Training Cisco 200-125 CCNA v3.0. Day 5. Connecting CISCO devices and IOS modes
Today we look at connecting Cisco devices and various IOS modes. Those who are just starting to get acquainted with Cisco will probably see this device for the first time. This is a Cisco 1921 router. By what signs can you find out that this is a router?

The first thing that gives you a hint is the power switch. Remember that Cisco switches do not have a switch. In addition, the switch will necessarily have several ports, because it is a switch with 12, 24 or more ports.
As a rule, the router has 2 gigabit ports, and possibly a fast Ethernet port. On the left you see the free space, covered with plugs. It is intended for additional modules, and in principle, a switch module can be inserted here, but usually the router simply has a couple of ports for connecting switches and an Internet cable.
Of course, as a CCNA specialist, you will need to know what a router is, what a series of routers and switches are, but this is a different matter. So, all devices manufactured by Cisco have these two ports: a console port labeled with a light blue color and located above either the AUX port. Both of these ports are intended for external device configuration, that is, you can access the device, even if the operating system is not working. Simply put, through these ports you can download the router.
Let's try to compare the router with your home computer. Most of us could help a relative or friend with a computer problem if one of them calls you and says that their computer is not working. You can remotely connect to another computer using Team viewer or any other program for remote access, find a solution to the problem and then install the necessary software, after which the computer must be restarted.
You can reboot it, but when your friend’s computer is “dead” when you restart, you don’t see what is happening on its screen during the bootup before the operating system appears, so ask your relative or friend to tell you by phone what is displayed on the monitor time. If the problem is not solved, then you will not be able to understand what its cause is, because you do not see the download process. But as a specialist in the IT industry, you must see what is going on in order to decide what needs to be done next to eliminate the problem.
Therefore, you should be able to remotely observe the boot process, you should see the BIOS, its settings, you should be able to check all these things. The console port of the router allows you to do all this. By connecting to it, you can observe everything that happens to the router at boot time before the Cisco IOS operating system is loaded.
What is the difference between Console and AUX ports? For the console port, a special Cisco console cable is used in the same light blue color as the router port is marked. It is also called the rollover cable. At one end of this cable there is an 8P8C connector, similar to a standard RJ45 connector, and on the other hand, a connector for connecting to a computer.
The AUX port performs the same function, but is usually used to connect a modem. The user can also connect to it to remotely configure the router.
The problem with the console cable shown on the slide is that it can only be connected to the computer’s serial port, but most modern computers do not have such a port. In this case, you can use the converter cable, which is shown on the left. It allows you to connect a device with a serial connector to the USB port of the computer.
If you use this converter, you will need to install a USB driver, when installed, your computer will automatically receive a COM port. Thus, you can connect to the router using special software.
Modern models of Cisco routers have a USB port, and if you see that it is located in the zone where the blue strip of the console port is located, then this is the USB console port. This means that if you use a regular USB cable with a miniUSB connector at one end, you can connect the router to the USB port of the computer with the other end of the cable. Cisco provides a special Cisco Windows USB driver that creates a COM port on the computer. After that you can use the terminal program, which you see on the next slide, and connect to the device via a computer.
Each router has a Gigabit Ethernet port, indicated by a light yellow tag, which allows you to connect to a different network device. Next to it, you see another USB port. As I said before, the latest series of routers are equipped with such ports for transmitting and storing an IOS image on external media. The difference between these two ports, miniUSB and USB, is that the first is the console port, and the second is for connecting an external device for storing information, such as flash memory. In the next series of video tutorials, we will look at switches and routers in more detail, and from this video tutorial you first need to remember where the console port is and what the console cable looks like.

After the router connects to the computer using the console cable through the console port, we can use the terminal program. There are 4 of the most popular programs for terminal management: free PuTTY, I prefer to call it “Putti”, although some people call it “Patty”, and I don’t know how to properly. This program can be downloaded for free at putty.org. There are 3 more similar programs, of which TeraTerm and HyperTerm also have free versions. Personally, I am a big fan of Secure SRT, believe me, after you try this program, you don’t even look in the direction of another terminal software.
But you can use the program that you like more. Any terminal software has basic configuration settings in which you need to select the Serial parameter as the type of connection with the device, the speed of data exchange with devices, which is 9600 for all Cisco devices, and the serial port number through which the connection is made, in this case COM1.
Most computers have at least one serial port, but if it is not there, you need to use a Serial to USB converter cable. In this case, you need to install a driver for the USB serial port, which will become a COM1 port. To do this, you need to go to the Device Manager of your computer, there are several ways to do this. After you open the Device Manager, you should open the list “COM & LPT ports” and select the port to which the router is connected. If it is a COM1 port, then you specify it in the Serial line and click the Open button, which opens your terminal session with the device.
After that, you get into the process of loading the router. In the right window, I highlighted in blue a compressed image of the IOS operating system.

After it is unpacked, all information on the technical characteristics of the router, the license for the right to use the software, etc. will appear on the screen. It also shows the firmware version of the router, in our case it is 15.1, and at the end of the download, the system configuration dialog will appear. In any Cisco device, be it a switch or a router, there is such a command line. I recommend that you always select the No answer to the "Continue with configuration dialog" prompt?
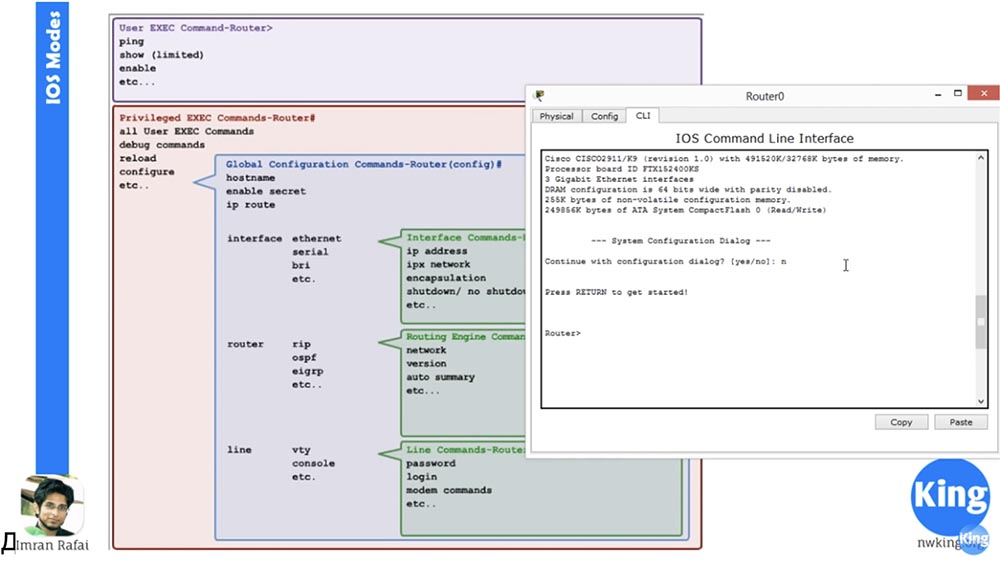
The fact is that if you continue the dialogue, you will enter the settings, most of which are not supported today, so the best choice would be to refuse the offer to use it and return to the command line.
The first mode that all these devices support is the user EXEC mode. This is the initial, lowest access mode to the device settings. How can you tell if you have a custom EXEC mode? This is indicated by the closed-bracket character> after the word Router. If you see this sign, then you are in user EXEC mode.
A feature of Cisco IOS is that if you type a question mark on the command line, you will see a list of commands that can be used in this mode.

These are the basic commands for the initial access level, but you can also enter a command such as quickly browsing the IP interface Router> show ip int br and see the connection status to this router for Gigabit Ethernet ports.

If you enter the "Show privileges" command, the router will report that the privilege level is 1, that is, you are working in the user EXEC mode.
The next, more advanced configuration control mode is the privileged EXEC mode. Now I will show how to use this mode. But first, I’ll talk about one more good thing about Cisco IOS — it’s so “smart” that it understands entering abbreviated commands.

When I type “show privi”, the program understands that the word “privileges” is meant, that is, I ask you to show me the privileges. If I just enter the letter e as a command, the program will say that 2 commands, enable and exit, begin with this letter, so I need to type a few more letters so that she understands exactly which command is meant.
For example, if I type en, the system will understand what the enable command means, therefore, with a full command set, or with a partial two-letter set, after pressing Enter, the program will execute the correct command. This is one of the reasons why Cisco hardware is so popular in the networking industry.
So, if you see the hash icon # after the word Router #, this means that you have entered the privileged EXEC mode. In this mode, you have more privileges than any simple Cisco user.
If I print the “show privileges” command, the system will report that the privilege level is 15, which is the highest privilege level. At this level, there are many more hardware configuration commands available to you than in the user EXEC mode. With these commands you can enter global configuration mode, you can save, read and delete configurations and perform many things that are not available in user mode.
The next Cisco IOS mode is called global configuration mode. It can be accessed by typing configure terminal in the command line.
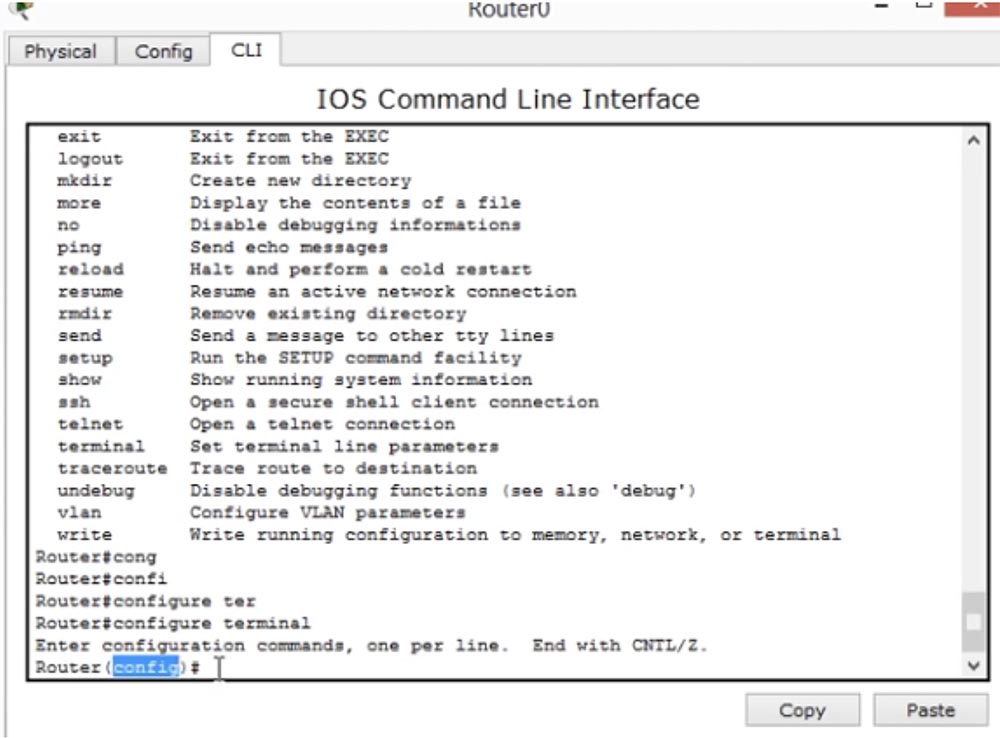
In this mode, after the word Router there will be not just a “lattice” symbol, but a word (config) with a “lattice”. Therefore, if you see the Router (config) # line, it means that you are in global configuration mode. In this mode, you can make changes to the Cisco IOS operating system itself. For example, if you want to change the hostname of this device, you type in the hostname NetworKing line, and after that you see that the Router's hostname has changed to NetworKing.

In this mode, you can make any changes to the system as you like. From here you can get to different levels. The next slide shows what exactly you can do while in different modes. For example, in user EXEC mode, you can ping devices, view the configuration, and include some parameters. In privileged mode, you can execute all user mode commands, debug commands, reload commands, configuration commands, etc. In global configuration mode, you can control the host name, activate hidden configuration settings and IP configuration settings. In addition, there are three configuration levels, each of which has its own set of commands.
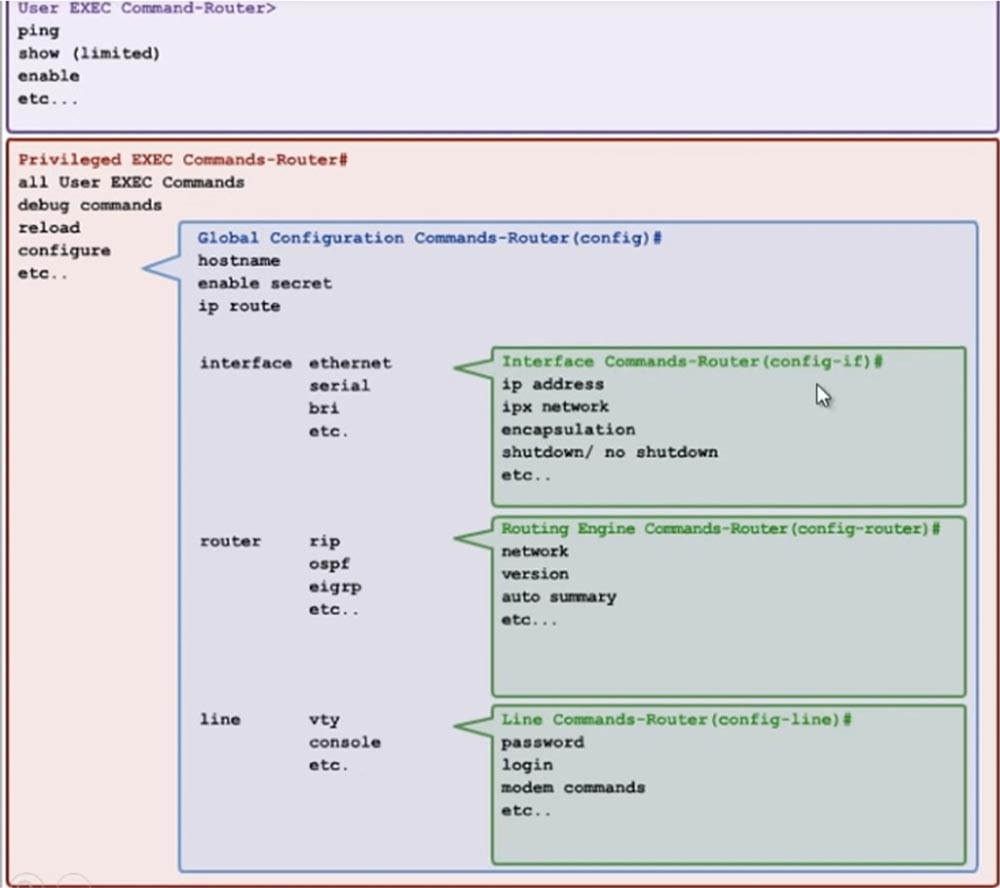
At the interface configuration level, you can control the parameters of a specific interface, at the router configuration level, you can manage all the parameters of the router, etc.
For example, from here you can configure the IP address for the Gigabit Ethernet port by setting the parameter 0/0. If a NetworKing (config-if) # header appears in the command line, if symbols mean that you are in global interface configuration mode. This means that all changes to the settings that you make will be applied only to a specific interface.
If you type a question mark, you will see a list of commands that you can enter in this mode for the corresponding configuration parameters: ip, ipv6, mac-addresses, and so on, all these commands refer only to the specific interface you have chosen.

If you enter the exit command, you will return one step higher to NetworKing (config) # mode, that is, to global configuration mode. To enter the configuration mode of the router parameters, type the router rip in the command line. The clue that you are now in router configuration mode will be a command line header of the form NetworKing (config-router) #. All changes that I will make in this mode will apply only to this routing protocol. If you print a question mark, you can familiarize yourself with all the commands and configuration options available in this mode.

So, we looked at how to enter the various configuration modes of the router. In this video lesson, not all commands are considered, but when in the next lessons we move on to a detailed study of switches and routers, we will look at the commands in more detail.
We will not cover absolutely all the teams, because the CCNA specialist does not need to know all the teams, but we will consider most of the teams related to your CCNA exam. I think I covered everything I planned to tell in this video tutorial, so thank you for watching. If you have any questions, email me or leave your comments right below this video.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until spring for free if you pay for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?

The first thing that gives you a hint is the power switch. Remember that Cisco switches do not have a switch. In addition, the switch will necessarily have several ports, because it is a switch with 12, 24 or more ports.
As a rule, the router has 2 gigabit ports, and possibly a fast Ethernet port. On the left you see the free space, covered with plugs. It is intended for additional modules, and in principle, a switch module can be inserted here, but usually the router simply has a couple of ports for connecting switches and an Internet cable.
Of course, as a CCNA specialist, you will need to know what a router is, what a series of routers and switches are, but this is a different matter. So, all devices manufactured by Cisco have these two ports: a console port labeled with a light blue color and located above either the AUX port. Both of these ports are intended for external device configuration, that is, you can access the device, even if the operating system is not working. Simply put, through these ports you can download the router.
Let's try to compare the router with your home computer. Most of us could help a relative or friend with a computer problem if one of them calls you and says that their computer is not working. You can remotely connect to another computer using Team viewer or any other program for remote access, find a solution to the problem and then install the necessary software, after which the computer must be restarted.
You can reboot it, but when your friend’s computer is “dead” when you restart, you don’t see what is happening on its screen during the bootup before the operating system appears, so ask your relative or friend to tell you by phone what is displayed on the monitor time. If the problem is not solved, then you will not be able to understand what its cause is, because you do not see the download process. But as a specialist in the IT industry, you must see what is going on in order to decide what needs to be done next to eliminate the problem.
Therefore, you should be able to remotely observe the boot process, you should see the BIOS, its settings, you should be able to check all these things. The console port of the router allows you to do all this. By connecting to it, you can observe everything that happens to the router at boot time before the Cisco IOS operating system is loaded.
What is the difference between Console and AUX ports? For the console port, a special Cisco console cable is used in the same light blue color as the router port is marked. It is also called the rollover cable. At one end of this cable there is an 8P8C connector, similar to a standard RJ45 connector, and on the other hand, a connector for connecting to a computer.
The AUX port performs the same function, but is usually used to connect a modem. The user can also connect to it to remotely configure the router.
The problem with the console cable shown on the slide is that it can only be connected to the computer’s serial port, but most modern computers do not have such a port. In this case, you can use the converter cable, which is shown on the left. It allows you to connect a device with a serial connector to the USB port of the computer.
If you use this converter, you will need to install a USB driver, when installed, your computer will automatically receive a COM port. Thus, you can connect to the router using special software.
Modern models of Cisco routers have a USB port, and if you see that it is located in the zone where the blue strip of the console port is located, then this is the USB console port. This means that if you use a regular USB cable with a miniUSB connector at one end, you can connect the router to the USB port of the computer with the other end of the cable. Cisco provides a special Cisco Windows USB driver that creates a COM port on the computer. After that you can use the terminal program, which you see on the next slide, and connect to the device via a computer.
Each router has a Gigabit Ethernet port, indicated by a light yellow tag, which allows you to connect to a different network device. Next to it, you see another USB port. As I said before, the latest series of routers are equipped with such ports for transmitting and storing an IOS image on external media. The difference between these two ports, miniUSB and USB, is that the first is the console port, and the second is for connecting an external device for storing information, such as flash memory. In the next series of video tutorials, we will look at switches and routers in more detail, and from this video tutorial you first need to remember where the console port is and what the console cable looks like.

After the router connects to the computer using the console cable through the console port, we can use the terminal program. There are 4 of the most popular programs for terminal management: free PuTTY, I prefer to call it “Putti”, although some people call it “Patty”, and I don’t know how to properly. This program can be downloaded for free at putty.org. There are 3 more similar programs, of which TeraTerm and HyperTerm also have free versions. Personally, I am a big fan of Secure SRT, believe me, after you try this program, you don’t even look in the direction of another terminal software.
But you can use the program that you like more. Any terminal software has basic configuration settings in which you need to select the Serial parameter as the type of connection with the device, the speed of data exchange with devices, which is 9600 for all Cisco devices, and the serial port number through which the connection is made, in this case COM1.
Most computers have at least one serial port, but if it is not there, you need to use a Serial to USB converter cable. In this case, you need to install a driver for the USB serial port, which will become a COM1 port. To do this, you need to go to the Device Manager of your computer, there are several ways to do this. After you open the Device Manager, you should open the list “COM & LPT ports” and select the port to which the router is connected. If it is a COM1 port, then you specify it in the Serial line and click the Open button, which opens your terminal session with the device.
After that, you get into the process of loading the router. In the right window, I highlighted in blue a compressed image of the IOS operating system.

After it is unpacked, all information on the technical characteristics of the router, the license for the right to use the software, etc. will appear on the screen. It also shows the firmware version of the router, in our case it is 15.1, and at the end of the download, the system configuration dialog will appear. In any Cisco device, be it a switch or a router, there is such a command line. I recommend that you always select the No answer to the "Continue with configuration dialog" prompt?

The fact is that if you continue the dialogue, you will enter the settings, most of which are not supported today, so the best choice would be to refuse the offer to use it and return to the command line.
The first mode that all these devices support is the user EXEC mode. This is the initial, lowest access mode to the device settings. How can you tell if you have a custom EXEC mode? This is indicated by the closed-bracket character> after the word Router. If you see this sign, then you are in user EXEC mode.
A feature of Cisco IOS is that if you type a question mark on the command line, you will see a list of commands that can be used in this mode.

These are the basic commands for the initial access level, but you can also enter a command such as quickly browsing the IP interface Router> show ip int br and see the connection status to this router for Gigabit Ethernet ports.

If you enter the "Show privileges" command, the router will report that the privilege level is 1, that is, you are working in the user EXEC mode.
The next, more advanced configuration control mode is the privileged EXEC mode. Now I will show how to use this mode. But first, I’ll talk about one more good thing about Cisco IOS — it’s so “smart” that it understands entering abbreviated commands.

When I type “show privi”, the program understands that the word “privileges” is meant, that is, I ask you to show me the privileges. If I just enter the letter e as a command, the program will say that 2 commands, enable and exit, begin with this letter, so I need to type a few more letters so that she understands exactly which command is meant.
For example, if I type en, the system will understand what the enable command means, therefore, with a full command set, or with a partial two-letter set, after pressing Enter, the program will execute the correct command. This is one of the reasons why Cisco hardware is so popular in the networking industry.
So, if you see the hash icon # after the word Router #, this means that you have entered the privileged EXEC mode. In this mode, you have more privileges than any simple Cisco user.
If I print the “show privileges” command, the system will report that the privilege level is 15, which is the highest privilege level. At this level, there are many more hardware configuration commands available to you than in the user EXEC mode. With these commands you can enter global configuration mode, you can save, read and delete configurations and perform many things that are not available in user mode.
The next Cisco IOS mode is called global configuration mode. It can be accessed by typing configure terminal in the command line.

In this mode, after the word Router there will be not just a “lattice” symbol, but a word (config) with a “lattice”. Therefore, if you see the Router (config) # line, it means that you are in global configuration mode. In this mode, you can make changes to the Cisco IOS operating system itself. For example, if you want to change the hostname of this device, you type in the hostname NetworKing line, and after that you see that the Router's hostname has changed to NetworKing.

In this mode, you can make any changes to the system as you like. From here you can get to different levels. The next slide shows what exactly you can do while in different modes. For example, in user EXEC mode, you can ping devices, view the configuration, and include some parameters. In privileged mode, you can execute all user mode commands, debug commands, reload commands, configuration commands, etc. In global configuration mode, you can control the host name, activate hidden configuration settings and IP configuration settings. In addition, there are three configuration levels, each of which has its own set of commands.

At the interface configuration level, you can control the parameters of a specific interface, at the router configuration level, you can manage all the parameters of the router, etc.
For example, from here you can configure the IP address for the Gigabit Ethernet port by setting the parameter 0/0. If a NetworKing (config-if) # header appears in the command line, if symbols mean that you are in global interface configuration mode. This means that all changes to the settings that you make will be applied only to a specific interface.
If you type a question mark, you will see a list of commands that you can enter in this mode for the corresponding configuration parameters: ip, ipv6, mac-addresses, and so on, all these commands refer only to the specific interface you have chosen.

If you enter the exit command, you will return one step higher to NetworKing (config) # mode, that is, to global configuration mode. To enter the configuration mode of the router parameters, type the router rip in the command line. The clue that you are now in router configuration mode will be a command line header of the form NetworKing (config-router) #. All changes that I will make in this mode will apply only to this routing protocol. If you print a question mark, you can familiarize yourself with all the commands and configuration options available in this mode.

So, we looked at how to enter the various configuration modes of the router. In this video lesson, not all commands are considered, but when in the next lessons we move on to a detailed study of switches and routers, we will look at the commands in more detail.
We will not cover absolutely all the teams, because the CCNA specialist does not need to know all the teams, but we will consider most of the teams related to your CCNA exam. I think I covered everything I planned to tell in this video tutorial, so thank you for watching. If you have any questions, email me or leave your comments right below this video.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending to friends, 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of the entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to share the server? (Options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until spring for free if you pay for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel Dodeca-Core Xeon E5-2650v4 128GB DDR4 6x480GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 249 in the Netherlands and the USA! Read about How to build an infrastructure building. class c using servers Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 worth 9000 euros for a penny?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/440612/