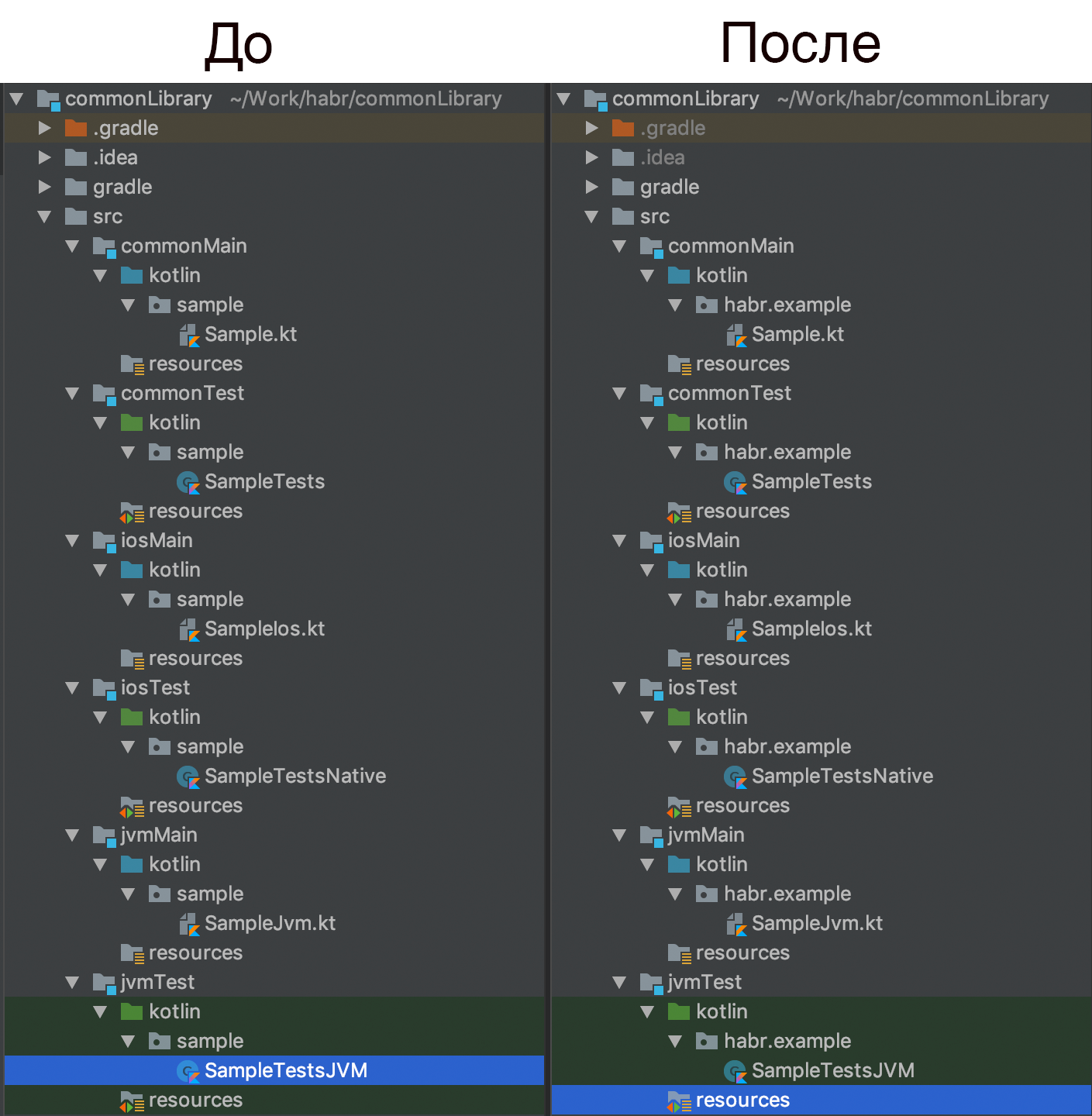
- It's time to start publishing, call the
wrapper. After that, we will have a .gradlew.gradlewin the project and it will be possible to work with it from the terminal.
- Run from the terminal
./gradlew publishToMavenLocal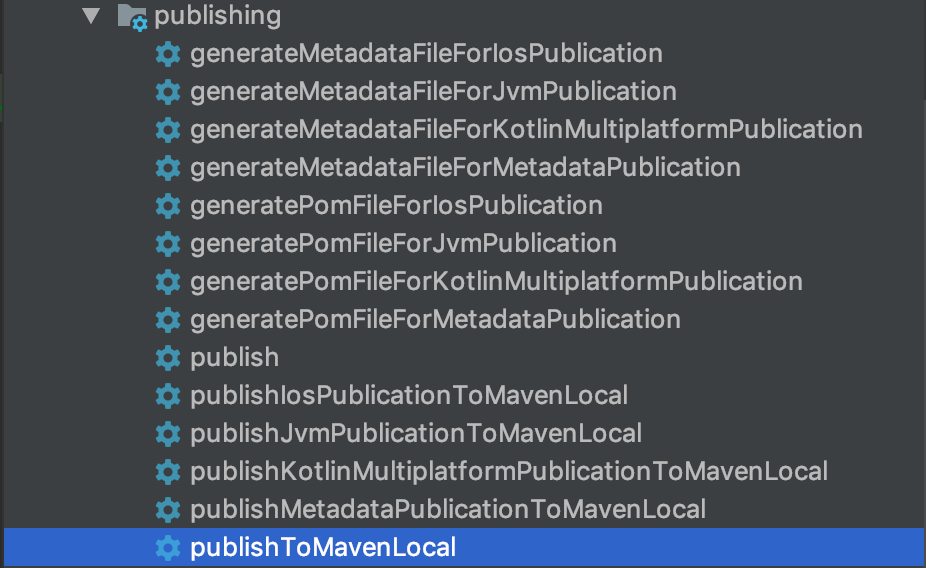
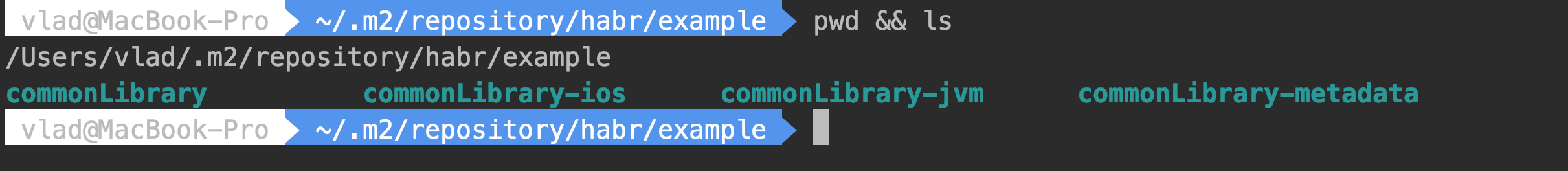
- After that, in the local maven repository, we will have 4 folders in which our libraries will be located
Part 2
Creating an Android Application
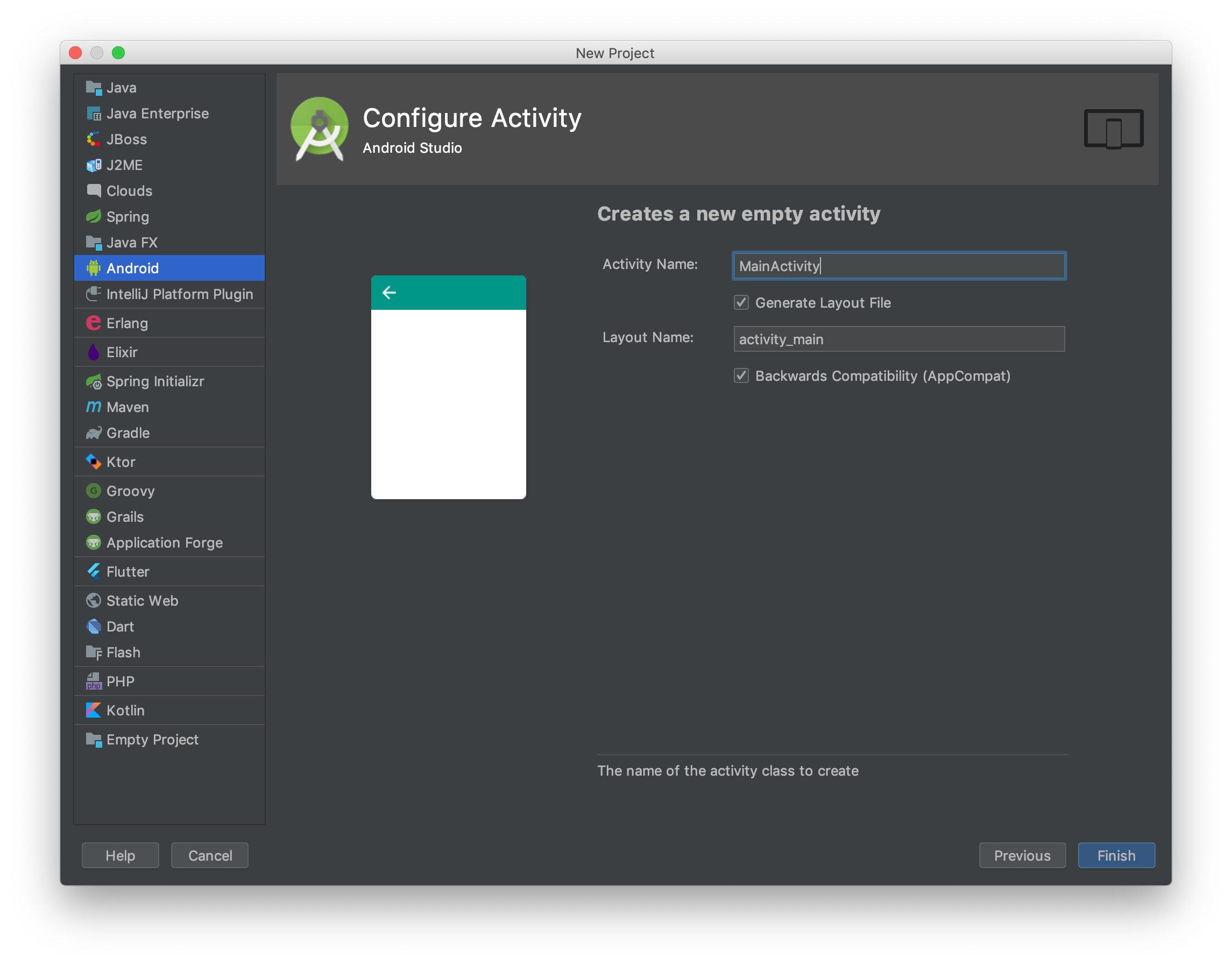
Create android project
It's all standard





- At the time of this writing, the project is generated with a “bat” dependency, so we remove it at the end of
jre7, it will turn outkoltin-stdlib, after that the project will start to build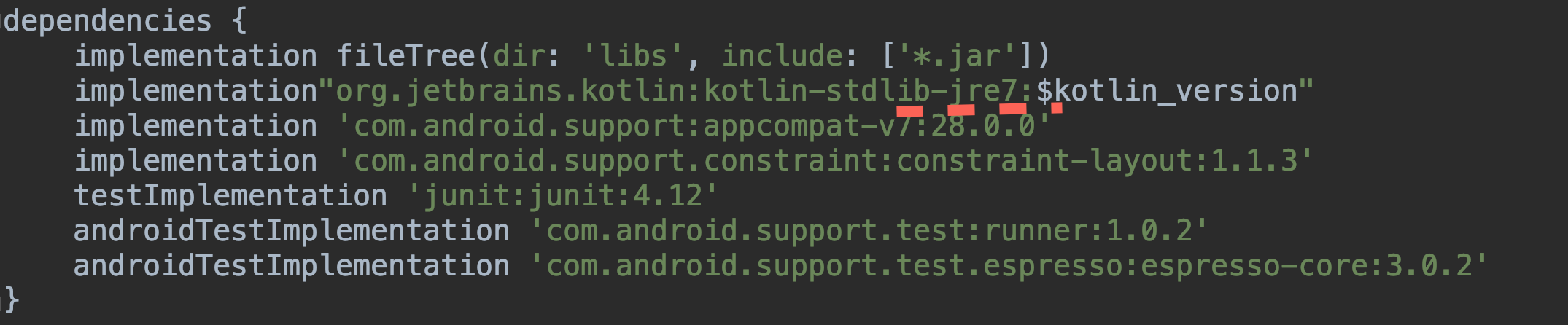
- Open
build.gradleand addmavenLocalrepositoriessection. Important! Therepositoriessection should be the one insideallprojectsand not inbuildScript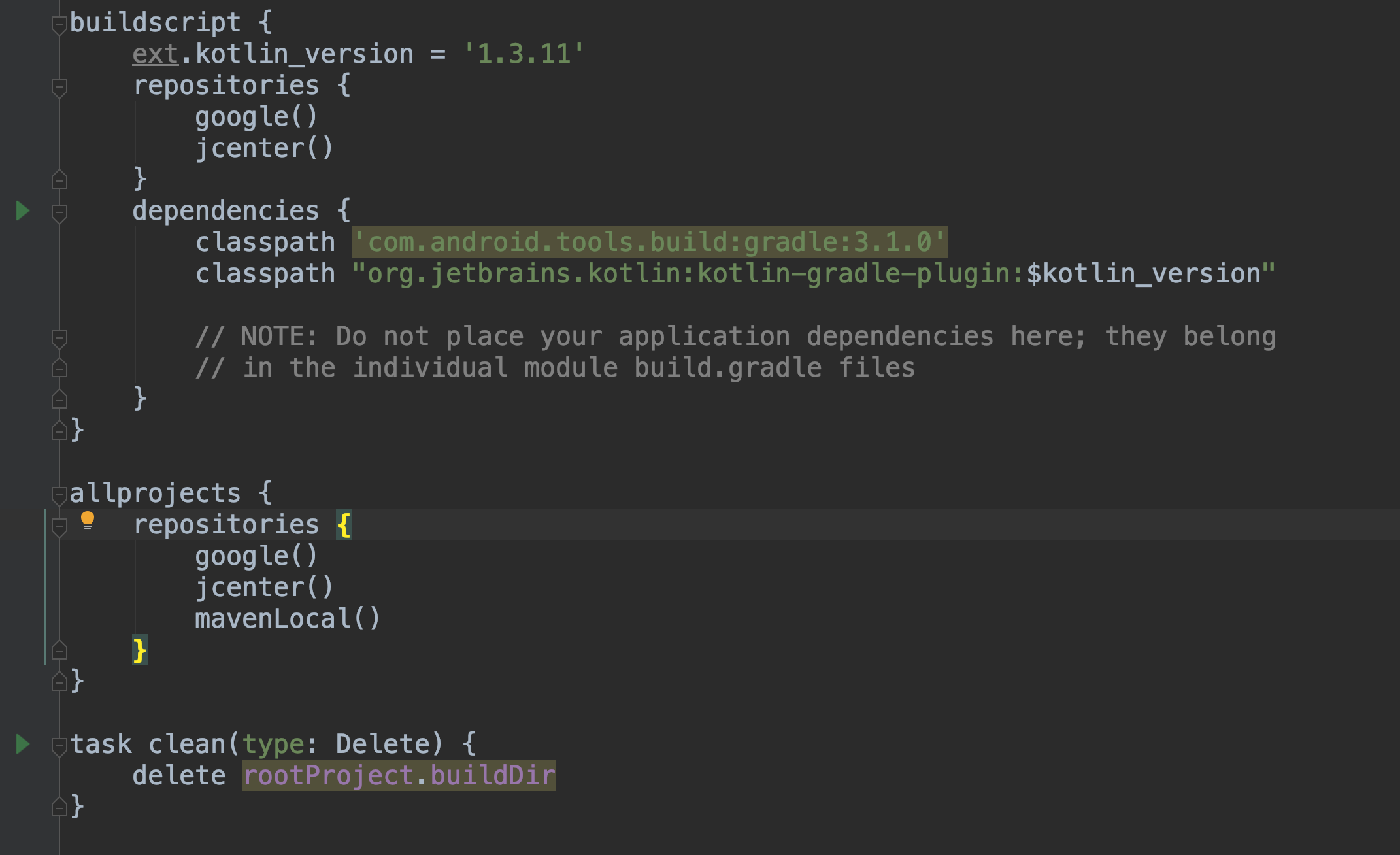
- Now we can add our library as a dependency.
implementation 'habr.example:commonLibrary-jvm:0.0.1'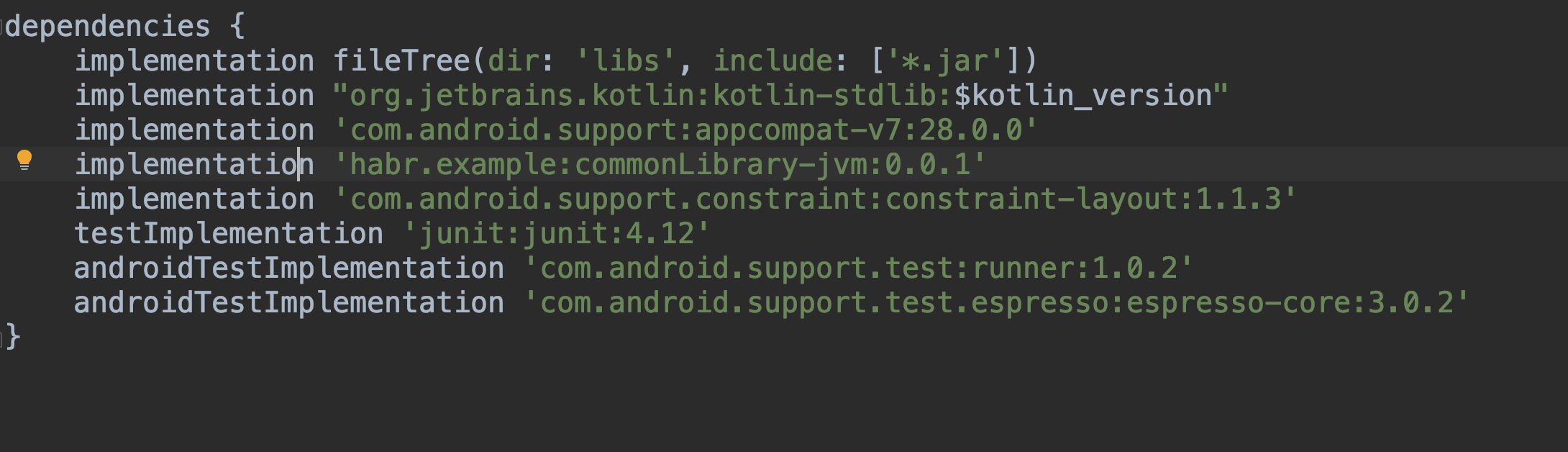
- Open
activity_main.xmland specifymain_activity_textinTextViewid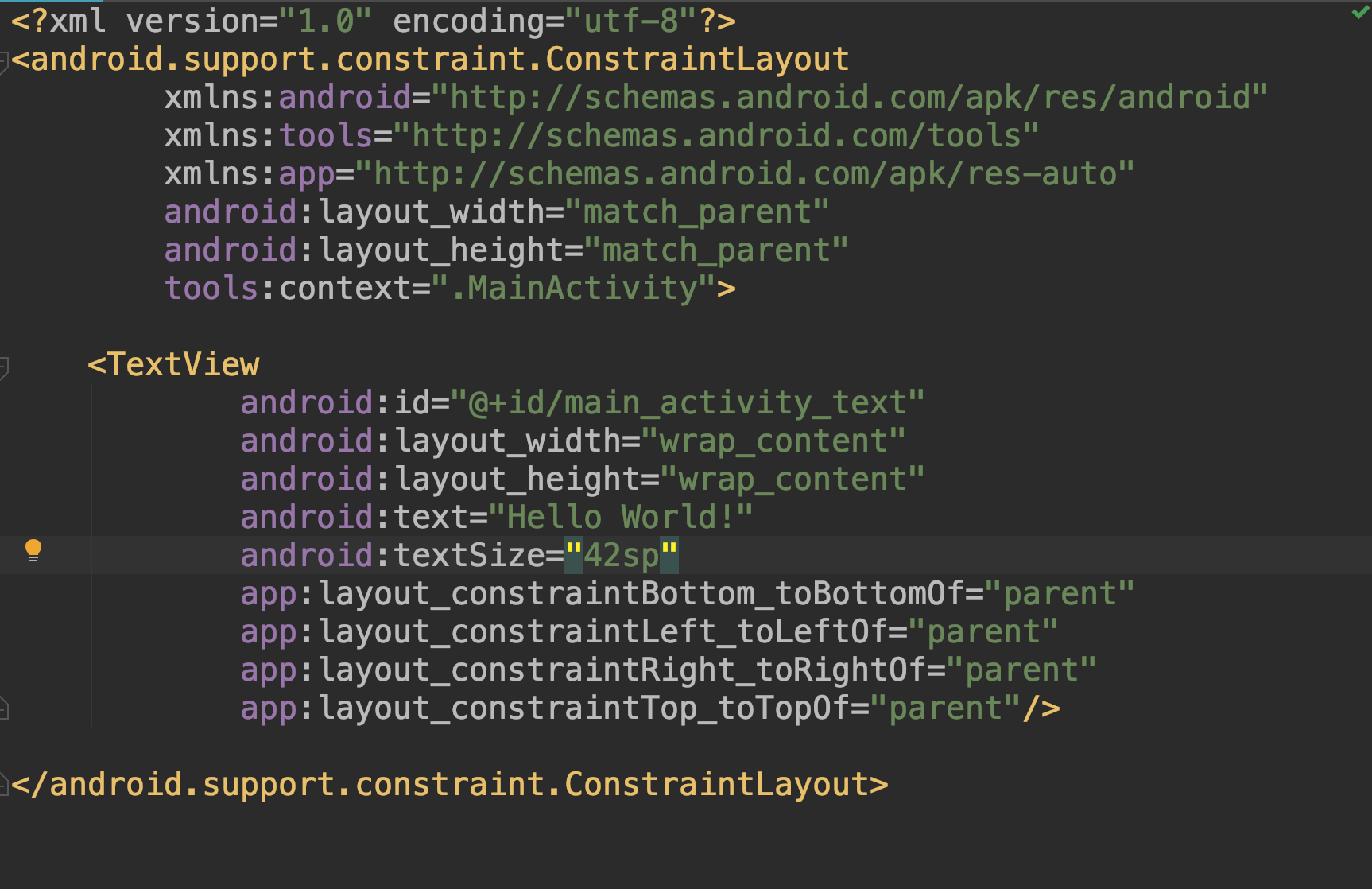
- In
MainActivity.ktjust set the text in thisTextView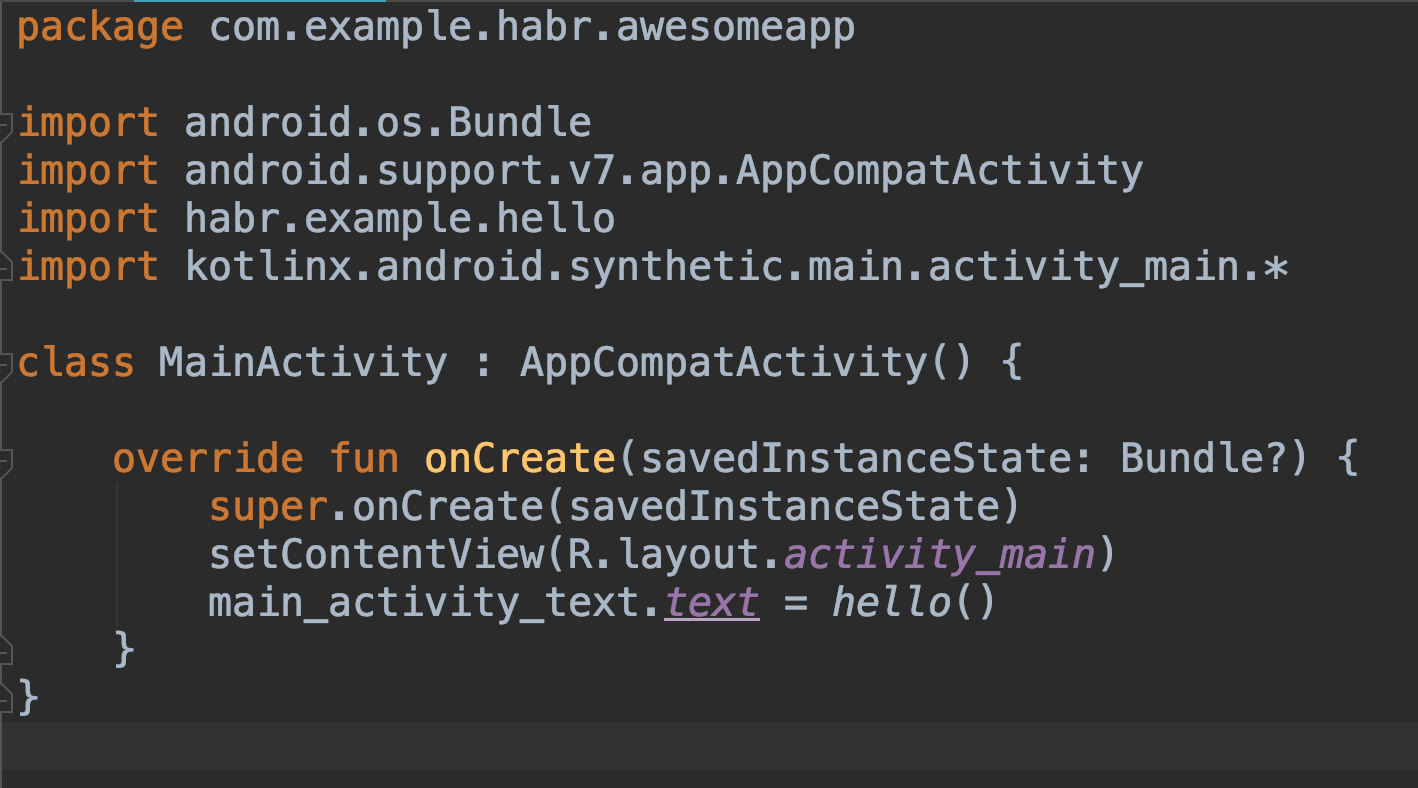
- Great, by this moment we have an Android application that can use the
hello()function from our library.hello () on the emulator
Part 3
Create an iOS project
- Choose Single View App

- Fill in the basic information and select the folder. Here it is important to choose the folder root for our other projects, since in it Xcode will create a subfolder with the name of the project
- First we add
CocoaPods. To do this, runpod initin the project folder, close the project inXcodeand runpod install. We see that the installation was completed successfully.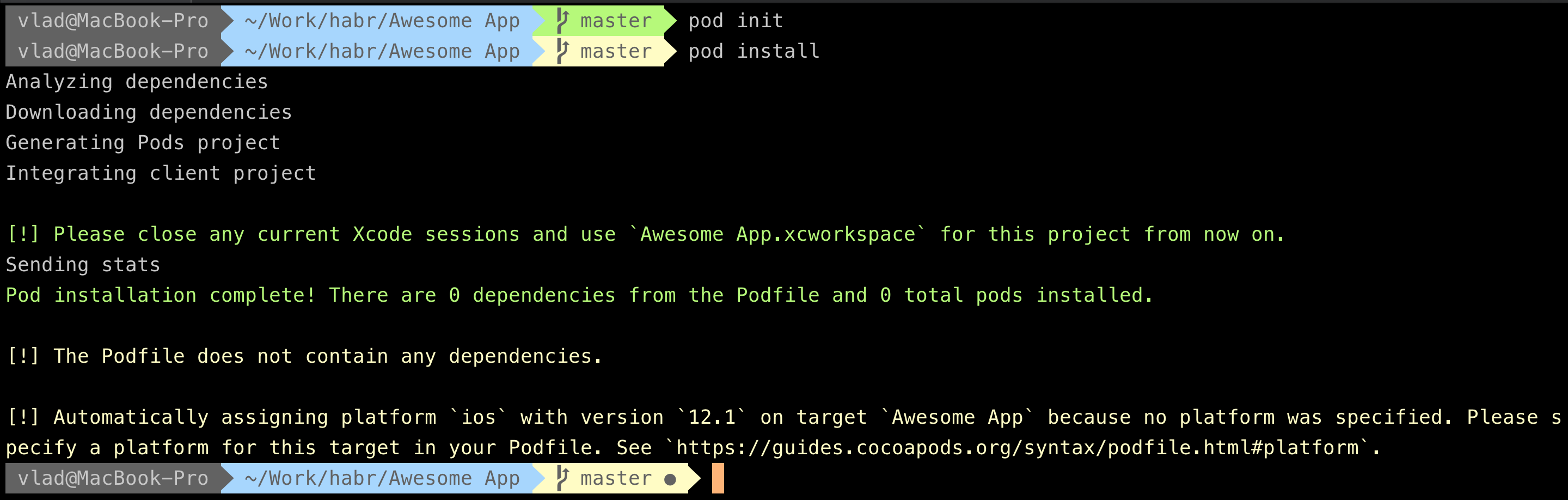
- Important! On the
CocoaPodssite,CocoaPodsnot recommended to add the/Podsfolder to.gitignore, but I did it anyway. Since after addingflutter, we will reconfigure dependencies for eachbuild. So far, I like this solution more than cluttering up.git - Open the project through the file
Awesome App.xcworkspace
- We open the terminal, in it we go to the folder of our
commonLibraryand run./gradlew linkDebugFrameworkIos. After that,iOSFrameworkappears in ourbuildfolderiOSFramework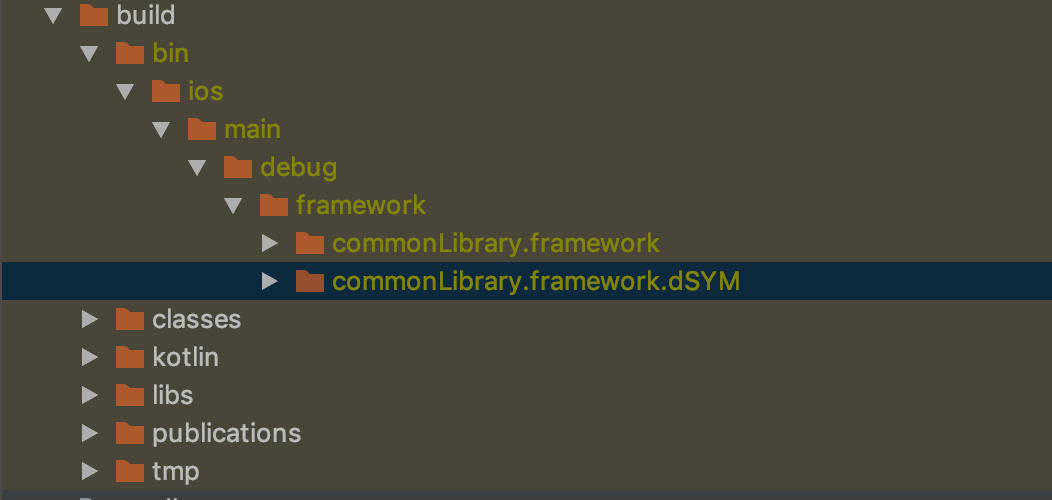
- Choose Target
- And for this Target we add a binary
- Choose Add Other

- Specify the path to the
framework, which was obtained in step 6 (commonLibrary.framework)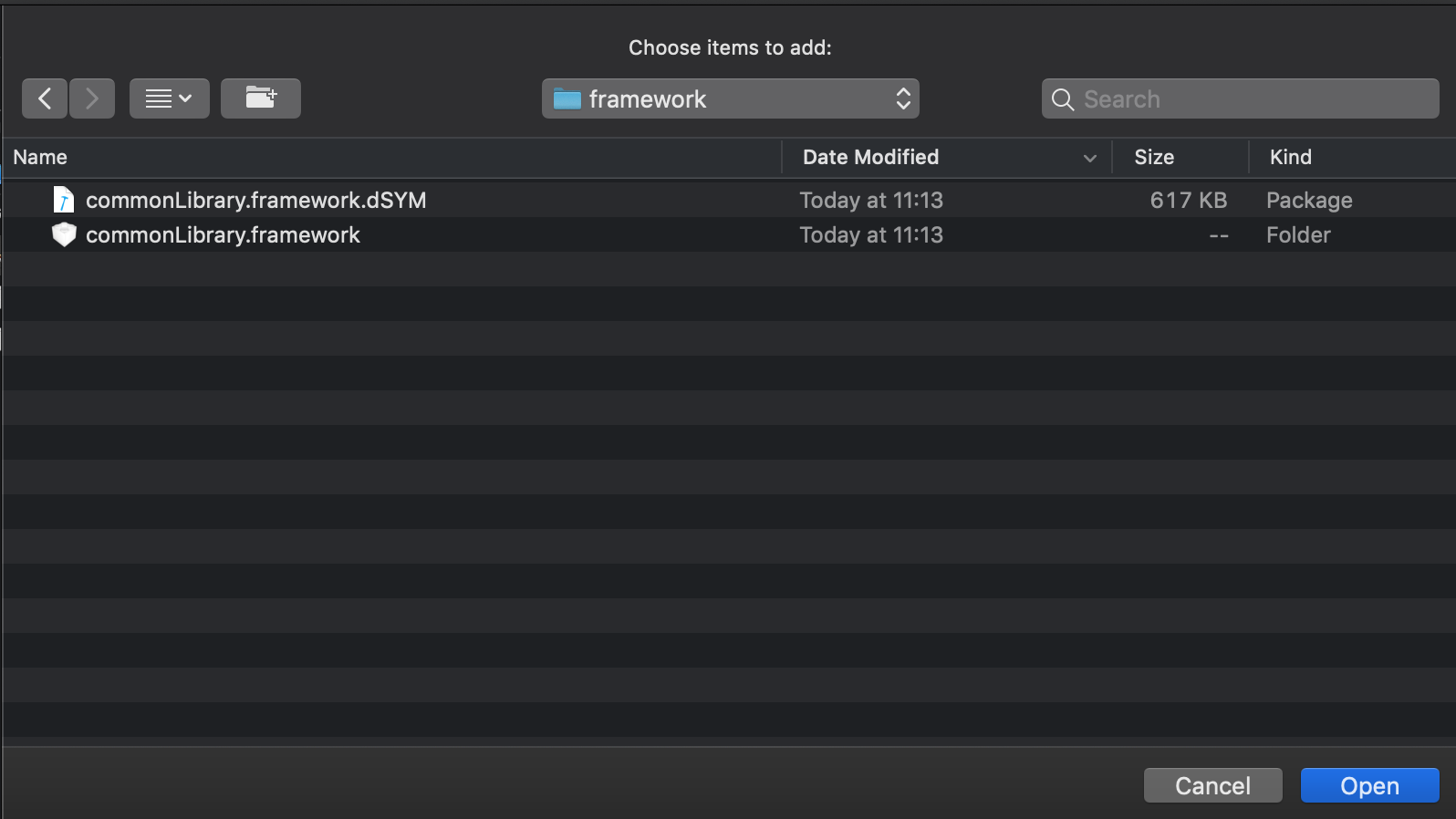
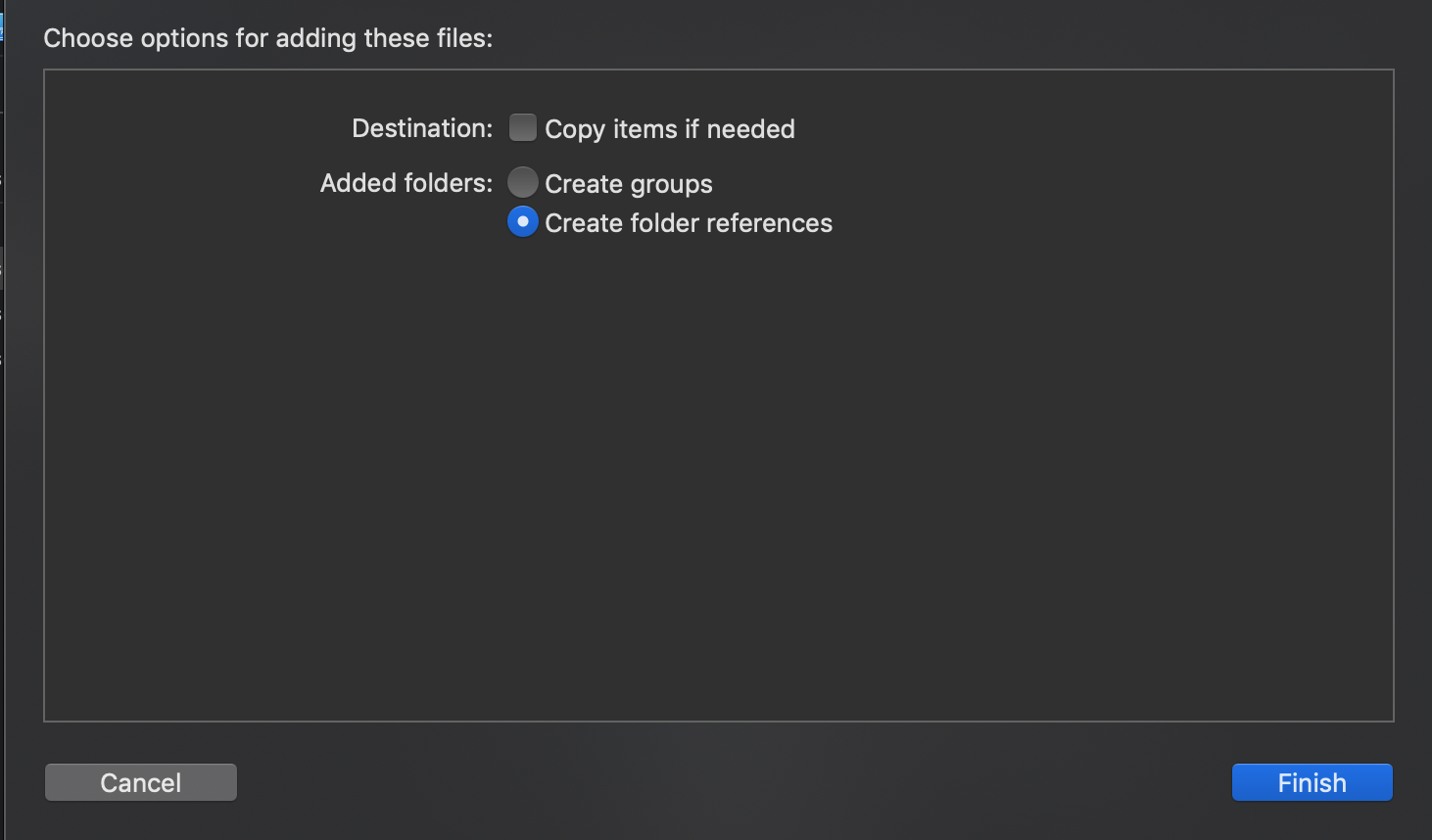
- Now in the project we should display this
framework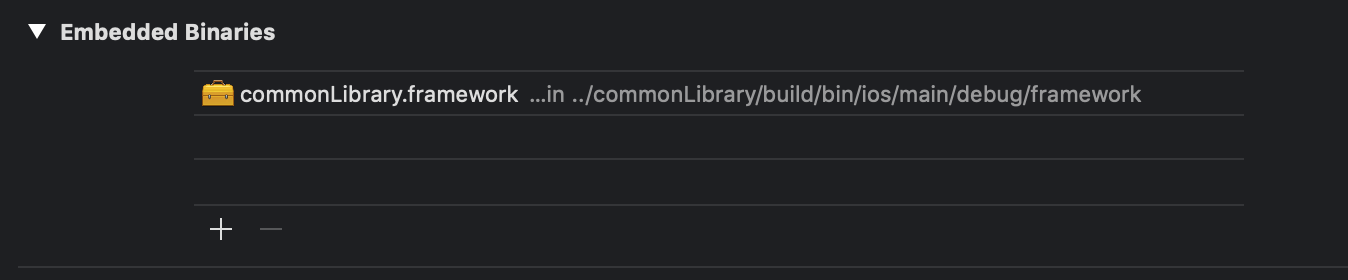
- Go to
Build Settingsand disableEnable Bitcode
- Now you need to specify exactly where to look for our
framework, open theFramework Search Path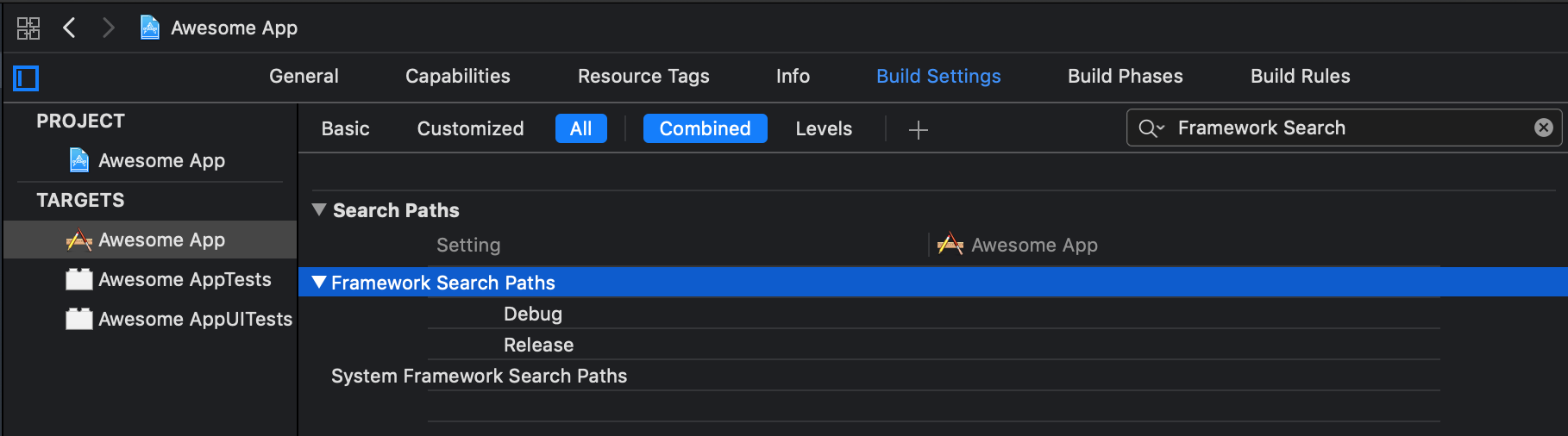
- Specify the path
"${PODS_ROOT}/../../commonLibrary". Be sure to chooserecursive. Of course, you can do without it, if you more accurately configure the path. But, since this is only the beginning of the project, now it is important for us to make sure that this whole bundle will work. And we can change the way and then
- It is necessary to make so that at each
buildinXcodeourframeworkwith the help ofgradle. OpenBuild Phases
- Add a new
Script Phase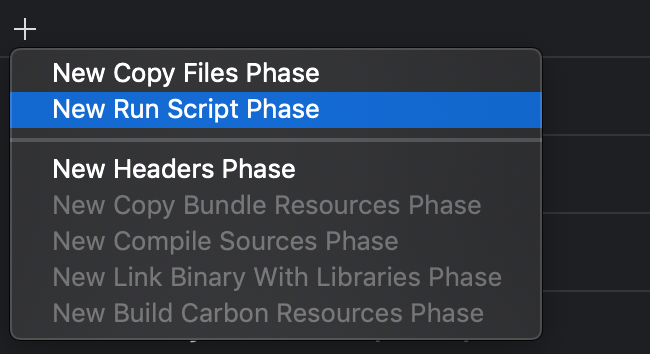
- Add script code.
cd "${PODS_ROOT}/../../commonLibrary" echo $(pwd) ./gradlew linkIos
Here we just go to the project folder of our library and run./gradlew linkIos. The callecho $(pwd)needed only to show in the console which folder we are in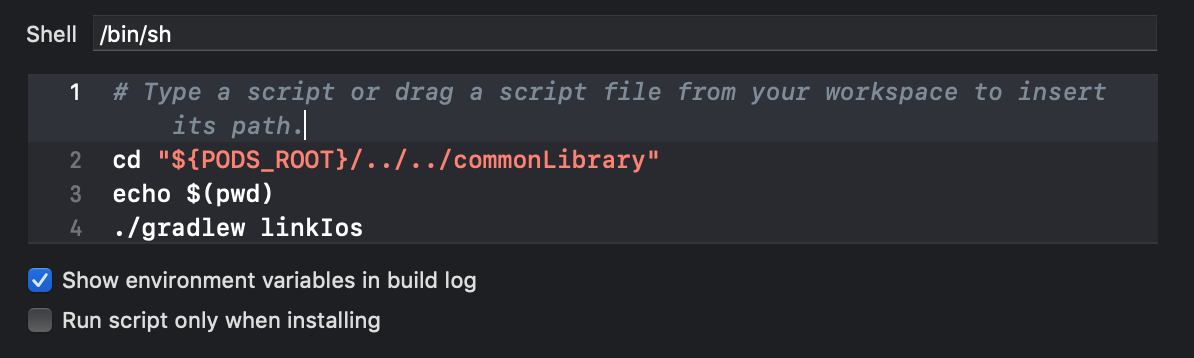
- We shift our
build phaseto the very top, right aftertarget dependencies
- Now open the
ViewControllerand add a call to our function from the library.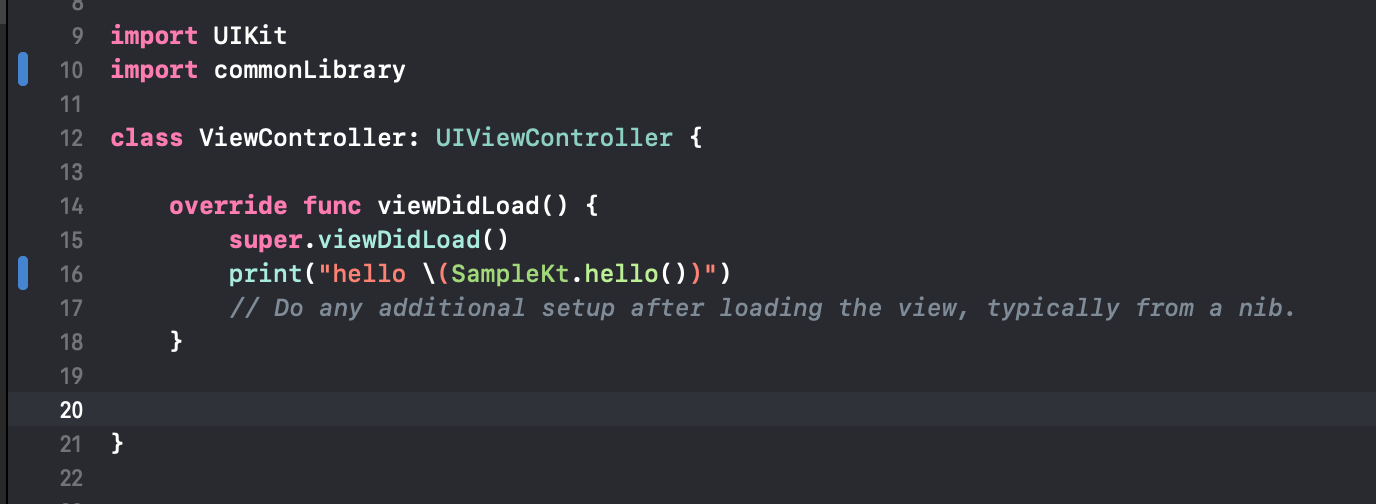
- We start our project and see
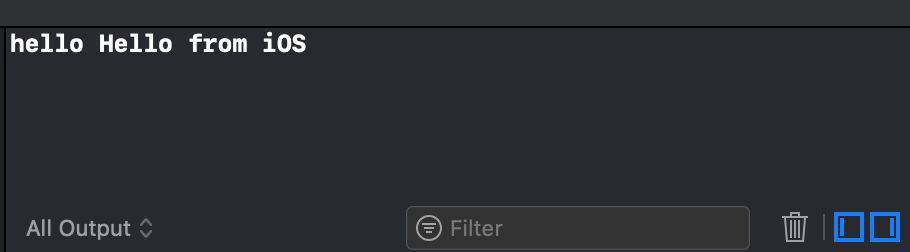
Great, it means that we correctly connected the Kotlin Library to the iOS project.
All that remains is to add flutter, as a framework for writing UI, to our applications and you can start developing the product.
Part 4
Adding Flutter to Android Application
Here the article on github really helped me.
- Go to the root folder where all our projects are located and do
flutter create -t module flutter_ui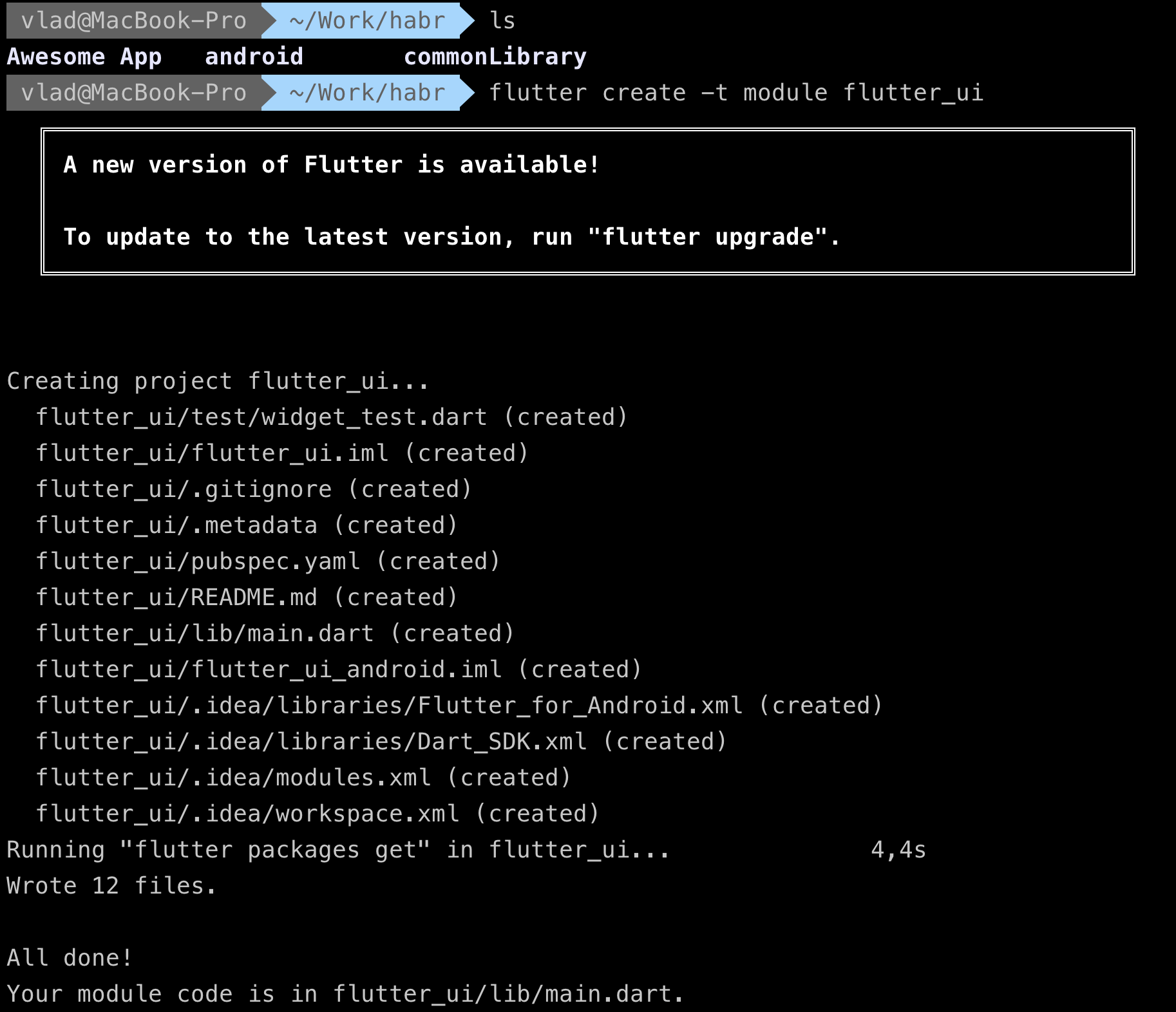
- Open
settings.gradleand enable our flutter module as a subproject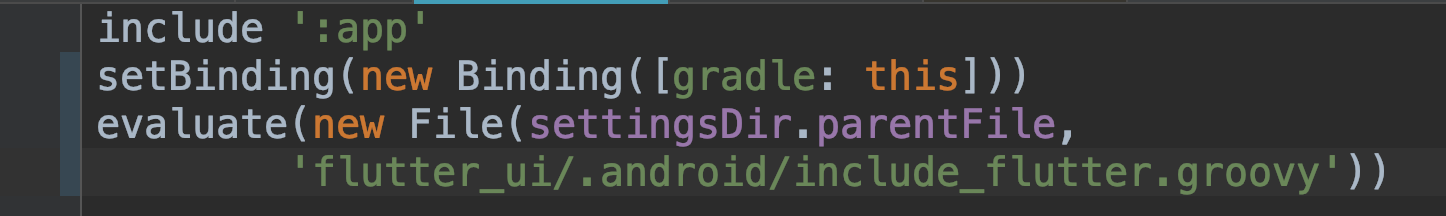
- Open the build.gradle file and add our project depending
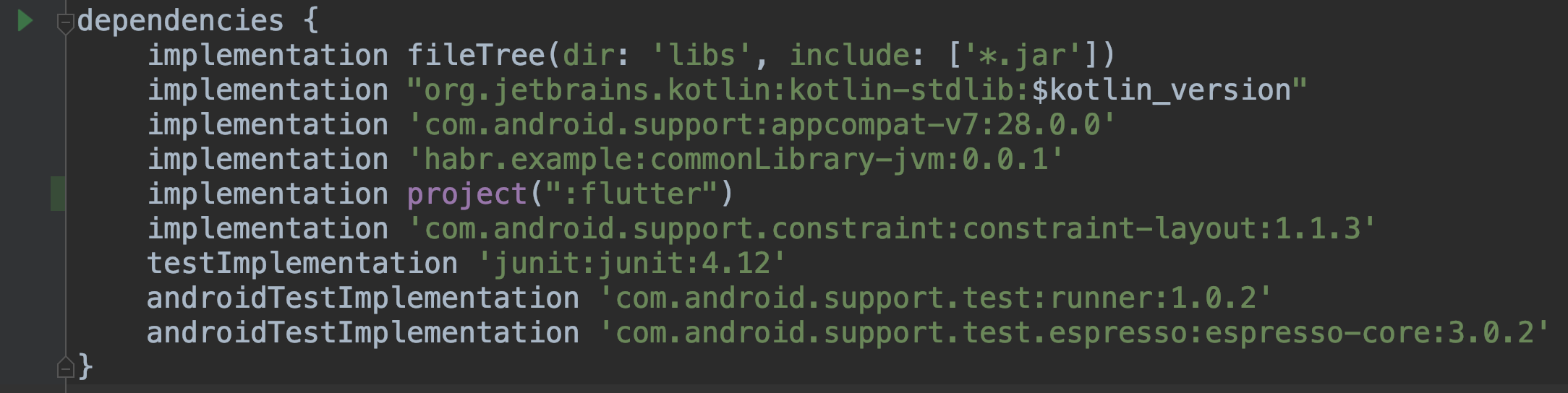
MainActivity.kttoFlutterActivity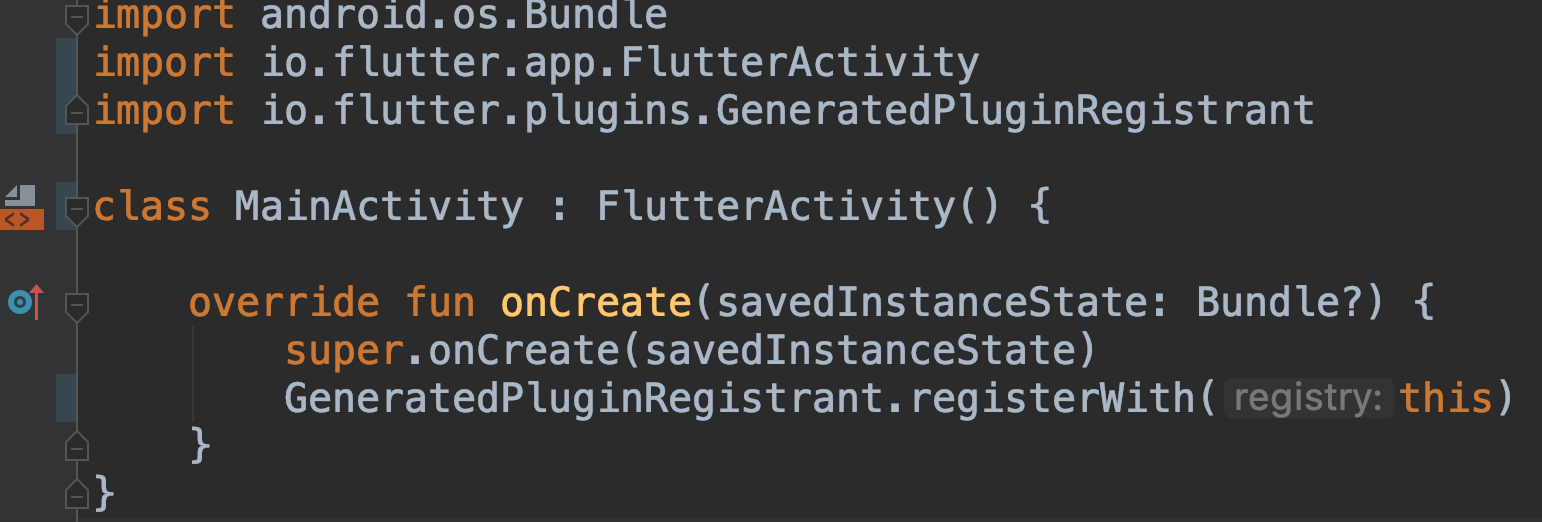
- Add
App.kt, in which we will initializeFlutterwhen the application starts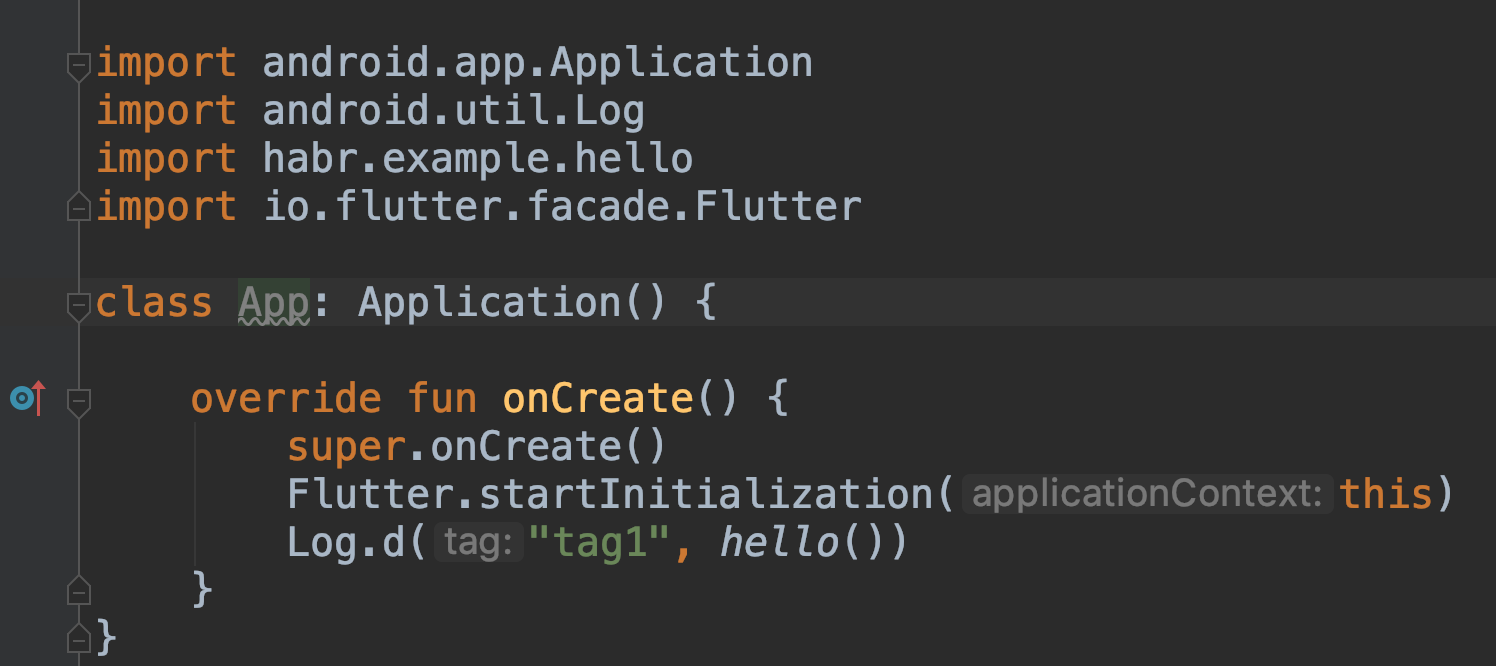
- We change the manifest and say that now we have a class for
Application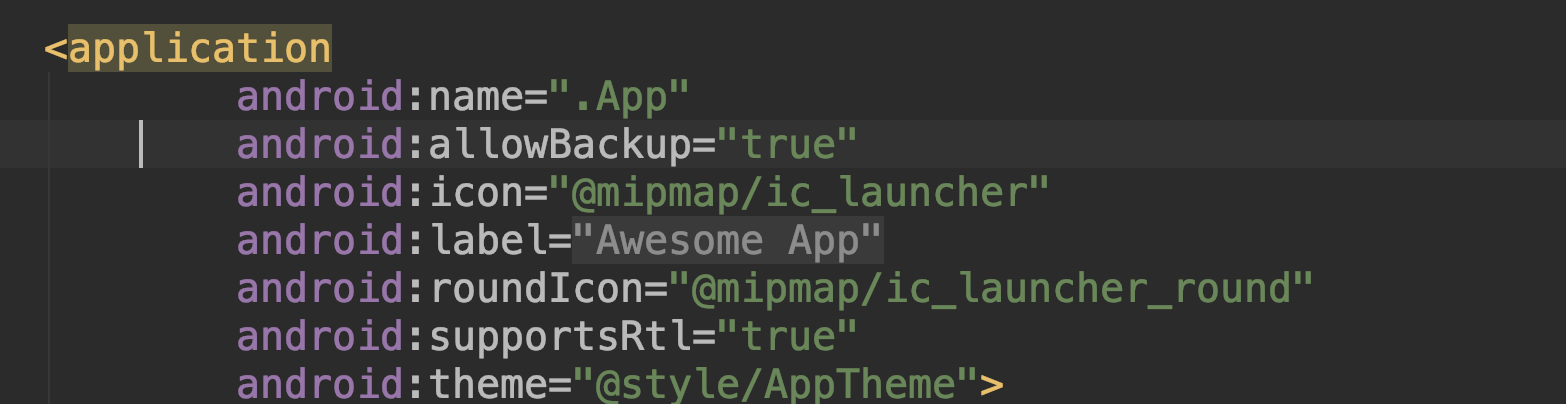
- Be sure to add
java8, without this flutter will not start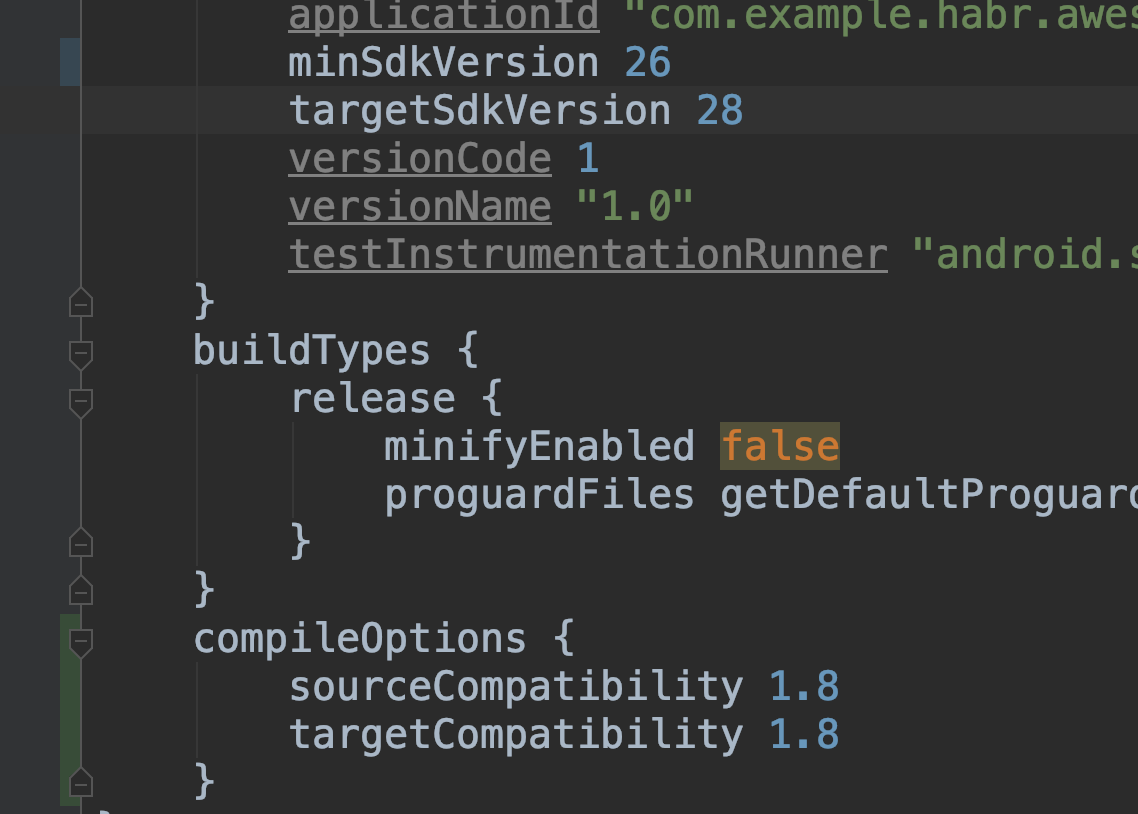
- We see the UI in the Hello from JVM logs, which means that we have gathered the UI on Flutter and the main library on Kotlin / Native
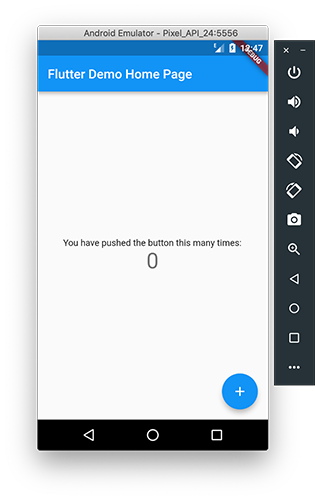
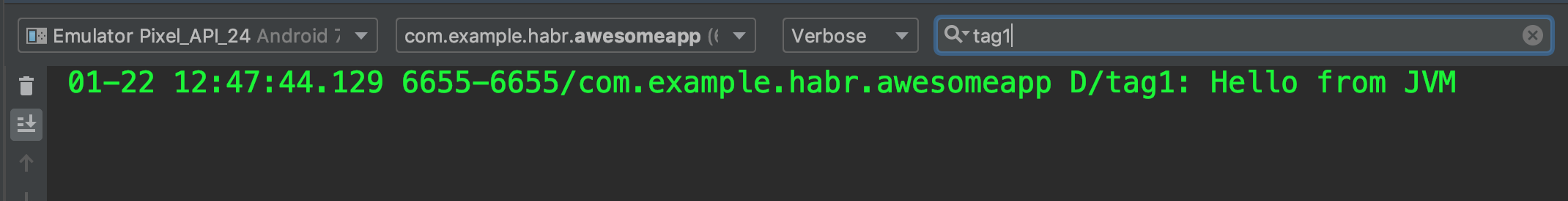
- Add a method to the
MainActivity.kt, which we will call from Flutter. Here, on an event from Flutter, we return ourhello()from the kotlin-library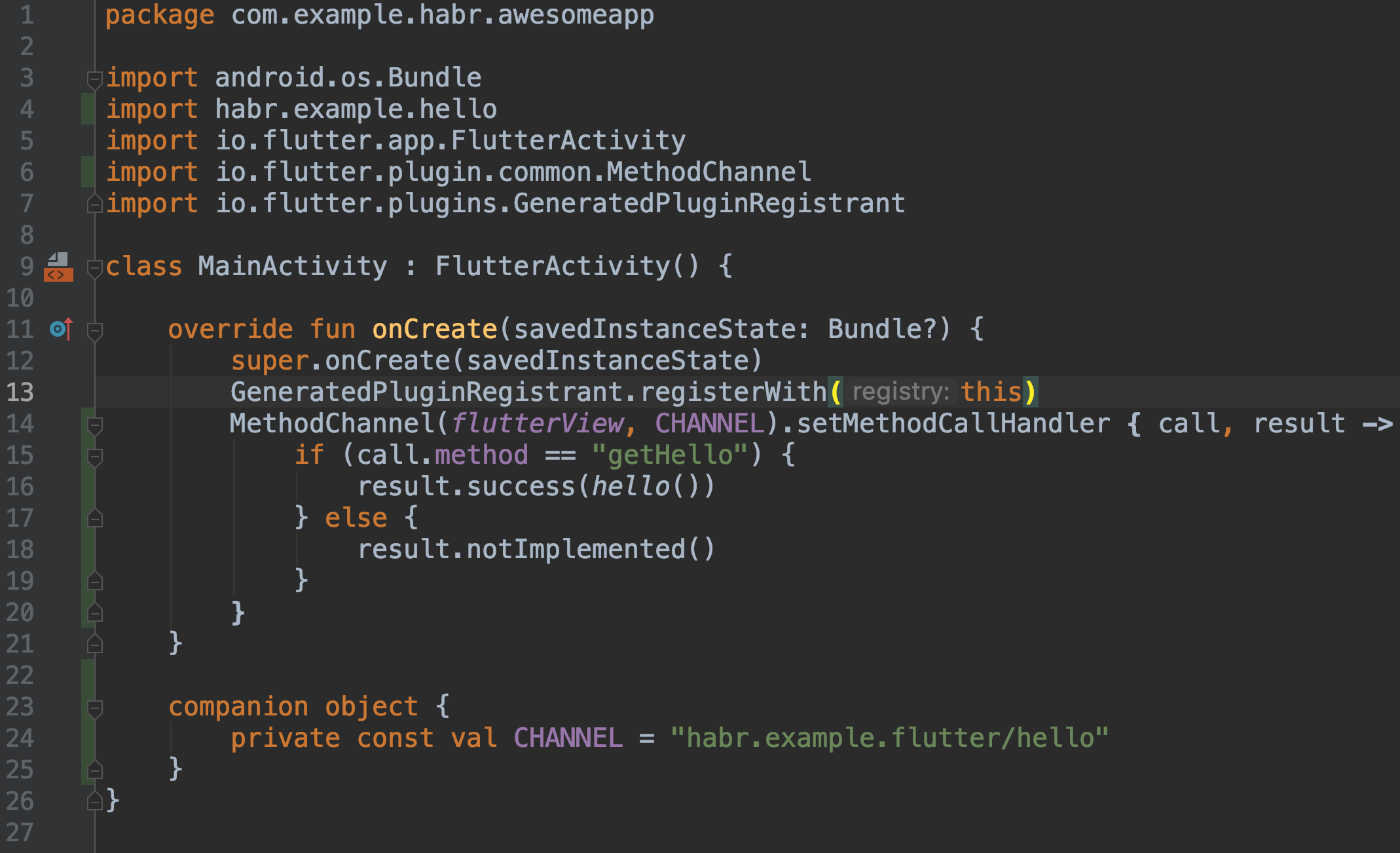
- And add to
main.dartcode that will call the method in theiOS/Android-частиapplication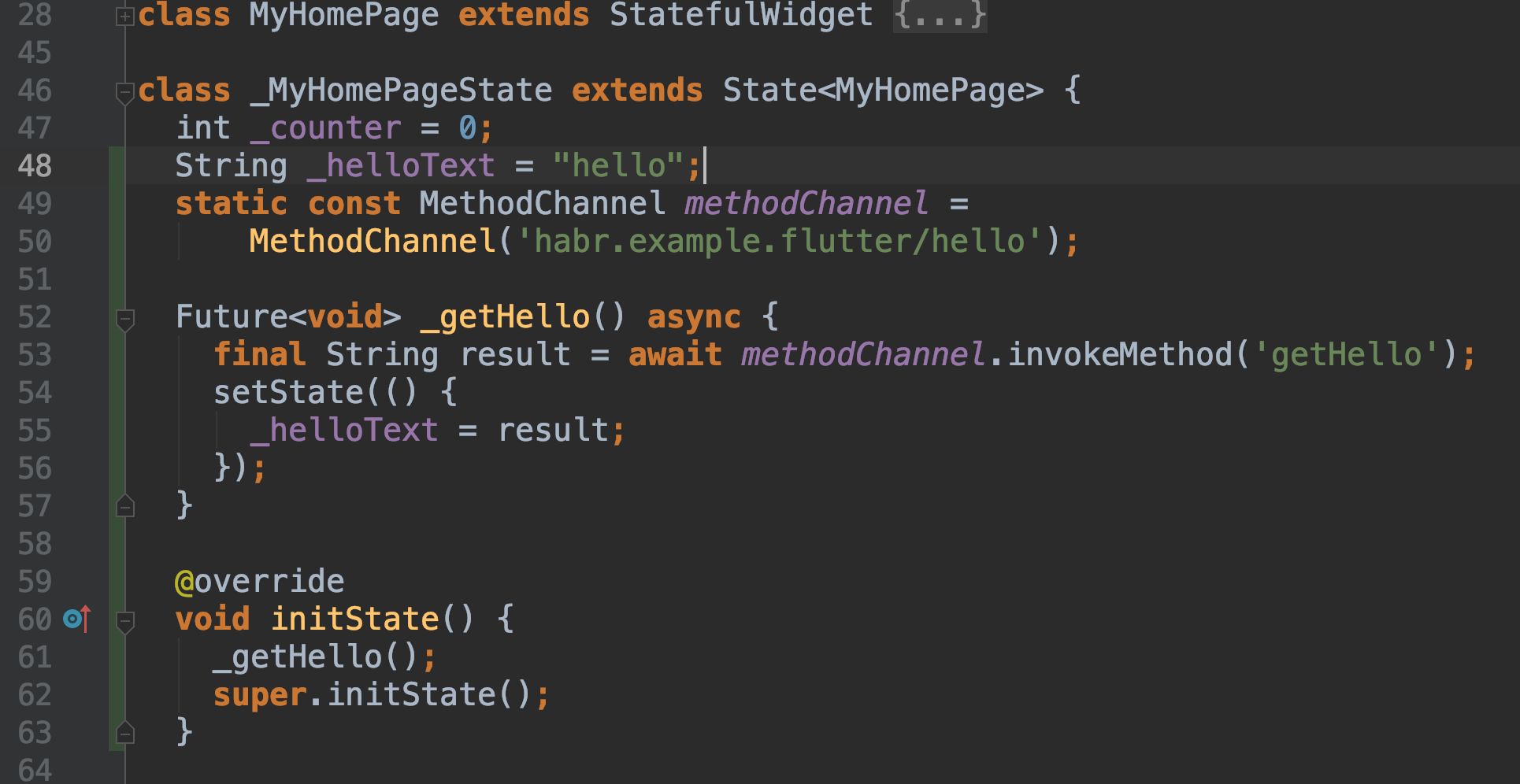
- Get

Part 5
Adding Flutter to an iOS Application
- Update our
Podfileflutter_application_path = File.expand_path("../flutter_ui", File.dirname(path)) eval(File.read( File.join( flutter_application_path, '.ios', 'Flutter', 'podhelper.rb')), binding)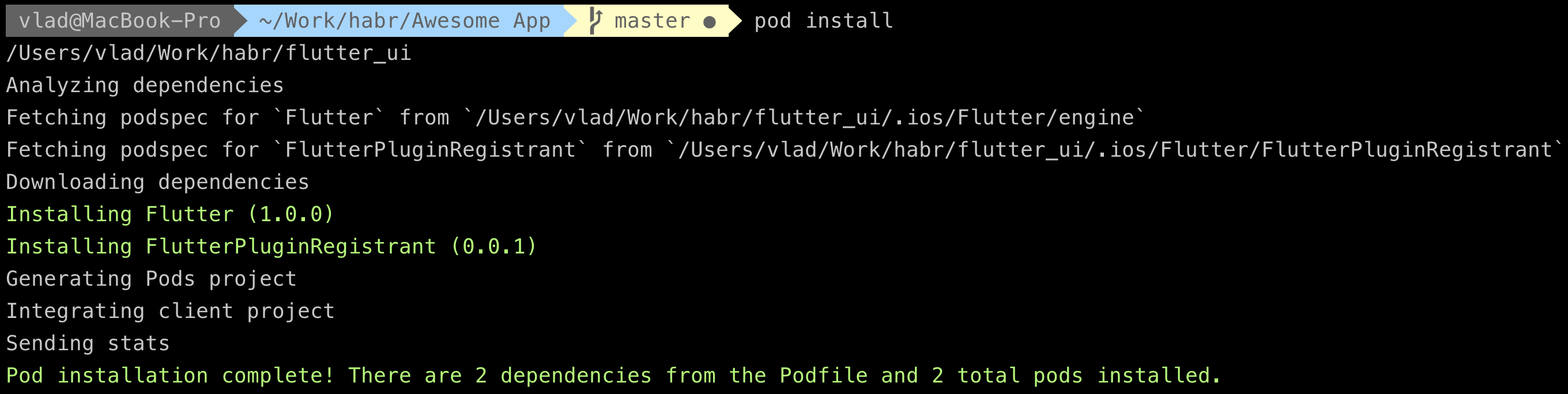

- Is important . Add
$(inherited)to the first line of theframework search paths. Be sure to check that yourframework search pathsnot empty.
When you change dependencies insome/path/my_flutter/pubspec.yaml, you need to runflutter packages getfromsome/path/my_flutterto update the dependencies inpodhelper.rb. After that, you need to runpod installfromsome/path/MyApp - Add another 1
Build Phase, only for Flutter. Above what we added in part 3 of theScript phase"$FLUTTER_ROOT/packages/flutter_tools/bin/xcode_backend.sh" build "$FLUTTER_ROOT/packages/flutter_tools/bin/xcode_backend.sh" embed
AppDelegateourAppDelegatewithFlutterAppDelegate
- Update
ViewController
- Wrap our
ViewControllerinNavigatorController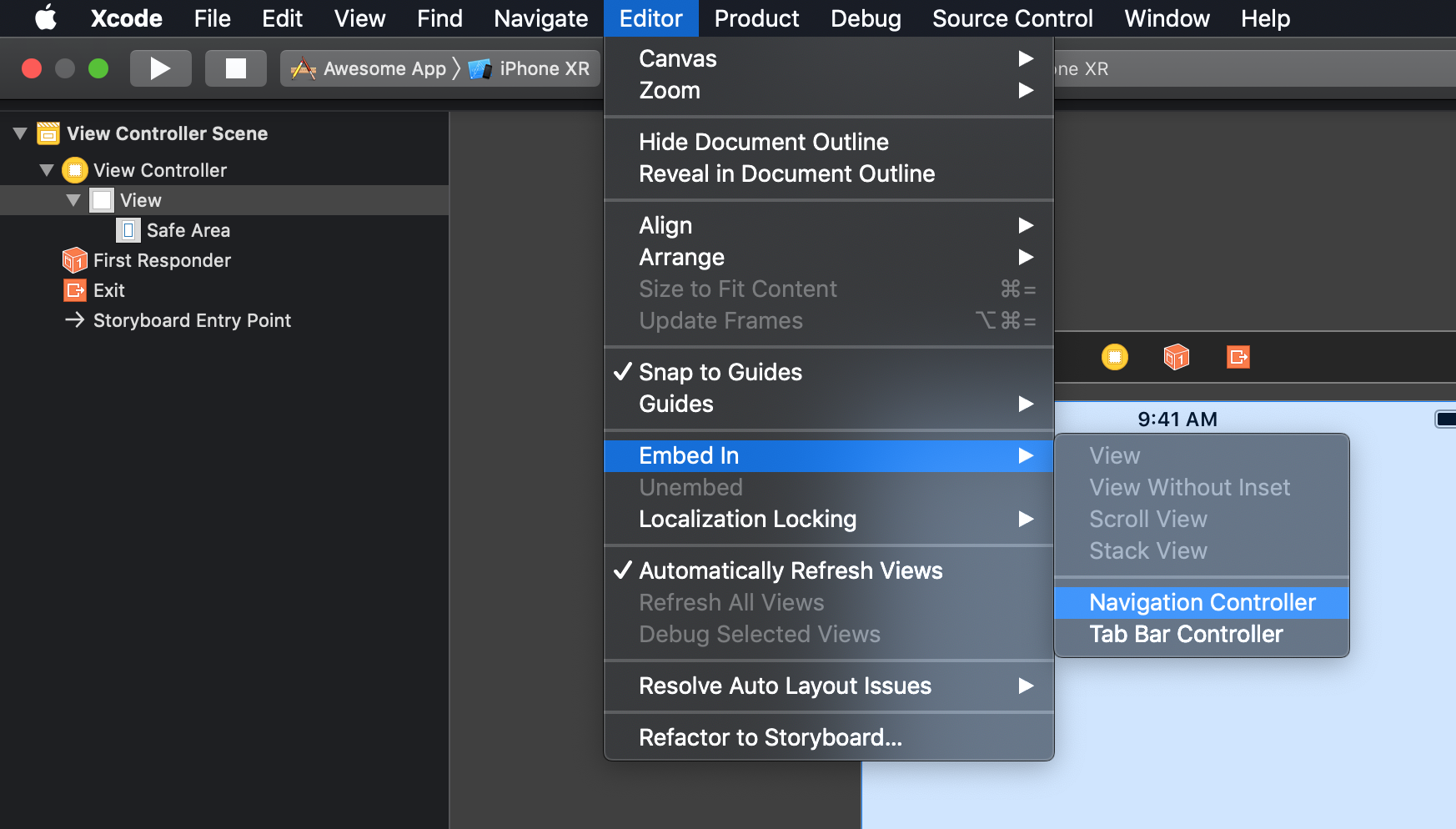
- Now the application starts. But, so far, we have no connection between the library and flutter.

- Add this link using
FlutterMethodChannel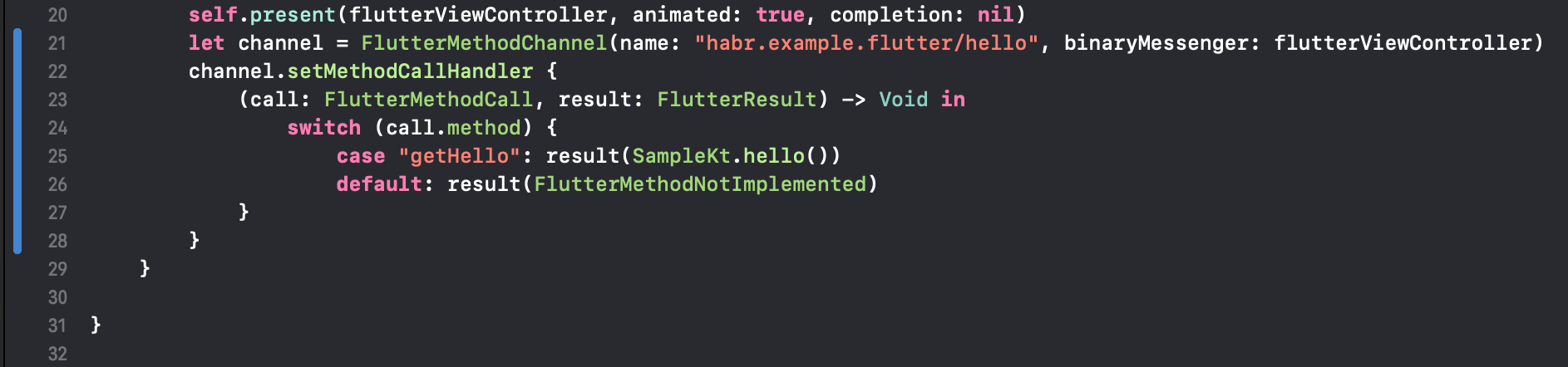
- Great, now the iOS application uses
flutterfor theUIandkotlinfor the main logic
Conclusion
What is important to say here: I do not pretend that you have learned something new or unique. I just shared my experience, because in order to make it all work together, I spent about 4 working days. And I could not find examples of project code that uses both Kotlin / Native and Flutter simultaneously
Final Projects
List of links that helped me, but not immediately
- Flutter himself
- Communication between native code and UI flutter platform-channels
- Add flutter to existing github application
- Kotlin Native native-overview
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/437176/