Wireless Wi-Fi programmable room thermostat with air quality monitor and other useful features
In the autonomous heating system of my apartment there is a commercially available wireless room thermostat. The system, of course, functions without it: the thermostat was purchased to save gas consumption and increase comfort.
The thing is very useful, but, in my opinion, somewhat morally obsolete. It was decided to collect something similar to the thermostat bought, adding for a start to the layout of the thermostat more convenient setting and connecting to the Internet.
What happened as a result - read on. I hope, besides me, the project will be interesting to others.
Acquaintance
Features and Specifications:
- Communication between thermostat nodes is carried out over the air at a radio frequency.
- During the day, the thermostat maintains constant three temperature setpoints.
- Thermostat settings (work program, air boundary parameters, others) are set remotely via Wi-Fi from the form in the browser.
- The thermostat has an air quality monitor feature that measures temperature, carbon dioxide levels and air humidity.
- The thermostat is equipped with a real-time clock with synchronization of the clock with the time server via the Internet.
- The thermostat is controlled from the interface of the Blynk mobile application. In addition, the Blynk application accepts and displays the results of temperature measurements, the content of CO 2 and air humidity.
- The thermostat automatically goes offline when there is no Wi-Fi.
- From the thermostat, messages are sent to the e-mail if the temperature, CO 2 content or air humidity are outside the threshold values.
- In the thermostat, besides the temperature, it is possible to maintain the remaining measured air parameters within the prescribed limits.
- At the end of the heating season, the thermostat will not have to be hidden: the air quality monitor will remain in operation, sending messages to the post office and the clock.
The thermostat consists of two devices. In the first device, the control signal of the heating device or system is generated and transmitted to the second device; let's call this device an analyzer. The second device receives the signal, decrypts it and controls the heat source - let it be a contactor. The connection between the analyzer and the contactor is wireless, at a radio frequency.

Assembly
To assemble the device, you will need components, a list of which and their estimated cost at the prices of the AliExpress website are given in the table.
| Component | Price, $ |
| analyzer | |
| Wi-Fi fee NodeMCU CP2102 ESP8266 | 2.53 |
| Temperature and humidity sensor DHT22 | 2.34 |
| CO2 content sensor MH Z-19 | 18.50 |
| RTC DS3231 Watch | 1.00 |
| Screen OLED LCD blue 0.96 "I2C 128x64 | 1.95 |
| RF module 433MHz, transmitter (set price: transmitter, receiver) | 0.99 |
| 4-channel logic level converter 3.3V-5V (Logical Layer Converter) | 0.28 |
| Voltage stabilizer LM7805 (10 pcs.) | 0.79 |
| Adapter AC100-240V 50 / 60Hz DC12V 2A | 10.70 |
| Development board (fiberglass), contacts, etc. | 2.00 |
| contactor | |
| Arduino Pro Mini 5V Module | 1.45 |
| RF module 433MHz (receiver) | - |
| 2 channel relay module | 0.98 |
| AC-DC adapter HLK-PM01 | 4.29 |
| Development board (fiberglass), contacts, etc. | 2.00 |
| Total: | 49.80 |
If you plan to assemble a thermostat with minimum dimensions, then you need to replace the 4-channel logic level converter with a 2-channel and 2-channel relay module with a 1-channel.
Both devices are assembled on fiberglass laminate boards. Installation - mounted. The modules are installed on the panels assembled from the “combs” of the contacts. This approach has several advantages: the components are easily dismantled, the installation for a new version of the sketch changes easily, and finally, in the case of a homemade product you cannot see in what way it is made.
The antennas at the transmitter and receiver are 17.3 cm long wire. The increased transmitter power and the simplest antennas ensure reliable communication within the apartment.
Analyzer

The analyzer brain is an ESP8266 controller on the NodeMCU CP2102 module board. It receives signals from sensors and generates control signals for the transmitter and the screen.
When installing the DHT22 sensor on the board, the measured temperature is 1.5 ... 2 ° C higher than the real one (even without the case!). Therefore, you should place the temperature sensor away from the elements with high heat emission LM7805 and NodeMCU CP2102. In addition, it would be nice to install the LM7805 voltage regulator on the radiator and it is definitely necessary to ensure good air convection in the housing to lower the temperature and reduce the measurement error. Another way to get rid of the error is to remove the DHT22 sensor for the volume of the case - this option is simpler and I chose it.
The analyzer is supplied with a constant voltage of 12V from the AC / DC adapter. Further, the LM7805 constant voltage regulator forms a voltage of 5V. Transmitter power supply - 12V. When testing the device, when the analyzer and the contactor are near on the desktop, the analyzer can be powered from the computer's USB port by applying voltage to the NodeMCU CP2102 module with a standard USB - microUSB cable. The power supply voltage of the NodeMCU CP2102 and MH Z-19 is 5V, the power supply of the remaining circuit nodes (3.3V) is formed by the stabilizer of the NodeMCU CP2102 module.
The DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor is connected to pin D6 of the NodeMCU CP2102 module. The DC3231 clock and the 0.96 "display are connected to ESP8266 (on the NodeMCU CP2102 module) via the I2C two-wire interface, and the Tx, Rx outputs of the CO2 MH Z-19 content sensor are connected to the Rx, Tx outputs of ESP8266, respectively. The transmitter enters the NodeMCU CP2102 via a converter logical levels, which converts the signal from the NodeMCU CP2102 with an amplitude of about 3.3V to a signal whose amplitude is close to the supply voltage of the 12V transmitter.
If you use a battery instead of a battery in the clock module, do not forget to break the battery charge circuit, otherwise the battery will swell up after several weeks of working under voltage. With self-powered watches, the accuracy of 2 sec / year is provided to you.
A snapshot analyzer for downloading to the ESP8266 is located under the spoiler.
/* * Беспроводной программируемый по Wi-Fi комнатный термостат с монитором качества воздуха и другими полезными функциями (анализатор) */ #include <FS.h> #include <Arduino.h> #include <ESP8266WiFi.h> //https://github.com/esp8266/Arduino // Wifi Manager #include <DNSServer.h> #include <ESP8266WebServer.h> #include <WiFiManager.h> //https://github.com/tzapu/WiFiManager //e-mail #include <ESP8266WiFiMulti.h> //https://github.com/esp8266/Arduino/blob/master/libraries/ESP8266WiFi/src/ESP8266WiFiMulti.h #include <ESP8266HTTPClient.h> ESP8266WiFiMulti WiFiMulti; char address[64] {"e-mail"}; //e-mail, address // HTTP requests #include <ESP8266HTTPClient.h> // OTA updates #include <ESP8266httpUpdate.h> // Blynk #include <BlynkSimpleEsp8266.h> // Debounce #include <Bounce2.h> //https://github.com/thomasfredericks/Bounce2 // JSON #include <ArduinoJson.h> //https://github.com/bblanchon/ArduinoJson //clock #include <pgmspace.h> #include <TimeLib.h> #include <WiFiUdp.h> #include <Wire.h> #include <RtcDS3231.h> //https://github.com/Makuna/Rtc RtcDS3231<TwoWire> Rtc(Wire); #define countof(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0])) //timer #include <SimpleTimer.h> SimpleTimer timer; // ссылка на таймер unsigned int timerCO2; //период опроса MH-Z19 unsigned int timerBl; //период отправки данных на Blynk unsigned int timerMail; //период отправки сообщений на емейл // GPIO Defines #define I2C_SDA 4 // D2 - OLED #define I2C_SCL 5 // D1 - OLED #define DHTPIN 12 //D6 cp2102 // Humidity/Temperature #include <DHT.h> #define DHTTYPE DHT22 // DHT 22 DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); #define mySerial Serial // Use U8g2 for i2c OLED Lib #include <SPI.h> #include <U8g2lib.h> U8G2_SSD1306_128X64_NONAME_F_SW_I2C u8g2(U8G2_R0, I2C_SCL, I2C_SDA, U8X8_PIN_NONE); byte x {0}; byte y {0}; // Blynk token char blynk_token[33] {"Blynk token"}; //Transmitter #include <RCSwitch.h> RCSwitch transmitter = RCSwitch(); unsigned long TimeTransmitMax; // переменная для хранения точки отсчета времени передачи сигнала ВКЛ/ВЫКЛ передатчиком // Setup Wifi connection WiFiManager wifiManager; // Network credentials String ssid {"am-5108"}; String pass {"vb" + String(ESP.getFlashChipId())}; //flag for saving data bool shouldSaveConfig = false; //переменные float t {-100}; //температура int h {-1}; //влажность int co2 {-1}; //содержание co2 float Chs = 0.2; //чуствительность (гистерезис) термостата по температуре (диапазон: 0.1(большая тепловая инерция) - 0.4 (малая тепловая инерция)) char Tmx[]{"25.0"}, Hmn[]{"35"}, Cmx[]{"1000"}, tZ[]{"2.0"}; //пороговые значения t, h и co2, час. пояс float Cmax, Tmax, Hmin, tZone; char Temperature0[]{"20.0"}, Temperature1[]{"22.0"}, Temperature2[]{"19.0"};//температура стабилизации термостата во временных интервалах float TemperaturePoint0, TemperaturePoint1, TemperaturePoint2, TemperaturePoint1Mn, TemperaturePoint2Mn, TemperaturePoint1Pl, TemperaturePoint2Pl; float TemperaturePointA0 = 21.0; //температура стабилизации термостата в автономном режиме char Hour1[]{"6"}, Hour2[]{"22"}; //временные точки термостата, час float HourPoint1, HourPoint2; float MinPoint1 = 0, MinPoint2 = 0; int n, j, m; //счетчик часов, минут int progr = 0; //счетчик программ работы термостата во времени суток int timeSummerWinter = 0; // летнее(1)/зимнее(0) время int a = 1; //режим работы термостата: 1 - онлайн, 2 - автономный bool buttonBlynk = true; //признак ВКЛ(true)/ВЫКЛ(falce) виртуальной кнопки V(10) Blynk //NTP, clock uint8_t hh,mm,ss; //containers for current time char time_r[9]; char date_r[12]; // NTP Servers: //static const char ntpServerName[] = "us.pool.ntp.org"; static const char ntpServerName[] = "time.nist.gov"; WiFiUDP Udp; unsigned int localPort = 2390; // local port to listen for UDP packets time_t getNtpTime(); void digitalClockDisplay(); void printDigits(int digits); void sendNTPpacket(IPAddress &address); void digitalClockDisplay() { // digital clock display of the time Serial.print(hour()); printDigits(minute()); printDigits(second()); Serial.print(" "); Serial.print(day()); Serial.print("."); Serial.print(month()); Serial.print("."); Serial.print(year()); Serial.println(); } void printDigits(int digits) { // utility for digital clock display: prints preceding colon and leading 0 Serial.print(":"); if (digits < 10) Serial.print('0'); Serial.print(digits); } //NTP code const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time is in the first 48 bytes of message byte packetBuffer[NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold incoming & outgoing packets time_t getNtpTime() { int tZoneI; tZoneI = (int)tZone; IPAddress ntpServerIP; // NTP server's ip address while (Udp.parsePacket() > 0) ; // discard any previously received packets Serial.println("Transmit NTP Request"); // get a random server from the pool WiFi.hostByName(ntpServerName, ntpServerIP); Serial.print(ntpServerName); Serial.print(": "); Serial.println(ntpServerIP); sendNTPpacket(ntpServerIP); uint32_t beginWait = millis(); while (millis() - beginWait < 1500) { int size = Udp.parsePacket(); if (size >= NTP_PACKET_SIZE) { Serial.println("Receive NTP Response"); Udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read packet into the buffer unsigned long secsSince1900; // convert four bytes starting at location 40 to a long integer secsSince1900 = (unsigned long)packetBuffer[40] << 24; secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[41] << 16; secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[42] << 8; secsSince1900 |= (unsigned long)packetBuffer[43]; return secsSince1900 - 2208988800UL + tZoneI * SECS_PER_HOUR + timeSummerWinter * SECS_PER_HOUR; //tZoneI } } Serial.println("No NTP Response (:-()"); return 0; // return 0 if unable to get the time } // send an NTP request to the time server at the given address void sendNTPpacket(IPAddress &address) { // set all bytes in the buffer to 0 memset(packetBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // Initialize values needed to form NTP request // (see URL above for details on the packets) packetBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI, Version, Mode packetBuffer[1] = 0; // Stratum, or type of clock packetBuffer[2] = 6; // Polling Interval packetBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock Precision // 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root Dispersion packetBuffer[12] = 49; packetBuffer[13] = 0x4E; packetBuffer[14] = 49; packetBuffer[15] = 52; // all NTP fields have been given values, now // you can send a packet requesting a timestamp: Udp.beginPacket(address, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123 Udp.write(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); Udp.endPacket(); } void synchronClockA() { WiFiManager wifiManager; Rtc.Begin(); Serial.print("IP number assigned by DHCP is "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println("Starting UDP"); Udp.begin(localPort); Serial.print("Local port: "); Serial.println(Udp.localPort()); Serial.println("waiting for sync"); setSyncProvider(getNtpTime); if(timeStatus() != timeNotSet){ digitalClockDisplay(); Serial.println("here is another way to set rtc"); time_t t = now(); char date_0[12]; snprintf_P(date_0, countof(date_0), PSTR("%s %02u %04u"), monthShortStr(month(t)), day(t), year(t)); Serial.println(date_0); char time_0[9]; snprintf_P(time_0, countof(time_0), PSTR("%02u:%02u:%02u"), hour(t), minute(t), second(t)); Serial.println(time_0); Serial.println("Now its time to set up rtc"); RtcDateTime compiled = RtcDateTime(date_0, time_0); // printDateTime(compiled); Serial.println(""); if (!Rtc.IsDateTimeValid()) { // Common Cuases: // 1) first time you ran and the device wasn't running yet // 2) the battery on the device is low or even missing Serial.println("RTC lost confidence in the DateTime!"); // following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled // it will also reset the valid flag internally unless the Rtc device is // having an issue } Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled); RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime(); if (now < compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is older than compile time! (Updating DateTime)"); Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled); } else if (now > compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is newer than compile time. (this is expected)"); } else if (now == compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is the same as compile time! (not expected but all is fine)"); } // never assume the Rtc was last configured by you, so // just clear them to your needed state Rtc.Enable32kHzPin(false); Rtc.SetSquareWavePin(DS3231SquareWavePin_ModeNone); } } void synchronClock() { Rtc.Begin(); wifiManager.autoConnect(ssid.c_str(), pass.c_str()); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { delay(500); Serial.print("."); } Serial.println(" "); Serial.print("IP number assigned by DHCP is "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); Serial.println("Starting UDP"); Udp.begin(localPort); Serial.print("Local port: "); Serial.println(Udp.localPort()); Serial.println("waiting for sync"); setSyncProvider(getNtpTime); if(timeStatus() != timeNotSet){ digitalClockDisplay(); Serial.println("here is another way to set rtc"); time_t t = now(); char date_0[12]; snprintf_P(date_0, countof(date_0), PSTR("%s %02u %04u"), monthShortStr(month(t)), day(t), year(t)); Serial.println(date_0); char time_0[9]; snprintf_P(time_0, countof(time_0), PSTR("%02u:%02u:%02u"), hour(t), minute(t), second(t)); Serial.println(time_0); Serial.println("Now its time to set up rtc"); RtcDateTime compiled = RtcDateTime(date_0, time_0); Serial.println(""); if (!Rtc.IsDateTimeValid()) { // Common Cuases: // 1) first time you ran and the device wasn't running yet // 2) the battery on the device is low or even missing Serial.println("RTC lost confidence in the DateTime!"); // following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled // it will also reset the valid flag internally unless the Rtc device is // having an issue } Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled); RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime(); if (now < compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is older than compile time! (Updating DateTime)"); Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled); } else if (now > compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is newer than compile time. (this is expected)"); } else if (now == compiled) { Serial.println("RTC is the same as compile time! (not expected but all is fine)"); } // never assume the Rtc was last configured by you, so // just clear them to your needed state Rtc.Enable32kHzPin(false); Rtc.SetSquareWavePin(DS3231SquareWavePin_ModeNone); } } void Clock(){ RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime(); //Print RTC time to Serial Monitor hh = now.Hour(); mm = now.Minute(); ss = now.Second(); sprintf(date_r, "%d.%d.%d", now.Day(), now.Month(), now.Year()); if (mm < 10) sprintf(time_r, "%d:0%d", hh, mm); else sprintf(time_r, "%d:%d", hh, mm); Serial.println(date_r); Serial.println(time_r); } //callback notifying the need to save config void saveConfigCallback() { Serial.println("Should save config"); shouldSaveConfig = true; } void factoryReset() { Serial.println("Resetting to factory settings"); wifiManager.resetSettings(); SPIFFS.format(); ESP.reset(); } void printString(String str) { Serial.println(str); } void readCO2() { static byte cmd[9] = {0xFF,0x01,0x86,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x79}; //команда чтения byte response[9]; byte crc = 0; while (mySerial.available())mySerial.read(); //очистка буфера UART перед запросом memset(response, 0, 9);// очистка ответа mySerial.write(cmd,9);// запрос на содержание CO2 mySerial.readBytes(response, 9);//читаем 9 байт ответа сенсора //расчет контрольной суммы crc = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) { crc += response[i]; } crc = ((~crc)+1); { //проверка CRC if ( !(response[0] == 0xFF && response[1] == 0x86 && response[8] == crc) ) { Serial.println("CRC error"); } else { //расчет значения CO2 co2 = (((unsigned int) response[2])<<8) + response[3]; Serial.println("CO2: " + String(co2) + "ppm"); } } } void sendMeasurements() { float t1 {-100}; int h1 {-1}, i; // Temperature t1 = dht.readTemperature(); if ((t1 > -1) and (t1 < 100)) t = t1; Serial.println("T: " + String(t) + "C"); // Humidity h1 = dht.readHumidity(); if ((h1 > -1) and (h1 < 100)) h = h1; Serial.println("H: " + String(h) + "%"); // CO2 readCO2(); } void sendToBlynk(){ Blynk.virtualWrite(V1, t); Blynk.virtualWrite(V2, h); Blynk.virtualWrite(V3, co2); Blynk.virtualWrite(V4, TemperaturePoint0); } void noData() { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 48; y = 40; u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "***"); } void drawOn() { float TemperatureP0; char Online_ch[]{" Online"}; TemperatureP0 = TemperaturePoint0 - Chs; dtostrf(TemperatureP0, 4, 1, Temperature0); //преобразование float в char String Temperature0_i; Temperature0_i = String(Temperature0); char Temperature0_i_m [16]; Temperature0_i.toCharArray(Temperature0_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Temperature0_p; String onl1 = "OnLine T<"; Temperature0_p = onl1 + Temperature0_i_m; char Temperature0_p_m [16]; Temperature0_p.toCharArray(Temperature0_p_m, 16); String Tmx_i; Tmx_i = String(Tmx); char Tmx_i_m [16]; Tmx_i.toCharArray(Tmx_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Tmx_p; String onl2 = "OnLine T>"; Tmx_p = onl2 + Tmx_i_m; char Tmx_p_m [16]; Tmx_p.toCharArray(Tmx_p_m, 16); String Cmx_i; Cmx_i = String(Cmx); char Cmx_i_m [16]; Cmx_i.toCharArray(Cmx_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Cmx_p; String onl3 = "OnL CO2>"; Cmx_p = onl3 + Cmx_i_m; char Cmx_p_m [16]; Cmx_p.toCharArray(Cmx_p_m, 16); String Hmn_i; Hmn_i = String(Hmn); char Hmn_i_m [16]; Hmn_i.toCharArray(Hmn_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Hmn_p; String onl4 = "OnLine H<"; Hmn_p = onl4 + Hmn_i_m; char Hmn_p_m [16]; Hmn_p.toCharArray(Hmn_p_m, 16); //string 3 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 0; y = 64; u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Online_ch); if ((hh>=HourPoint1) and (hh<=HourPoint2) and (t<TemperatureP0)) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Temperature0_p_m); else if (t > Tmax) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Tmx_p_m); else if (co2 > Cmax) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Cmx_p_m); else if (h < Hmin) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Hmn_p_m); switch((millis() / 100) % 4) { // Temperature case 0: { String info_t; String paramT; String tmpr = "T("; String grad = "C):"; const char degree {176}; paramT = tmpr + degree + grad; char paramT_m [12]; paramT.toCharArray(paramT_m, 12); info_t = String(t); char info_t_m [12]; info_t.toCharArray(info_t_m, 5); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, paramT_m); //string 2 if ((t > -100) and (t < 100)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_t_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_t_m); } else noData(); } break; //Humidity case 1: { String info_h; info_h = String(h); char info_h_m [12]; info_h.toCharArray(info_h_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "H(%):"); //string 2 if ((h > -1) and (h < 100)){ u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_h_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_h_m); } else noData(); } break; //CO2 case 2: { String info_co2; info_co2 = String(co2); char info_co2_m [12]; info_co2.toCharArray(info_co2_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 8; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "CO2(ppm):"); //string 2 if ((co2 > -1) and (co2 <= 2000)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_co2_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_co2_m); } else noData(); } break; //time, date case 3: { //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(date_r))/2; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, date_r); //string 2 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(time_r))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, time_r); } break; } u8g2.sendBuffer(); } void drawOff() { float TemperatureP0A; char OffLine_ch[]{"Offline Tst=21"}; TemperatureP0A = TemperaturePointA0 - Chs; // dtostrf(TemperatureP0A, 4, 1, TemperaturePointA0); //преобразование float в char String TemperaturePointA0_i; TemperaturePointA0_i = String(TemperaturePointA0); char TemperaturePointA0_i_m [16]; TemperaturePointA0_i.toCharArray(TemperaturePointA0_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String TemperaturePointA0_p; String onl1 = "Offline T<"; TemperaturePointA0_p = onl1 + TemperaturePointA0_i_m; char TemperaturePointA0_p_m [16]; TemperaturePointA0_p.toCharArray(TemperaturePointA0_p_m, 16); //string 3 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 0; y = 64; u8g2.drawStr(x, y, OffLine_ch); if (t<TemperatureP0A) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, TemperaturePointA0_p_m); switch((millis() / 100) % 4) { // Temperature case 0: { String info_t; String paramT; String tmpr = "T("; String grad = "C):"; const char degree {176}; paramT = tmpr + degree + grad; char paramT_m [12]; paramT.toCharArray(paramT_m, 12); info_t = String(t); char info_t_m [12]; info_t.toCharArray(info_t_m, 5); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, paramT_m); //string 2 if ((t > -100) and (t < 100)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_t_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_t_m); } else noData(); } break; //Humidity case 1: { String info_h; info_h = String(h); char info_h_m [12]; info_h.toCharArray(info_h_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "H(%):"); //string 2 if ((h > -1) and (h < 100)){ u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_h_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_h_m); } else noData(); } break; //CO2 case 2: { String info_co2; info_co2 = String(co2); char info_co2_m [12]; info_co2.toCharArray(info_co2_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 8; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "CO2(ppm):"); //string 2 if ((co2 > -1) and (co2 <= 2000)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_co2_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_co2_m); } else noData(); } break; //time, date case 3: { //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(date_r))/2; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, date_r); //string 2 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(time_r))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, time_r); } break; } u8g2.sendBuffer(); } void drawOffBlynk() { float TemperatureP0; char OffBlynk_ch[]{" OffBlynk"}; TemperatureP0 = TemperaturePoint0 - Chs; dtostrf(TemperatureP0, 4, 1, Temperature0); //преобразование float в char String Temperature0_i; Temperature0_i = String(Temperature0); char Temperature0_i_m [16]; Temperature0_i.toCharArray(Temperature0_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Temperature0_p; String onl1 = "OffBL T<"; Temperature0_p = onl1 + Temperature0_i_m; char Temperature0_p_m [16]; Temperature0_p.toCharArray(Temperature0_p_m, 16); String Tmx_i; Tmx_i = String(Tmx); char Tmx_i_m [16]; Tmx_i.toCharArray(Tmx_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Tmx_p; String onl2 = "OffBL T>"; Tmx_p = onl2 + Tmx_i_m; char Tmx_p_m [16]; Tmx_p.toCharArray(Tmx_p_m, 16); String Cmx_i; Cmx_i = String(Cmx); char Cmx_i_m [16]; Cmx_i.toCharArray(Cmx_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Cmx_p; String onl3 = "OnL CO2>"; Cmx_p = onl3 + Cmx_i_m; char Cmx_p_m [16]; Cmx_p.toCharArray(Cmx_p_m, 16); String Hmn_i; Hmn_i = String(Hmn); char Hmn_i_m [16]; Hmn_i.toCharArray(Hmn_i_m, 16); u8g2.clearBuffer(); String Hmn_p; String onl4 = "OffBL H<"; Hmn_p = onl4 + Hmn_i_m; char Hmn_p_m [16]; Hmn_p.toCharArray(Hmn_p_m, 16); //string 3 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 0; y = 64; u8g2.drawStr(x, y, OffBlynk_ch); if ((hh>=HourPoint1) and (hh<=HourPoint2) and (t<TemperatureP0)) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Temperature0_p_m); else if (t > Tmax) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Tmx_p_m); else if (co2 > Cmax) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Cmx_p_m); else if (h < Hmin) u8g2.drawStr(x, y, Hmn_p_m); switch((millis() / 100) % 4) { // Temperature case 0: { String info_t; String paramT; String tmpr = "T("; String grad = "C):"; const char degree {176}; paramT = tmpr + degree + grad; char paramT_m [12]; paramT.toCharArray(paramT_m, 12); info_t = String(t); char info_t_m [12]; info_t.toCharArray(info_t_m, 5); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, paramT_m); //string 2 if ((t > -100) and (t < 100)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_t_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_t_m); } else noData(); } break; //Humidity case 1: { String info_h; info_h = String(h); char info_h_m [12]; info_h.toCharArray(info_h_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 16; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "H(%):"); //string 2 if ((h > -1) and (h < 100)){ u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_h_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_h_m); } else noData(); } break; //CO2 case 2: { String info_co2; info_co2 = String(co2); char info_co2_m [12]; info_co2.toCharArray(info_co2_m, 12); //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = 8; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, "CO2(ppm):"); //string 2 if ((co2 > -1) and (co2 <= 2000)) { u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(info_co2_m))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, info_co2_m); } else noData(); } break; //time, date case 3: { //string 1 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(date_r))/2; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, date_r); //string 2 u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_inb24_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(time_r))/2; y = y + 2 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, time_r); } break; } u8g2.sendBuffer(); } void drawBoot(String msg = "Loading...") { u8g2.clearBuffer(); u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_9x18_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(msg.c_str())) / 2; y = 32 + u8g2.getAscent() / 2; u8g2.drawStr(x, y, msg.c_str()); u8g2.sendBuffer(); } void drawConnectionDetails(String ssid, String pass, String url) { String msg {""}; u8g2.clearBuffer(); msg = "Connect to WiFi:"; u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_7x13_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(msg.c_str())) / 2; y = u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, msg.c_str()); msg = "net: " + ssid; x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(msg.c_str())) / 2; y = y + 1 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, msg.c_str()); msg = "pw: "+ pass; x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(msg.c_str())) / 2; y = y + 1 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, msg.c_str()); msg = "Open browser:"; x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(msg.c_str())) / 2; y = y + 1 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, msg.c_str()); // URL // u8g2.setFont(u8g2_font_6x12_mf); x = (128 - u8g2.getStrWidth(url.c_str())) / 2; y = y + 1 + u8g2.getAscent() - u8g2.getDescent(); u8g2.drawStr(x, y, url.c_str()); u8g2.sendBuffer(); } bool loadConfigS(){ Blynk.config(address); Serial.print("e-mail: "); Serial.println( address ); Blynk.config(Tmx); Serial.print("T max: "); Serial.println( Tmx ); Blynk.config(Cmx); Serial.print("CO2 max: "); Serial.println( Cmx ); Blynk.config(Temperature0); Serial.print("Temperature 0: "); Serial.println( Temperature0 ); Blynk.config(Temperature1); Serial.print("Temperature1: "); Serial.println( Temperature1 ); Blynk.config(Temperature2); Serial.print("Temperature2: "); Serial.println( Temperature2 ); Blynk.config(Hmn); Serial.print("H min: "); Serial.println( Hmn ); Blynk.config(Hour1); Serial.print("Hour 1: "); Serial.println( Hour1 ); Blynk.config(Hour2); Serial.print("Hour 2: "); Serial.println( Hour2 ); Blynk.config(tZ); Serial.print("Time Zone: "); Serial.println( tZ ); Blynk.config(blynk_token, "blynk-cloud.com", 8442); Serial.print("token: " ); Serial.println( blynk_token ); } bool loadConfig() { Serial.println("Load config..."); File configFile = SPIFFS.open("/config.json", "r"); if (!configFile) { Serial.println("Failed to open config file"); return false; } size_t size = configFile.size(); if (size > 1024) { Serial.println("Config file size is too large"); return false; } // Allocate a buffer to store contents of the file. std::unique_ptr<char[]> buf(new char[size]); // We don't use String here because ArduinoJson library requires the input // buffer to be mutable. If you don't use ArduinoJson, you may as well // use configFile.readString instead. configFile.readBytes(buf.get(), size); StaticJsonBuffer<200> jsonBuffer; JsonObject &json = jsonBuffer.parseObject(buf.get()); if (!json.success()) { Serial.println("Failed to parse config file"); return false; } // Save parameters strcpy(blynk_token, json["blynk_token"]); strcpy(address, json["address"]); strcpy(Tmx, json["Tmx"]); strcpy(Cmx, json["Cmx"]); strcpy(Temperature0, json["Temperature0"]); strcpy(Temperature1, json["Temperature1"]); strcpy(Temperature2, json["Temperature2"]); strcpy(Hmn, json["Hmn"]); strcpy(Hour1, json["Hour1"]); strcpy(Hour2, json["Hour2"]); strcpy(tZ, json["tZ"]); } void configModeCallback (WiFiManager *wifiManager) { String url {"http://192.168.4.1"}; printString("Connect to WiFi:"); printString("net: " + ssid); printString("pw: "+ pass); printString("Open browser:"); printString(url); printString("to setup device"); drawConnectionDetails(ssid, pass, url); } void setupWiFi() { //set config save notify callback wifiManager.setSaveConfigCallback(saveConfigCallback); // Custom parameters WiFiManagerParameter custom_tZ("tZ", "Time Zone", tZ, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_tZ); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Temperature0("Temperature0", "Temperature 0", Temperature0, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Temperature0); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Hour1("Hour1", "Hour 1", Hour1, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Hour1); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Temperature1("Temperature1", "Temperature 1", Temperature1, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Temperature1); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Hour2("Hour2", "Hour 2", Hour2, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Hour2); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Temperature2("Temperature2", "Temperature 2", Temperature2, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Temperature2); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Cmx("Cmx", "Cmax", Cmx, 7); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Cmx); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Hmn("Hmn", "Hmin", Hmn, 5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Hmn); WiFiManagerParameter custom_Tmx("Tmx", "Tmax", Tmx,5); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_Tmx); WiFiManagerParameter custom_address("address", "E-mail", address, 64); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_address); WiFiManagerParameter custom_blynk_token("blynk_token", "Blynk Token", blynk_token, 34); wifiManager.addParameter(&custom_blynk_token); wifiManager.setAPCallback(configModeCallback); wifiManager.setTimeout(180); if (!wifiManager.autoConnect(ssid.c_str(), pass.c_str())) { a++; Serial.println("mode OffLINE :("); loadConfigS(); synchronClockA(); } //save the custom parameters to FS if (shouldSaveConfig) { Serial.println("saving config"); DynamicJsonBuffer jsonBuffer; JsonObject &json = jsonBuffer.createObject(); json["blynk_token"] = custom_blynk_token.getValue(); json["address"] = custom_address.getValue(); json["Tmx"] = custom_Tmx.getValue(); json["Cmx"] = custom_Cmx.getValue(); json["Temperature0"] = custom_Temperature0.getValue(); json["Temperature1"] = custom_Temperature1.getValue(); json["Temperature2"] = custom_Temperature2.getValue(); json["Hmn"] = custom_Hmn.getValue(); json["Hour1"] = custom_Hour1.getValue(); json["Hour2"] = custom_Hour2.getValue(); json["tZ"] = custom_tZ.getValue(); File configFile = SPIFFS.open("/config.json", "w"); if (!configFile) { Serial.println("failed to open config file for writing"); } json.printTo(Serial); json.printTo(configFile); configFile.close(); //end save } //if you get here you have connected to the WiFi Serial.println("WiFi connected"); Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); } BLYNK_WRITE(V10) { if (param.asInt() == 1) { buttonBlynk = true; Blynk.virtualWrite(V10, HIGH); drawBoot("Thermo ON"); } else { buttonBlynk = false; Blynk.virtualWrite(V10, LOW); drawBoot("Thermo OFF"); } } void mailer() { // wait for WiFi connection if((WiFiMulti.run() == WL_CONNECTED)) { HTTPClient http; Serial.print("[HTTP] begin...\n"); http.begin("http://skorovoda.in.ua/php/aqm42.php?mymail="+String(address)+"&t="+String(t) +"&h="+String(h)+"&co2="+String(co2)+"&ID="+String(ESP.getChipId())); Serial.print("[HTTP] GET...\n"); // start connection and send HTTP header int httpCode = http.GET(); // httpCode will be negative on error if(httpCode > 0) { // HTTP header has been send and Server response header has been handled Serial.printf("[HTTP] GET... code: %d\n", httpCode); // file found at server if(httpCode == HTTP_CODE_OK) { String payload = http.getString(); Serial.println(payload); } } else { Serial.printf("[HTTP] GET... failed, error: %s\n", http.errorToString(httpCode).c_str()); } http.end(); } } void HystTemperatureA() { float TemperaturePointA0Mn, TemperaturePointA0Pl; TemperaturePointA0Mn = TemperaturePointA0-Chs; TemperaturePointA0Pl = TemperaturePointA0+Chs; if (t<TemperaturePointA0Mn) { if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000){ TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B11111110, 8); Serial.println ("t<TemperaturePointA0Mn Thermostat ON"); } } else if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000) { TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B10000000, 8); Serial.println ("t>TemperaturePointA0Mn Thermostat OFF"); } if (t<TemperaturePointA0Pl) { if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000){ TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B11111110, 8); Serial.println ("t<TemperaturePointA0Pl Thermostat ON"); } } else if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000) { TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B10000000, 8); Serial.println ("t>TemperaturePointA0Pl Thermostat OFF"); } } void HystTemperature() { float TemperaturePoint0Mn, TemperaturePoint0Pl; TemperaturePoint0Mn = TemperaturePoint0-Chs; TemperaturePoint0Pl = TemperaturePoint0+Chs; if (t<TemperaturePoint0Mn) { if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000){ TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B11111110, 8); Serial.println ("t<TemperaturePoint0Mn Thermostat ON"); } } else if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000) { TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B10000000, 8); Serial.println ("t>TemperaturePoint0Mn Thermostat OFF"); } if (t<TemperaturePoint0Pl) { if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000){ TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B11111110, 8); Serial.println ("t<TemperaturePoint0Pl Thermostat ON"); } } else if (millis() - TimeTransmitMax > 120000) { TimeTransmitMax = millis(); transmitter.send(B10000000, 8); Serial.println ("t>TemperaturePoint0Pl Thermostat OFF"); } } void TransmitterA(){ transmitter.send(B10101010, 8); //B10101010 - признак работающего передатчика HystTemperatureA(); } void Transmitter(){ transmitter.send(B10101010, 8); //B10101010 - признак работающего передатчика if (n>=24) n = 0; if (m>=60) m = 0; progr = 0; if ((hh >= HourPoint1) and (hh < HourPoint2)){ progr = 1; if (mm >= MinPoint1) progr = 1; if (mm < MinPoint2) progr = 1; } else if (hh >= HourPoint2) { progr = 2; if (mm >= MinPoint2) progr = 2; } if (buttonBlynk==true) { Serial.println ("BLynk: Термостат ВКЛ"); if (progr == 0) { TemperaturePoint0 = TemperaturePoint0; HystTemperature(); Serial.println ("Термостатирование: t = " + String(TemperaturePoint0)); } else if (progr == 1) { TemperaturePoint0 = TemperaturePoint1; HystTemperature(); Serial.println ("Термостатирование: t = " + String(TemperaturePoint0)); } else if (progr == 2){ TemperaturePoint0 = TemperaturePoint2; HystTemperature(); Serial.println ("Термостатирование: t = " + String(TemperaturePoint0)); } } else { transmitter.send(B10000000, 8); Serial.println ("BLynk: Термостат ВЫКЛ"); } if (co2 > Cmax) { transmitter.send(B11111101, 8); Serial.println("co2 > Cmax"); } else transmitter.send(B00000010, 8); if (h < Hmin) { transmitter.send(B11111011, 8); Serial.println("h < Hmin"); } else transmitter.send(B00000100, 8); if (t > Tmax) { transmitter.send(B11110111, 8); Serial.println("t > Tmax"); } else transmitter.send(B00001000, 8); } void connectBlynk(){ if(String(blynk_token)== "Blynk token"){ drawBoot("OFFBLYNK!"); delay (3000); } else { drawBoot("Connect. Blynk"); Serial.println("Connecting to blynk..."); while (Blynk.connect() == false) { delay(500); Serial.println("Connecting to blynk..."); } } } void setup() { // factoryReset(); //форматирование RAM mySerial.begin(9600); Serial.begin(115200); transmitter.enableTransmit(2); u8g2.begin(); // инициализация экрана drawBoot("Loading..."); // инициализация файловой системы if (!SPIFFS.begin()) { Serial.println("Failed to mount file system"); ESP.reset(); } // загрузка параметров drawBoot("Connect. WiFi"); setupWiFi(); timerCO2 = timer.setInterval(15000, readCO2); buttonBlynk = true; if(a == 1){ // Load config drawBoot("Load Config"); if (!loadConfig()) { Serial.println("Failed to load config"); factoryReset(); } else { Serial.println("Config loaded"); } Blynk.config(address); Serial.print("e-mail: "); Serial.println(address); Blynk.config(Tmx); Serial.print("T max: "); Serial.println(Tmx); Blynk.config(Cmx); Serial.print("CO2 max: "); Serial.println(Cmx); Blynk.config(Temperature0); Serial.print("Temperature 0: "); Serial.println(Temperature0); Blynk.config(Temperature1); Serial.print("Temperature1: "); Serial.println(Temperature1); Blynk.config(Temperature2); Serial.print("Temperature2: "); Serial.println(Temperature2); Blynk.config(Hmn); Serial.print("H min: "); Serial.println(Hmn); Blynk.config(Hour1); Serial.print("Hour 1: "); Serial.println(Hour1); Blynk.config(Hour2); Serial.print("Hour 2: "); Serial.println(Hour2); Blynk.config(tZ); Serial.print("Time Zone: "); Serial.println(tZ); Blynk.config(blynk_token, "blynk-cloud.com", 8442); Serial.print("token: " ); Serial.println(blynk_token); //преобразование char в float Tmax = atof (Tmx); Cmax = atof (Cmx); TemperaturePoint0 = atof (Temperature0); TemperaturePoint1 = atof (Temperature1); TemperaturePoint2 = atof (Temperature2); Hmin = atof (Hmn); HourPoint1 = atof (Hour1); HourPoint2 = atof (Hour2); tZone = atof (tZ); //синхронизация часов drawBoot("Clock synchr."); synchronClock(); //периодичность вызова функций timerCO2 = timer.setInterval(15000, readCO2); timerBl = timer.setInterval(5000, sendToBlynk); connectBlynk(); // подключение до Blynk Blynk.virtualWrite(V10, HIGH); //установка кнопки V10 в состояние ВКЛ buttonBlynk = true; } } void loop(){ if (a == 2) { Serial.println(":( OffLINE"); timer.run(); Clock(); sendMeasurements(); TransmitterA(); drawOff(); delay(1000); } else if (a == 1) { Serial.println(":) OnLINE"); timer.run(); Clock(); Blynk.run(); BLYNK_WRITE(V10); Transmitter(); sendMeasurements(); if(String(blynk_token) == "Blynk token") drawOffBlynk(); else drawOn(); if (j>=24) j =0; if (hh == j){ if ((mm==30) and ((ss<30) )){ if ((t > Tmax) or (co2 > Cmax) or (h < Hmin) or ((progr == 0) and (t<(TemperaturePoint0-1.0)) or ((progr == 1) and (t<(TemperaturePoint1-1.0)) or ((progr == 2) and (t<(TemperaturePoint2-1.0)))))) mailer(); } } j++; } } If at least one of the parameters of the air is outside the limits of the programmed threshold values, then at half of each hour the device sends an email to the email:
Emails are sent by a php script. The script is uploaded to my mail server. You will need it if you plan to send messages from another resource.
<?php // тест - http://skorovoda.in.ua/php/aqm42.php?mymail=my_login@my.site.net&t=22.2&h=55&co2=666 $EMAIL=0; $TEMPER=0; $vlaga=0; $carbon=0; $device=0; $EMAIL=$_GET["mymail"]; $device=$_GET["ID"]; echo $EMAIL; $TEMPER=$_GET["t"]; $vlaga=$_GET["h"]; $carbon=$_GET["co2"]; $mdate = date("H:i dmy"); echo <<<END <p>Температура: $TEMPER °С<p> <p>Влажность: $vlaga %<p> <p>Содержание углекислого газа: $carbon ppm<p> <p>--------------------<p> <p>Метеостанция №: $device<p> END; echo <<<END <p>$mdate</p> END; mail($EMAIL, "Air Quality Monitor " .$device. " v.051018"," Данное сообщение сформировано монитором качества воздуха №" .$device. " автоматически. Один или несколько параметров воздуха в помещении (температура, влажность или содержание углекислого газа) находятся за пределами заданных граничных значений. === Температура: ".$TEMPER."°C === "."Влажность: ".$vlaga."% === "."Содержание углекислого газа: ".$carbon." ppm === "."Проанализируйте информацию! === Время, дата: ".$mdate,"From: my_sensors@air-monitor.info \n") ?> 
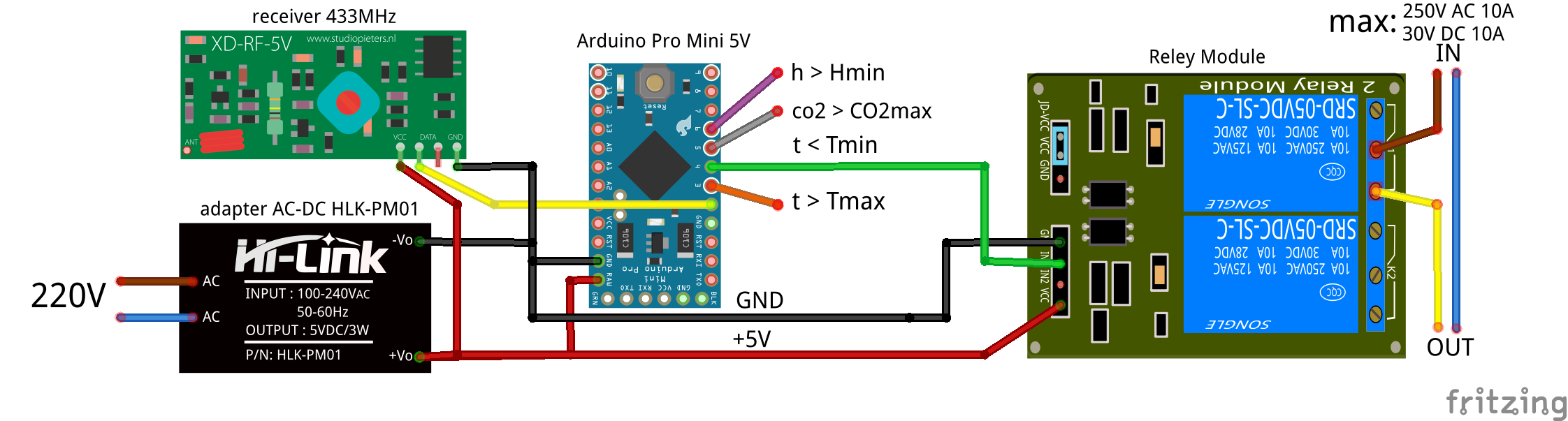
Contactor

The contactor is controlled by the Arduino Pro Mini module. It receives the signal from the RF receiver and generates signals exceeding the threshold values of air parameters.
The supply voltage of all nodes of the 5V contactor comes from the AC / DC adapter HLK-PM01.
The signals from the pins of the controller 6 (h> Hmin), 5 (co2> CO2max), 3 (t> Tmax) can be used to organize automatic humidification, forced ventilation or air conditioning. The advantage is that there is no need to lay a cable for transmitting the control signal from the sensor to one system or another - just place a contactor near one of the ends of the power wire or control the system.
For example, I plan, in addition to controlling the heating boiler, to connect to the contactor also a kitchen hood - the boiler and the hood are located nearby.
Sketch contactor for download to the Arduino Pro Mini - under the spoiler.
/ *
* Wireless Wi-Fi programmable room thermostat with air quality monitor and other useful features (contactor)
* /
#include <RCSwitch.h> //https://github.com/sui77/rc-switch
RCSwitch mySwitch = RCSwitch ();
void setup () {
pinMode (13, OUTPUT);
pinMode (3, OUTPUT);
pinMode (4, OUTPUT);
pinMode (5, OUTPUT);
pinMode (6, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite (3, HIGH);
digitalWrite (4, HIGH);
digitalWrite (5, HIGH);
digitalWrite (6, HIGH);
digitalWrite (13, LOW);
mySwitch.enableReceive (0);
}
void loop () {
if (mySwitch.available ()) {
int value = mySwitch.getReceivedValue ();
// t <Tmin
if (value == B11111110) digitalWrite (4, LOW);
else if (value == B10000000) digitalWrite (4, HIGH);
// co2> Cmax
if (value == B11111101) digitalWrite (5, LOW);
else if (value == B00000010) digitalWrite (5, HIGH);
// h <Hmin
if (value == B11111011) digitalWrite (6, LOW);
else if (value == B00000100) digitalWrite (6, HIGH);
// t> Tmax
if (value == B11110111) digitalWrite (3, LOW);
else if (value == B00001000) digitalWrite (3, HIGH);
// LED D13 Arduino - indicates the presence of communication transmitter-receiver (flashes - there is a connection)
if (value == B10101010) digitalWrite (13, HIGH); // B10101010 - code of the included transmitter, generated in the analyzer without conditions
else digitalWrite (13, LOW);
mySwitch.resetAvailable ();
}
}
`` `

Starting the thermostat to work
It's time to turn on the thermostat.
Step 1:
First, turn on the analyzer.

First you need to be patient and, without doing anything, wait 3 minutes. The thermostat will automatically go offline - without connecting via Wi-Fi to your home network and the Internet. After 3 minutes on the analyzer screen in three lines, everything that the thermostat turns on will begin to flash.

The first two lines on the screen do not require comments. The third line contains the thermostat operation mode ( Offline, Online or OffBlynk ) and information about the air flow outside the established threshold values. For example, Offline CO2> 1000 — the thermostat is offline, and the measured CO2 content is above a predetermined threshold of 1000 ppm.
The clock in offline mode will show the wrong time. They are not yet synchronized with the time server, and the time zone has not been entered - this is in the next step.
In the stand-alone mode, the temperature of the temperature control was set at 21 ° С during the day.
Step 2:
Having mastered the autonomous mode, turn off and then turn on the AC / DC adapter of the analyzer. A familiar message will appear on the screen, which was used to get used to within three minutes of waiting for the offline mode.
The device picked up the am-5108 access point. Find this point in the list of available networks and connect to it, the password is on the screen. Then open the page http://192.168.4.1 in the browser.

Click the Configure WiFi button (No Scan) . A page with the thermostat settings form will open:

The same form with empty fields and comments:

We give in the form the name and password of your home network, the identification key BLynk, and e-mail Change the default time zone, time (hours) and temperature for time points, as well as threshold values for temperature, humidity and CO 2 content.
Day two time points are divided into three time ranges - the first: from 00 h 00 min to point 1 ( Hour 1, Minute 1 ), the second: from point 1 ( Hour 1, Minute 1 ) to point 2 ( Hour 2, Minute 2 ) and the third: from point 2 ( Hour 2, Minute 2 ) to 00 hours 00 minutes . There are no fields for entering minutes on the form, minutes for points 1,2 can be changed in the sketch (variables MinPoint1, MinPoint2 ). In each of the three time ranges, you can set your own temperature - Temperature 0, Temperature 1 and Temperature 2 . If you plan to keep the same temperature constant throughout the day, then it is sufficient to set the value to Temperature 0 , and leave the fields for points 1,2 empty.
When choosing thresholds, you can focus on the indicators that I found on the Internet:
- Comfortable temperature at night while sleeping is 19 ... 21 ° C, in the daytime - 22 ... 23 ° C.
- The optimum relative humidity in the cold season is considered to be 30 ... 45% humidity, and in the warm season - 30 ... 60%. Maximum maximum humidity: in winter it should not exceed 60%, and in summer - 65%.
- The maximum level of carbon dioxide in the premises should not exceed 1000 ppm. The recommended level for bedrooms is no more than 600 ppm. The mark of 1400 ppm is the limit of permissible CO 2 content in the room. If it is more, the air quality is considered low.
By default, the daily program of thermostating (during the day - high temperature, at night - low) is set on the assumption that during the day one of the tenants is in the room, for example, working at home. The program is easy to change to fit your reality.
The e-mail field can be left blank. Then the opportunity to receive emails about the exit of air parameters beyond the threshold values will be lost. Without the Blynk key entered , it is impossible to control the thermostat and get information about the air parameters at a distance. However, the thermostat is not “lost”, if the fields with limiting values of air parameters remain empty, then only one function will remain: thermostating.
And further. Enter all numbers, please, in the variable format with a floating point, then the conversion to the desired format is performed in a sketch. Exception: time points 1,2 (hour) - integer format.
After saving the settings in the ESP8266 memory ( Save button), the analyzer will connect to the network and start working.
If you make a mistake (it happens!) Or decide to change the settings, you will have to load the sketch again into ESP8266 again. The first time is with the factoryReset () uncommented in Setup'e; and the second with commented out, then repeat step 2.
Step 3:
Now you can turn on the contactor.
With stable radio communication between the analyzer and the contactor - the D13 LED on the Arduino board flashes at a frequency of about 1 Hz.
If the contactor received from the analyzer a command to turn on the heater or heating system, the normally open relay contacts will close and the corresponding LED on the relay module will light up.
If there are no problems with the “idling” of the contactor, then we connect the heating device or the heating system electronics. The heating device should be connected with a wire of a certain cross-section. The specific indicator for calculating the cross section of copper wire is 5 A / mm 2 .

Step 4:
It's time to launch the Blynk app on your smartphone. There is a lot of information about the Blynk application on the Internet - there’s no point in repeating it.
Variables for Blynk (in order not to look for them in the analyzer sketch): temperature - V1 , humidity - V2 , CO 2 content - V3 , temperature of temperature control - V4 , virtual button - V10 .
On my smartphone, Blynk's interface (you can change it) looks like:

The graph shows the measured temperature (white), the temperature of the temperature control (yellow), the time interval is a day. Variables of humidity and CO 2 content are not displayed on the graph, since two additional scales severely limit the field of the graph, where you can see the curves themselves.
The signal from the virtual button THERMOSTAT is formed only at the moment of pressing the button. When you press a button on the analyzer screen, the message Thermo OFF flashes ! or Thermo ON! - depending on the previous state of the button. This message is relevant when testing the thermostat.
The screenshot below illustrates the process of heating with a 2 kW / hour fan heater for a room of about 5 square meters with an initial temperature of 16 ° C. Here - temperature (yellow), humidity (blue) and the content of CO 2 (red).

Synchronous with the temperature saw, the notched humidity curve on the graph is another confirmation of the well-known fact that the open heating element dries the air, and the peaks on the CO 2 content curve are evidence of my short visits to the room.
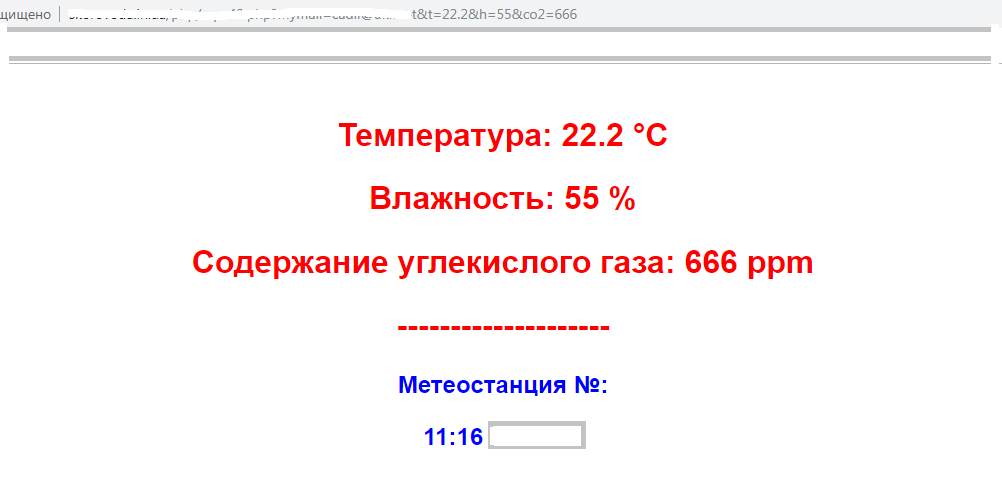
Now let's test the e-mail alert system. Let's enter into the address bar of the browser a commented line with the http-address from the code of the php-script. If you did not forget to specify your e-mail in the settings, and in the browser window - information, as in the picture below, then there will most likely not be any problems with receiving notifications. The test is especially useful when transferring a php script from my server to another.
Intentions
In the future, I plan to work on improving the thermostat (as they say, there is no limit to perfection!)
Tasks - a lot:
- Complete the thermostat with a wireless temperature sensor to measure the temperature outside.
- Replace the RF receiver-transmitter pair with another pair with a greater communication range at a supply voltage of 3 ... 5V. Ideally, I would like to assemble a contactor powered by two AA batteries during the heating season.
- Avoid manual formatting of the ESP8266 memory before changing the thermostat settings by reloading the sketch.
- Expand the programmable cycle of the thermostat from daily to weekly.
- Replace the monochrome screen with a color and high resolution. This will allow to show all information about the thermostat's operation in one frame, and the exit of air parameters beyond the established limits - by changing the color.
- Then do the circuit boards and the presentable appearance of the thermostat.
What else can be improved? Suggestions, comments are accepted. I’ll listen to constructive criticism.
findings
- Thanks to the Internet connection, the functionality of the thermostat has expanded significantly. In addition to the main function, it implements a number of others: from sending alerts by e-mail to the ability to automatically maintain indoor air quality.
- A new quality has appeared in the thermostat: it can be controlled via the Internet.
- Pleases the ease with which the thermostat is programmed: you only need to fill out the form on the browser page.
- Now it is possible to save personal data in the memory of a thermostat, as is done, for example, in routers.
My bookmarks on the topic with Habra
1. Wi-Fi thermometer on ESP8266 + DS18B20 for only $ 4
2. Compact home air monitor (CO2, temperature, humidity, pressure) with Wi-Fi and mobile interface
4. Overview of the infrared CO2 sensor MH-Z19
5. We measure the concentration of CO2 in the apartment with the help of MH-Z19
6. Practical experience using Blynk for CO2 sensor. Part 1
I want to express my gratitude to Sergey Silnov (@kumekay) . He shared with me the idea of entering variables into ESP8266 via Wi-Fi. Sergey realized the idea in the device, which is described in detail in the publication “ Compact home air monitor (CO2, temperature, humidity, pressure) with Wi-Fi and mobile interface ”. I am afraid that without Sergey’s hint this project would not have a happy ending soon.
PS The layout of the project worthily took the place of the old thermostat, since for the fourth heating season it occasionally began to “forget” to turn the heating system on and off.
Attention!
The author is not responsible for the possible negative when repeating the project. You are responsible for everything you do.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/440978/