Amateur radio measurements: when there is no frequency meter
In amateur radio practice, due to budget constraints, a situation often arises when a device needed for operation is unavailable. In such a situation, it is necessary to calculate the desired parameter from the results of indirect measurements, i.e. "Drill with a saw and cut with a gimlet."
In the process of debugging the device I was developing, it became necessary to calibrate the digital frequency synthesizer as part of this device. The task is trivial in the presence of an electron-counting frequency meter (ESCh). The problem was that I could not “borrow” the frequency meter.
If you describe the operation of a frequency synthesizer applied in a device quite simply, it generates a signal at an output with a frequency Fs by processing the input signal from a reference oscillator with a frequency Fxo :
An inexpensive crystal oscillator with a TXC 25.0F6QF package was used as the frequency-generating element of the reference oscillator. The exact frequency of the reference oscillator signal was not known. In the synthesizer settings, the reference frequency was indicated by a constant of 25000000 Hz . The frequency synthesizer itself was programmed to output a signal with a frequency of 9996 kHz .
Check the performance of the circuit
To test the performance of the synthesizer, the Rigol DS1102E digital oscilloscope was used. In the channel settings, frequency measurement was turned on.
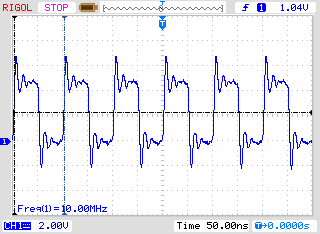
The oscilloscope on the outputs of the quartz resonator showed the measured value of 25.00 MHz, and the output of the synthesizer - 10.00 MHz. In principle, it was already quite good: the scheme worked.
Beat frequency method
The analogue of the calibration of frequency-generating chains by the beat method is the method of tuning musical instruments by the tuning fork. The sound extracted from the instrument is superimposed on the sound of the tuning fork. If the tones do not match, there are clearly audible "beating" frequencies. The tone of a musical instrument is adjusted before the appearance of “zero beats”, i.e. States when the frequencies match.
The use of a radio with a panoramic indicator
The easiest way to calibrate the frequency synthesizer using the beat method was to use a radio receiver with a panoramic indicator and a signal from the RWM radio station as a control signal.
The SoftRock RX Ensemble II with the HDSDR program was used as a control receiver. The receiver's scale was previously calibrated by signals from the RWM radio station at all three frequencies: 4996000, 9996000 and 14996000 Hz . The RWM radio signal at a frequency of 9996000 Hz was used as a control signal.

The screenshot shows the reception of the second RWM marks at a frequency of 9996000 Hz and the reception of the output signal of the synthesizer at a frequency of approximately 9997970 Hz . When specifying the frequency of the synthesizer, a constant of 25000000 Hz (nominal frequency of the quartz resonator) was used. During calibration, this constant was multiplied by the frequency ratio of 9997970 Hz and 9996000 Hz . As a result, the value of the real starting frequency of the quartz resonator 25004927 Hz was obtained. This value was entered as a constant in the device firmware. The screenshot shows the result of the calibration:

The frequency of the output signal of the synthesizer 9996 kHz exactly corresponds to the frequency of receiving the second RWM marks at a frequency of 9996000 Hz .

After calibration, the oscilloscope showed 25.00 MHz on the outputs of the quartz resonator, and 10.00 MHz at the synthesizer output, i.e. the same values as before calibration.
Using broadcast radio signals
In Perm, the RWM signal at a frequency of 9996 kHz is stably received during the daytime, and at the frequency of the day at 4996 kHz. If the passage of radio waves is unstable, and RWM signals are not accepted, on the website hfcc.org you can find the frequency and schedule of broadcast radio stations.
The carrier signals of broadcasting stations can also, if necessary, be used as control signals , since they usually have a frequency deviation of no more than 10 Hz from the broadcast frequency.
Brief conclusions
The simplest and most accurate way to measure the frequency of a signal in a radio frequency band is to measure the frequency with an electron-counting frequency meter.
It is possible to obtain an approximate value of the signal frequency by accepting it at a reference receiver with a calibrated scale.
When using the control receiver, it is possible to obtain the exact value of the signal frequency by “zero beats” of the measured signal with the control signal received from the reference source.
Necessary additions:
Calibration of the synthesizer could be carried out:
- Of course, with the help of ESCH.
- By the method of beatings with the help of a professional receiver without a panoramic indicator, for example, R-326, R-326M, R-250M2, etc. and RWM signals "by ear". It would not be as clear as with a panoramic indicator, and would take more time.
- Using a calibrated oscillator and oscilloscope on Lissajous figures . It looks very impressive, but requires additional expensive equipment.
And yet, the area of application by radio amateurs for the radio receivers mentioned above is very wide. They are used to monitor the air, to control the passage of radio waves, to monitor the listening signals when setting up radio stations, etc.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/439108/